- THE SECOND WORLD WAR
- The Invasion of Poland
- Conquest of Norway, Denmark, Holland, Belgium and France
- The Battle of Britain
- German Invasion of Soviet Union
- Pearl Harbour: Entry of USA
- The Battle of Stalingrad
- The ‘Second Front’
- End of the War in Europe
- Nuke Attack on JAPAN
- Resistance Movements
- The Damage Caused by the War
- EXERCISES
UPSC has included World History in General studies (Mains) syllabus from 2013. Hence Old NCERT, particularly Chapter 9 to 13 from Class 10= becomes necessary as the ‘foundation/base material’ for the topics of World History. But for non-Delhi candidates, it is almost impossible to get that book, because NCERT changed syllabus, hence book is no longer printed. Therefore I’m uploading the chapters one by one. And, just because these chapters are uploaded, doesn’t mean I’m stopping my Jack Sparrow series on [World History], it will continue at its own pace.
In the first part of Ch.12, we saw the events between the Two world wars. Now comes
THE SECOND WORLD WAR
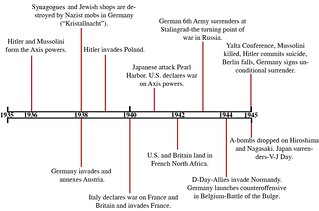
The Second World War, like the First, started in Europe and assumed the character of a world war. In spite of the fact that Western countries had acquiesced in all the aggressions of Japan, Italy and Germany from the invasion of Manchuria to the annexation of Czechoslovakia, the fascist countries’ ambitions had not been satisfied. These countries were planning another redivision of the world and thus had to come into conflict with the established imperialist powers. The Western policy of diverting the aggression of the fascist countries towards the Soviet Union had failed with the signing of the Soviet German Non-Aggression Pact. Thus the war began in Europe between the fascist countries and the major West European Powers—Britain and France. Within a few months it became a world war as it spread to more and more areas, ultimately involving almost every country in the world.
The Invasion of Poland
After the First World War, East Prussia had been separated from the rest of Germany. The city of Danzig which separated East Prussia from the rest of Germany had been made a free city independent of German control. Hitler had demanded the return of Danzig to Germany but Britain had refused to accept this demand.
On 1 September 1939 German armies marched into Poland. On 3 September Britain and France declared war on Germany. Thus the invasion of Poland marked the beginning of the Second World War, The German armies completed the conquest of Poland in less than three weeks as no aid reached Poland. In spite of the declaration of war, however, there was little actual fighting for many months. Therefore, the war during this period from September 1939 to April 1940 when Germany invaded Norway and Denmark is known as the ‘phoney war’.
Soon after the German invasion of Poland, the Soviet Union attacked eastern Poland and occupied the territories which were earlier in the Russian empire. It is believed that this occupation was a part of the secret provisions of the SovietGerman NonAggression Pact. In 1940, the Baltic States of Latvia, Estonia and Lithuania which had become independent after the First World War were also occupied by the Soviet Union. They, along with Moldavia, became republics of USSR. In November 1939, the Soviet Union also went to war against Finland.
Conquest of Norway, Denmark, Holland, Belgium and France
Germany launched her invasion of Norway and Denmark on 9 April 1940 and within three weeks completed the conquest of these two countries. In Norway, the German invaders were helped by Quisling, leader of Norway’s fascist party, who set up a puppet government in Norway under German occupation. The very name ‘Quisling’ has come to mean a traitor who collaborates with the invaders of his country. In early May began the invasion of Belgium and Holland which was completed before the end of May. Soon the German armies marched into France and by 14 June 1940, the capital city of Paris had fallen into German hands almost without a fight. In the meantime, Italy also had joined the war on the side of her ally, Germany. On 22 June 1940, the French government surrendered and signed a truce with Germany according to which about half of France was occupied by Germany. The remaining part remained under the French government which was required to disband the French army and provide for the maintenance of the German army in France. The French government which had surrendered to Germany ruled from Vichy. With the defeat of France, Germany became the supreme power over the continent of Europe. The war conducted by Germany with great speed and force is known as blitzkrieg which means a ‘lightning war’.
The Battle of Britain
Britain was the only major power left in Europe after the fall of France. Germany thought that Britain would surrender soon as she was without any allies in Europe. German air force began bombing raids on Britain in August 1940 with the aim of terrorizing her into surrender .The battle that ensued is known as the Battle of Britain. The Royal Air Force of Britain played a heroic role in its defence against air raids and conducted air raids on German territories in retaliation. The Prime Minister of Britain during the war years was Winston Churchill. Under his leadership, the people of Britain successfully resisted the German air raids with courage and determination.
In the meantime, Italy had started military operations in North Africa. She also invaded Greece, but the Italian attack in both the areas was repulsed. However, Germany succeeded in capturing the Balkans —Greece, Yugoslavia, Bulgaria and also large parts of North Africa.
German Invasion of Soviet Union
Having conquered almost the entire Europe, except Britain, Germany attacked the Soviet Union, despite the Non-Aggression Pact, on 22 June 1941. As mentioned before, Hitler had always coveted the vast territory and resources of the Soviet Union.
He thought that the destruction of the Soviet Union would take about eight weeks. Hitler had grossly underestimated the strength of the Soviet Union. In the first phase of the war with the Soviet Union, Germany achieved significant victories. Vast areas of the Soviet Union were devastated, Leningrad was besieged and German troops were marching towards Moscow. However, in spite of the initial German successes, the German onslaught was halted. The Soviet Union had built up her industrial and military strength. She resisted the German invasion heroically and the German hopes of a quick victory were thwarted.
With the German invasion of the Soviet Union, a new vast theatre of war had been opened. An important development that followed was the emergence of the BritishSovietAmerican unity to fight against aggression. Soon after the invasion, Churchill and Roosevelt declared British and American’ support, respectively, to the Soviet Union in the war against Germany and promised aid to her. Subsequently, agreements were signed between the Soviet Union and Britain, and Soviet Union and USA. It was as a result of this unity that Germany, Italy and Japan were ultimately defeated.
Pearl Harbour: Entry of USA
You have read before about the Japanese invasion of China in 1931. In 1937, the Japanese had started another invasion of China. Japan was one of the three members of the AntiComintern Pact along with Germany and Italy. In September 1940, these three countries had signed another pact which bound them together even more. Japan recognized the leadership of Germany and Italy in the establishment of a new order in Europe” and Japan’s leadership was recognized for establishing a new order in Asia. On 7 December 1941, the Japanese, without a declaration of war, conducted a massive raid on the American naval base at Pearl Harbor in Hawaii. The American Pacific Fleet which was stationed there was devastated. The Americans lost 20 warships, and about 250 aircrafts. About 3000 persons were killed. The Americans were completely taken unawares. Negotiations had been going on between the Japanese and American governments to settle their differences in Asia and the Pacific. The attack on Pearl Harbor in the midst of negotiations showed that the Japanese were determined to conquer Asia and the Pacific. With this the Second World War became truly global. The United States declared war on Japan on 8 December 1941 and soon after Germany and Italy declared war on the United States. Following the U.S. entry into the war, many countries in the Americas joined the war against Germany, Italy and Japan. The Japanese achieved significant victories in the war in Asia. Within six months of the attack on Pearl Harbor, they had conquered Malaya, Burma (now Myanmar), Indonesia, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Hongkong and numerous other areas.
By the middle of 1942, the fascist powers had reached the peak of their power. After that the decline began.
The Battle of Stalingrad
In January 1942 the unity of the countries fighting against the fascist powers was cemented. The representatives of 26 nations, including Britain, the United States and the Soviet Union, signed a declaration, known as the United Nations Declaration. The signatories to this Declaration resolved to utilize all their resources to pursue the war until victory was achieved and to cooperate with one another against the common enemy, and promised not to have a separate peace treaty.
One of the most important turning points in the war was the Battle of Stalingrad (now called Volgograd). In November and December 1941, the German advance on Moscow met with stubborn resistance and the invasion was repulsed. Germany then launched an offensive in southern Russia. In August 1942, the German troops 1 reached the outskirts of Stalingrad. For over five months, the battle raged. It involved about 2 million men, 2000 tanks and 2000 aeroplanes. The civilian population of Stalingrad joined the soldiers in the defence of the city. In February 1943, about 90,000 German officers and soldiers surrendered. In all, Germany had lost about 300,000 men in this battle. This battle turned the tide of the war
The ‘Second Front’
The fascist countries began to suffer reverses in other areas also. Japan had failed to capture Australia and Hawaii. In North Africa, the German and Italian troops were routed by early 1943. The destruction of the fascist army in North Africa was also a major turning point in the war. In July 1943, British and American troops occupied Sicily. Many sections in Italy had turned against Mussolini. He was arrested and a new government was formed. This government joined the war against Germany. However, German troops invaded northern Italy and Mussolini, who had escaped with the help of Germans, headed a proGerman government there. Meanwhile, British and American troops entered Italy and a long battle to throw the Germans out of Italy followed. The Soviet Union was attaining significant victories against Germany and had already entered Czechoslovakia and Rumania which had been under German occupation.
On 6 June 1944, more than 100,000 British and American troops landed on the coast of Normandy in France. By September their number had reached 2,000,000. The opening of this front played a very crucial role in the defeat of Germany. This is known as the opening of the ‘Second Front’. Since 1942 in Europe the most ferocious battles had been fought between Germany and the Soviet Union. The Soviet ‘Union had been demanding the opening of the second front for long, as this would compel Germany to fight on other fronts also and would thus hasten the defeat of Germany. From this time onwards the German armies were on the run on all fronts.
End of the War in Europe
After 6 June 1944, German armies had to face the forces of the Allies from three directions. In Italy, the British and American troops were advancing. Northern and western France and the city of Paris had been freed and the Allied troops were moving towards Belgium and Holland On the eastern front, the Germans were facing a collapse. The Soviet army from the east and other Allied troops from the west were closing on Germany. On May 1945 the Soviet armies entered Berlin. Hitler had committed suicide on the morning of the same day. On 7 May 1945 Germany unconditionally surrendered. The end of all hostilities in Europe became effective from 12,00 a.m. on 9 May 1945
Nuke Attack on JAPAN
After the defeat of Germany, the war in Asia continued for another three months. Britain and USA had launched successful operations against Japan in the Pacific and in the Philippines and Burma. In spite of serious reverses, however, the Japanese were still holding large parts of China. On 6 August 1945, an atom bomb, the deadliest weapon developed during the war, was dropped on the Japanese city of Hiroshima. This was the first time that the atom bomb had been used. With one single bomb, the city of Hiroshima was obliterated. Another atom bomb was dropped on the city of Nagasaki on 9 August 1945. The city was destroyed. In the meantime, the Soviet Union had declared war on Japan and had started military operations against Japanese forces in Manchuria and Korea. On 14 August Japan conveyed its acceptance of the Allied demand to surrender but the actual surrender took place on 2 September 1945. With the Japanese surrender, the Second World War came to an end.
Resistance Movements
In all the countries of Europe which had fallen victim to the aggressions of fascist countries, the people organised resistance movements. In many countries, the governments capitulated before the aggres sors without much fighting but people of those countries continued to resist the fascist rule. For example, when the government of France surrendered, the people of France organized a popular resistance movement against the German occupation. A French army was also formed outside France under the leadership of General de Gaulle which actively participated in the war. Similar armies of other countries were also organized. Inside the occupied countries, the resistance movements set up guerilla forces. Largescale guerilla activities were organized in many countries such as Yugoslavia and Greece. In many countries there were largescale uprisings. The heroic uprising of the Polish people in Warsaw is a glorious chapter m the history of the resistance movements. There were resistance movements within the fascist countries also. The fascist governments of Italy and Germany had physically exterminated hundreds of thousands of people who were opposed to fascism. However, many antifascists from these countries continued to fight against fascism inside and outside their countries. The antifascist forces in Italy were very powerful and played an important role in the war against Mussolini and in fighting against German troops in Italy. In France, Greece, and under the leadership of Marshal Tito, in Yugoslavia, the people fought most heroically against fascist aggression. The socialists, the communists and other antifascists played a very important part in the resistance movements, Millions of civilian fighters against fascism perished in the war.
The people in countries which were victims of aggression fought back valiantly. In Asia, the people of China had to bear the Mint of Japanese aggression from the early 1930s. The civil war that had broken out in China between the communists and the Kuomintang in the late 1920s was superseded by a massive national resistance against Japanese aggression. In other parts of Asia also which were occupied by Japan, for example in Indochina, Korea, Indonesia, the Philippines and Burma, people organized themselves into strong resistance movements. The peoples who had been fighting against British a French imperialism expressed their support to the war against fascism. Fascism was organized barbarism and was not considered an ally by the peoples who were struggling for their independence. For example, the Indian National Congress while fighting for the independence of India from British rule expressed itself against fascism.
The Damage Caused by the War
The Second World War was the most destructive war in history. The fascists had converted a large part of Europe into a vast graveyard and a slavecamp. The Nazis’ hatred of the Jews has been mentioned before. Inside Germany and in those parts of Europe which came under German occupation before and during the war, Jews were picked up and six million of them were exterminated. The labour of the countries occupied by Germany was utilized and most horrible labour camps were started. Millions of people were transferred to what are known as concentration camps and killed. Many of these camps such as those in Buchenwald, Oswiecim and Dachau were death camps where new ways of killing people were introduced. People were burnt in gas chambers. There were mass massacres Prisoners were made to dig mass graves, were shot and then buried in those graves. Certain kinds of factories were located near the concentration camps which produced goods made from human skins and bones. The kinds of tortures and brutalities that the fascists, particularly the German Nazis, perpetrated had no precedent nor did the mass scale on which they were practiced. Many of these brutalities came fully to light when Germany lost the war, after the discovery of places of mass murders and from the descriptions of those in the concentration camps who had survived. The atrocities committed by the Japanese in countries occupied by them were no less brutal. Inhuman medical experiments were conducted by Japanese ‘ doctors’ and ‘scientists’ on human beings.
The destruction caused by the war in terms of human lives has no precedent in history. Over 50 million people perished in the Second World War. Of them about 22 million were soldiers and over 28 million civilians. About 12 million people lost their lives in concentration camps or as a result of the terror unleashed by the fascists Some countries lost a large percentage Of their population. For example, Poland lost six million people, about five million of them civilians, which was about 20 per cent of the Polish population. The Soviet Union in absolute terms suffered the worst — about 20 million people which was about 10 per cent of the population. Germany lost over six million people, about 10 per cent of her population. Besides the human losses, the economy and material resources of many countries were badly damaged. Many ancient cities were almost completely destroyed. The total cost of the Second World War has been estimated at the staggering figure of $ 1,384,900,000,000.
Many new weapons of destruction were devised and used in the Second World War. The most dreadful of these was the atom bomb. The atom bomb was first devised in the United States during the Second World War. Scientists of many countries, including those who had come to the United States to escape the fascist tyranny in Europe, had helped in developing it. The project to develop the bomb was taken up when a number of scientists, suspecting that the Nazi Germany was developing the atom bomb, approached the US government. They had feared that if the Nazis developed the bomb, they would use it to terrorize the world into submission. The atom bomb was first tested in July 1945. By then, Germany had already surrendered. Many of those who had helped in its development appealed to the US government not to use it against Japan against whom the war was still continuing. They also warned of the danger of starting a race in the production of atomic weapons if the atom bomb was used against Japan. However, the government of the United States used the atom bombs against the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, as has already been mentioned. The two bombs killed over 320,000 people almost instantaneously and completely wiped out large parts of the two cities. The effects of these bombs on the health of those who survived and on their children continue to this day. The government of the United States justified the use of the atom bomb on the ground that it brought the Second World War immediately to a close and thus helped to save human lives which would have been lost if the war had continued. Many other people, including many Scientists who had helped in making the bomb. condemned the use of the atom bomb. After the defeat of Germany and the ending of the war in Europe, Japan was not in a position to continue the war and her capitulation was a matter of days. Some scholars hold the view that the main reason for using the atom bomb was to establish the superiority of USA in the world after the war as at that time she alone possessed these weapons. In any case, the prediction of the scientists that the use of the atom bomb would lead to a race for producing atomic weapons came true. Within a few years after the Second World War, some other countries also developed atomic weapons. Also other nuclear weapons, thousands of times more destructive than the ones used against Japan, were developed which, if used, can completely destroy all human life on earth.
EXERCISES
- What were the main features of the fascist and Nazi movements?
- Explain the consequences of the economic crisis of 1929-33.
- What is meant by the term ‘Axis Powers’
- Describe the consequences of the victory of fascism on Italy and Germany.
- What were the main aims of the foreign policies of Italy and Germany ? Of Japan ?
- Describe the main events between 1936 and 1939 which created conditions for another
- world war.
- What did the Western powers do to counter the aggressive acts of Japan, Italy and Germany between 1931 and 1938?
- Describe the growth of national movements in Asia after the First World War. Name the Asian countries which won their independence between 1919 and 1939
- Explain the terms: ‘Phoney War’, Second Front, the Battle of Britain
- On an outline map of Europe, show the countries which were occupied by Germany between 1936 and August 1939.
- On an outline map of Asia, show the areas which were under Japanese occupation during the Second World War.
- Try to collect the views of Jawaharlal Nehru and the Indian National Congress on fascism from books on Indian freedom movement.
- Read about the new weapons developed after the Second World War Write an essay comparing the destructive power of these weapons with those used in the Second World War.
- Do you think Western policy of appeasement of the fascist powers brought about the Second World War? Why? Or why not?
- What was the basic reason for the policy of appeasement?
- Do you think the United States was justified in using the atom bomb against Japan?
- Why did the Soviet Union sign the Non-Aggression Pact with Germany? What did she gain from it? Discuss

![[Art Culture] Ancient-Texts: Purana, Mahapuranas, Upapuranas, Characteristics](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/CleanShot-2022-12-29-at-09.47.10-500x383.jpg)
![[Model Answer] GSM1-2017/Q4: World History- Decolonization problems in Malay Peninsula](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/c-aoaw-danny-gama-maatin-500x383.jpg)
![[Answerkey] Prelim-2017: History, Culture, Indus Valley Horse, & Science-Technology with explanation for all four sets (A,B,C,D)](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/c-ana-CSAT17-diwaane-500x383.jpg)
hello Sir ,
i am in dire need of old NCERT books( history, geo, civics)2005 or previous editions. could you please help me here.
Can I get a download link to the old ncert history books
Dear Sir,
Can you provide a download link for old syllabus ncert history books 11th and 12th.
With Regards
Balaji s
hi….
many people are not aware of this fact….NCERT old edition both india and world are re printed by orient blackswan. you can buy it online….here is the link for bipin chandra indian history (old ncert)
http://www.flipkart.com/history-modern-india-1st/p/itmdytkey5nk8u58?pid=9788125036845&otracker=from-search&srno=t_1&query=modern+india&ref=869aeb24-c77a-4324-b943-92806ea0173d
old ncert world history by arjun dev
http://www.flipkart.com/history-world-late-nineteenth-early-twenty-first-century-01/p/itmdytkeuehwav7y?pid=9788125036876&otracker=from-search&srno=t_1&query=world+history+arjun+dev&ref=ed1ed4f3-e7f6-4566-882a-73ce2fb710b5
good luck
Sir why you have stopped updating current affairs? Please post it.
Sir my name Anjan, I am study the civilservice. My question can I read only class 11–12th NCERT ? All subject.
Sir my name is Anjan Can u tell me all sudject of civilservice exam related good books names.
Needed World History NCERT OLD 11th and 12th Contemptory World Part 1 and 2 by Arjun Dev
Is your IAS Course available in Hindi Medium