- What is the difference between Shia and Sunni Muslims?
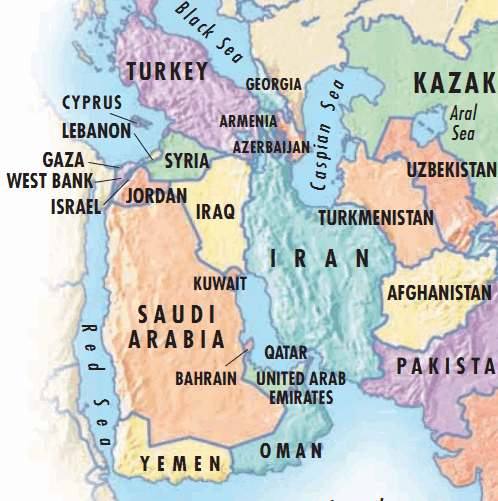
- Syria
- President Assad Family
- Syrian Unrest
- Who supports Assad and why?
- Who is against Assad and why?
- Reaction of the world
- Kofi Annan peace plan for Syria
- Houla massacre
- UN General Assembly
- India’s problem
At the heart of most Political unrests in Middle east, lies the Shia – Sunni conflict. So first question
What is the difference between Shia and Sunni Muslims?
- Both Shia and Sunni agree on the fundamentals of Islam and share the same Holy Book (The Quran), but Differences originate from the question of who would succeed the Prophet Muhammad as leader of the Muslim community after his death.
| Sunni | Shia |
| They chose Abu Bakr, a close Companion of the Prophet Muhammad, as the Caliph (politico-social leader) of Muslim community. | They wanted Prophet Muhammad’s son-in-law Ali to be appointed as Caliph (politico-social leader) of Muslim community. |
Syria
- Damascus =Syria’s capital
- Aleppo =Syria’s largest city.
President Assad Family
- Bashar al-Assad’s father ruled Syria for nearly 30 years and died in 2000.
- From 2000 to this date, Bashar Al Assad is the President of Syria.
- al-Assad family is Alawite, a small branch of Shia Muslims.
- But nearly 75% of Syria’s population is Sunni Muslims.
- Bashar has filled key positions in his government with either his family members or the Alawite Minority Muslims.
- Combined with rampant corruption, inflation, unemployment, Syria was sitting on a volcano about to erupt.
Syrian Unrest
- In January 2011, revolution in Tunisia marked the start of the so-called Arab Spring.
- In March 2011, violence broke out in Daraa, Syria, after a group of children and teenagers were arrested for writing political graffiti. Dozens of people were killed when security forces cracked down on protesters.
- Demonstrators soon called for al-Assad to leave office, following in the footsteps of Egypt’s Hosni Mubarak and Tunisia’s Zine el Abidine Ben Ali.
- Al-Assad promised to make changes, and he lifted the country’s state-of-emergency law, which for 48 years gave the regime the power to detain anyone without charge and hold them indefinitely.
- But just four days after the emergency law was lifted in April 2011, the Syrian regime sent thousands of troops into Daraa for a wide-scale crackdown
- Since then, the violence has only increased, spreading throughout the country and becoming a full-fledged civil war between the regime and an armed resistance. More than 10,000 citizen had been killed by Assad’s Military crackdown.
Who supports Assad and why?
| Who | Why they support Assad? |
| Iran | Because ruled by Shia |
| Hezbollah | Because it is a Shia Militant group cum Political party based in Lebanon. |
| Russia | Has a naval port and large diaspora. [we already discussed that in detail, earlier Click ME] |
| China |
|
Who is against Assad and why?
| Who? | Why against Assad? |
|---|---|
| Junta of Syria | Common sense. |
| Saudi Arabia | because ruled by Sunnis. |
| Bahrain | Same as above. |
| USA |
|
Reaction of the world
- United States and many of its Western allies have imposed economic sanctions against Syria, condemning al-Assad and demanding that he leave power.
- But they have not persuaded the U.N. Security Council [UNSC] to do the same.
- China and Russia — two of Syria’s commercial partners — have vetoed several proposed resolutions on Syria in the UNSC.
- OIC has suspended Syria’s membership.
- Saudi and Bahrain are providing weapons to the Syrian rebels.
Kofi Annan peace plan for Syria
- Also known as six-point peace plan for Syria
- February 2012, Kofi Annan was appointed as the joint U.N.-Arab League special envoy to Syria to settle down the Syrian crisis.
- March 2012, he submitted 6-point peace plan to UN
- According to this plan, Assad would ceasefire and withdraw the troops and crackdown. Then Government and rebels would do talks, negotiation, allow more Sunnis in parliament. Foreign Reporters would be allowed to do news-coverage etc.etc.etc. but it didn’t materialize because
Houla massacre
- it is a region in Syria, where 100+ civilians were killed in May 2012.
- Syrian government alleged that Al-Qaeda terrorist groups were responsible for the killings
- while Houla residents and opposition groups allege Syrian military’s hand behind the incident.
Why Kofi Annan’s Mission failed?
- After this Houla massacre, the Rebels started attacking Government establishments again, and thus providing convenient excuse to President Assad to continue mass-murdering innocent civilians, again.
- Kofi got frustrated and resigned from the envoy job after working for around 6 months. [From February to August 2012] and he gave following reasons why he couldn’t solve Syrian crisis
- 1. Syrian government’s intransigence [stubbornness]
- 2. the growing militancy of Syrian rebels [as long as they use violence, Assad gets convinient excuse to use military]
- 3. Divided Security Council [UNSC] that failed to forcefully back his effort. Since Kofi took on the job, Russia and China have twice used their veto power to block strong Western- and Arab-backed action against President Bashar Assad’s regime.
- U.N. Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon said he accepted Kofi’s resignation with deep regret, adding that the he’ll search for successor to Kofi, who will stay on until Aug. 31. 2012
UN General Assembly
- Has 193 members.
- In August 2012, it passed the resolution that denounced Syria’s crackdown on its people and demanded that the country lockdown its chemical and biological weapons.
- India abstained from this voting.
India’s problem
- India needs Saudi Arab for energy security and for keeping pressure on Pakistan over Kashmir and terror issues.
- At the same time, India can’t ignore the strategic significance of Iran for its regional policy towards Afghanistan, Pakistan and Central Asia. [recall the Chahbahar port article.]
- Overall, India has signaled its broad support for the Arab League and its positions on Syria.
- But India is reluctant to back any externally induced regime change in Syria.
All of the articles on [Diplomacy] are archived at mrunal.org/diplomacy

![[IR By Pavneet 4/5] Art of Answer-writing: Directive Word#2 “DISCUSS” – Impediments to India’s permanent membership at UN Security Council (UNSC)](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/webinar-pvnt-c-500x383.png)
I really fail to understand why some guys are arguing like-biased.or why Mr Mrunal is not reading The Hindu or Frontline as far as i know UPSC has no where mentioned that ur answers shall include all points from hindu or any magazine and more over The hindu has a little left orientation.So if u dont agree with Mr Mrunal on some accounts keep it to urself and find ur own way to answer.But plz dont argue with some one who is already putting a lot of efforts to give us as much as information in a clear ,comprehensive manner
Some people have his this habit of locking horns with other people without any reason.They Also keep looking for reasons to insult somebody.One thing i want to say is that Mr Mrunal deserve the accolade for the hard work he is doing.Well done Mate.
thanks sir for such a mine of info which u provide . u have the nack of making the info pretty simple – the quality of a good teacher. thumbs down to all the losers criticizing u ( sp those reading NYT and watching al jazeera ha ha )
thankyou very much sir for such lucid explanation….went through some criticising comments above….they even dont know how to criticise and type of words that should be used for it….they just cant digest the enormous love and affection that you receive from the followers of your blog, hence doing blah-blah-blah…..
please ignore them and continue the holy work…its very-2 beneficial for the aspirants like us….thanks again..!!!
I do not understand the criticism here.
If you feel the articles posted here biased, do not read the blog. In any case you do not pay for it.
Above all as an UPSC aspirant you are expected to read from a plethora of sources.
This blog is just one of the source (and probably best by a margin).
If you do not like go read something else, why criticise and discourage somebody who is helping others.
And if you want to help others nobody is stopping you from writing your own blog.
Aswani Kumar. Are you a bureaucrat yet? Eager to know. Because you seem to read only wikipedia and other sources which are available on the internet. I think an aspirant needs book and the basic knowledge can be supplemented with internet. You seem to have a superficial knowledge and act like a hollow pot which makes the loudest noise.
Aswani Kumar. Are you a bureaucrat yet? Eager to know. Because you seem to read only wikipedia and other sources which are available on the internet. I think an aspirant needs book and the basic knowledge can be supplemented with internet. You seem to have a superficial knowledge and act like a hollow pot which makes the loudest noise.
Thank you Mrunal Sir. Your Articles might have not yet updated to its last happenings about the topic. But the explanations are crystal clear with all the rationale explanations. Thank you again sir. May God bless you.