- Problems with government schemes
- 12th FYP: food processing
- Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI)
- National Policy on Handling and Storage of Foodgrains
- PEG scheme
- FCI reforms
- Gramin Bhandaran Yojana
- National Horticulture Mission (NHM)
- National Centre for Cold Chain Development (NCCD)
- Scheme for Agri Market
- Agmarknet
- Dairy Schemes
- Agro Export zones (AEZ)
- Misc. Bodies
In the previous article, we saw the basic details related to food processing industry. Click me if you didn’t. Time to dive into government schemes, policies, plans.
Problems with government schemes
- Agriculture is a State subject. No scheme can be successful without coherence between the Centre and States in policies and strategies. But we have plethora of bodies and departments @center and state level=empires within empires. Even Left hand doesn’t know what right hand is doing. Problem is compounded when ruling parties are different at state and center level.
- Most schemes have Low ceiling (they just give a few lakh rupees) + as plant size increases, the MSME tax benefits decrease. So, food-entrepreneur setups two small plants using money two schemes, rather than one big plant. Smaller the plant=>poor economies of scale=>high production cost, can’t invest in marketing-research, innovation, export quality products.
- These Subsidies/grants are “back-ended” (meaning ca$H is not given before you start the project, but only after the project is completed or in final stage)
- But Parameters of project approval/ file-Processing= non-transparent (just like our UPSC). Timely clearance of project files=nope. Sometimes they don’t even give reasons for rejecting project. Food-Entrepreneur is unsure whether bureaucrats will approve his file or not (+bribe demand)
- Significant time lags from the date of application for financial assistance, to release of funds= affects the project schedule= cost overruns for the investor.
- Most schemes seek to get investors to pump money in certain infrastructure without providing the necessary support for the utilization of the infrastructure. (e.g. asking pvt player to setup cold storage, without guaranteeing continuous electricity supply).
- Overenthusiasm =Excess capacity. Example: many tax-benefits given to groundnut oil refining industry=new units keep popping up even when groundnut cultivation is not sufficient to provide raw material to all refineries. Result: No unit runs on full capacity, industrial sickness, loan defaults, NPA.
- Inputs of Panchayati raj institution, cottage industries, local entrepreneurs are considered irrelevant in scheme design.
- Lack of focus/financing for freezer cabinets in retail outlets/kirana stores, vending machines for tea/coffee/beverages.
- Working capital requirements are high for food processing industry (thanks so many intermediaries, electricity, high duties on imported chemicals etc.) But these schemes only give money for initial project/machines. Don’t provide support for working capital (i.e. cost of day to day operations, buying raw material, electricity-utility bills etc.)
Solution: Integrate all schemes offered by various Ministries and allied agencies.
After years of stupidity and badass thuggary, finally they woke up during 12th Five year plan drafting. Now they’re converging various schemes of Horticulture board, Agriculture ministry, Food processing ministry and Commerce ministry under the National Mission on food processing. ok, better late than never but even small time players like Thailand and Vietnam have reformed before we did. So they’re already ahead in the race of capturing export market. Anyways, lets check various plans, missions, schemes.
12th FYP: food processing
Starting with some (stupid) numbers:
| work | 12th FYP projection (crores) |
| Horticulture development | more than 50,000 cr. |
| post-harvest management + cold storages | more than 7000 cr. |
| food processing | more than 15000 cr. (in 11th FYP this was barely 4000 crores) |
12th FYP wants following:
| overall |
|
| Schemes |
|
| Finance |
|
| Fancy Things |
|
| Export |
|
Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI)
Side note: The new Mains syllabus contains Ministries and Departments of the Government so, in that context, while we’re doing the food processing, better prepare this ministry’s functions as well:
Functions of MoFPI
- Launch National Mission on Food Processing
- R&D in food processing, Specialized packaging for food processing industries, Technical assistance and advice to food processing industry
- Enhance Processing level and reduction in wastages
- Food Safety & Quality assurance
- Financial assistance, grant-in-aids, tariff issues related to
- Fruits and vegetable, Food grain milling industry,
- Dairy products, poultry, eggs, meat, Fish processing
- Bread, oilseeds, meals (edible), breakfast foods, biscuits, confectionery, other ready to eat food products
- Alcoholic drinks, beer, Aerated waters / soft drinks and other processed foods
- strengthen institutions such as
- National Institute for Food Technology and Entrepreneurship Management (NIFTEM)
- Indian Institute of Crop Processing Technology (IICPT)
- Indian Grape Processing Board (IGPB)
- National Meat & Poultry Processing Board (NMPPB)
MoFPI is responsible to 2 fancy missions +3 (bogus) schemes & given ~700 crores in 2013’s budget.
| 2 fancy missions | 3 schemes |
|
+ some chillar schemes for HRD, R&D. |
Let’s see their salient features:
Vision 2015 Food processing
- by Ministry of Food processing
- adopted In 2005
| What? | targets by 2015 |
| processing perishable food produce | 20% |
| value addition to food produce | 35 |
| India’s share in global food trade | 3% |
| investment | 100 thousand crore |
This vision2015 document was prepared by Rabo India Finance ltd. It talks about individual sectors (dairy, meat, tea, coffee etc.) We’ll see those points later during articles on individual sector.
National Mission on Food Processing (NMFP)
- Launched under 12th Five year plan.
- for decentralized implementation of various schemes under Ministry of Food processing with help of state governments.
Contribution ratio:
| Centre | state | |
| North East | 90 | 10 |
| Except North East | 75 | 25 |
Will do following:
- increase agricultural productivity
- increase farmers income
- Help state governments to create synergy between their agricultural plans vs. food processing sector.
- Help state governments in institutional and infrastructural gaps
- Create efficient Supply Chains for agricultural produces.
- Skill development, training and entrepreneurship for both post-harvest management and food processing industry.
- Give capital/technology/skill to MSMEs so they can setup/modernize food processing units
- Help food processing industry to meet quality /food safety standards for both desi and foreign markets.
This national food processing mission has following schemes:
- Technology Up-gradation / Setting up / Modernization / Expansion of Food Processing Industries
- cold chain facilities for Non-Horticultural produces and Reefer Vehicles
- Primary Processing Centres/Collection Centres in rural areas
- Modernization of Abattoirs
- Modernization of Meat Shops
- Human Resource Development (HRD)
- Promotional Activities
- Up-gradation of Quality of Street Food
National Food Processing Development Council (NFPDC)
| function | provide guidance to all schemes of Ministry of Food Processing including above national mission on food processing. |
| composition |
|
^this is ~200 words. From UPSC point of view, the Aukaat of NMFP is not beyond 15 marks questions on ‘salient features’. Hence not covering any further. Moving to the three schemes
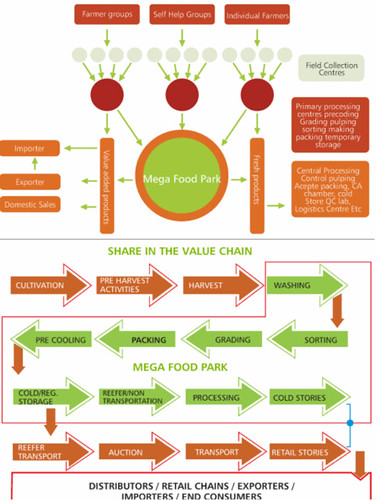
#1: Mega Food Parks:
Mega food parks will be setup in 12th Five year plan. Government allotted more than 1700 crores for it.
- First, a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) will be created to setup the Mega Food Park.
- So, What is this special purpose vehicle, does it look like Tata Sumo or Tata safari? Long thing cut short: you’re aware of debt vs equity. SPV = a limited company setup with money from farmers’ associations, private players, financial institutions, state level agencies etc. (meaning they’re are equity holders)
- Then Government will give them grant to cover **% of project cost. Thus Food Park is setup and everyone benefits.
Financial assistance for mega Food Park:
| Area | Government gives grant: __ % of the project cost |
| General | 50 |
| North East, Hill area, areas under integrated Tribal development plan | 75 |
- Maximum of Rs 50 crore per project.
- Land cost not included in project cost.
Facilities @Mega Food park
| Core Infrastructure Facilities |
|
| Non-Core Facilities |
|
| Common Facilities |
|
| Basic Infrastructure |
|
| Services |
|
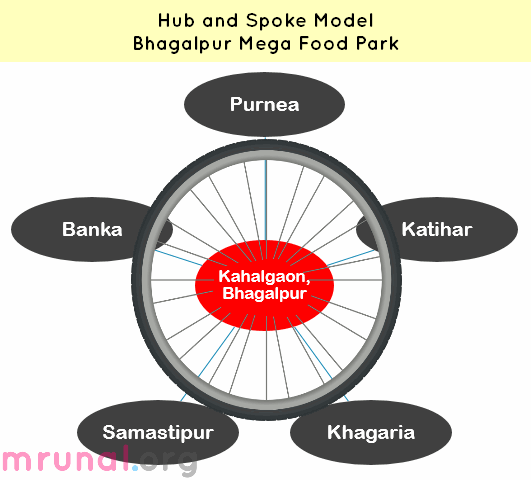
Hub and Spoke Model
Mega food parks are based on the “hub and spoke” model. So what is this Hub and Spoke model?
Imagine a bicycle wheel: it has a strong central hub with a series of connecting spokes. Thus we have
- One Central Processing Centre (CPC) as the hub
- Multiple Primary Processing Centres (PPC) that supply raw material to the hub
| Three Tiers: | What? |
| SHG |
|
| Field collection Center |
|
| Primary Processing Center (PPC) |
|
^ Similar concept for eggs and milk. click the following diagram and concept will become clear:
- Here, each tier is viable, independent and linked with higher players in the market.
- This way thousands of farmers directly connected to food industries located in the Mega food park, without any commission agents= Small, marginal, poor farmers will get more money.
Location Factors: Bhagalpur and Chittor
| Details | Srini Mega Food park, Andhra | Bhagalpur Mega food Park, Bihar |
| Central Processing Center (CPC) | Mogili Village in Chittoor District | Kahalgaon in Bhagalpur district |
| Primary Processing Centers (PPC) |
|
|
| Location Advantages |
|
|
| Sidenotes | Country’s first Mega food park launched in 2012 | #Epicfail. Few days back, main promoter company (Kevantar Ltd) left the project because of land acquisition problem. |
back to the mega-food park topic:
Benefits of Each Mega Food park
- will benefit 6000 farmers / producers directly and 25000-30000 farmers indirectly.
- will generate ~40,000 direct and indirect jobs.
- New employment opportunities created within rural areas= It’ll reduce
- rural-urban migration,
- unplanned urbanization,
- slums/social problems in cities
- will accommodate 30-40 Food Processing Industries in it.
- will have annual turnover of ~500 crore.
- will provide efficient supply chain management from farm gate to retail outlet.
- common facilities=reduces operational cost
- farmers can utilize the Cold Storages, Ripening Chambers, and Ware houses = less wastage, no distress sales
- good transportation facilities viz reefer trucks and vans
- Food entrepreneur can establish backward linkages (with farmers) and forward linkage (with retailers) = compact supply chain=more profits.
#2: Cold Chain infra
Full name of scheme: Establishment of Cold Chain, Value addition and Preservation Infrastructure
Looks like FoodPRO ministry doesn’t have any ‘intelligent’ babu to comeup with a fancy name/abbreviation for this scheme. Atleast they could have named it after you know who. But alas $harad Pawar is the b0$$ of Foodpro ministry, perhaps that’s why schemes are not allowed to be named after you know who.
Anyways what does this cold storage scheme do?
Helps creating integrated cold chain and preservation infrastructure facilities without any break from farm to consumer. Under this scheme, following facilities created:
- Minimal processing centre at the farm gate level having facilities like weighing, sorting, grading, pre-cooling, cold storage and normal storage facilities;
- Mobile pre- cooling vans and reefer trucks;
- Distribution hubs having facilities such as multi-purpose cold stores, variable humidity stores, blast freezing etc.
- food irradiation plants
Financial assistance
| Area | Government gives grant: __ % of the project cost |
| General | 50 |
| North East, Hill area, areas under integrated Tribal development plan | 75 |
Maximum grant: Rs.10 crore per project.
We’ll see more details on cold storage with respect to fruit-veggies processing in separate article later.
#3: Abattoir modernization
Abattoir= slaughterhouse/ butcher house. Food processing ministry runs a scheme for them. This scheme Under PPP mode with involvement of local bodies (Panchayats or municipalities) via
- build-own-operate (BOO)
- build-operate-transfer (BOT)
- Joint venture(JV) basis.
Features:
- establish new modern abattoirs
- modernize existing abattoirs
- promote scientific and hygienic slaughtering.
- Modern technology for waste management.
- better by product utilization (bones, skin etc.)
- provide chilling facility, retail cold chain management etc.
Financial assistance
| area | grant for __ % of the project cost |
| General | 50 |
| North East, Hill area, areas under integrated Tribal development plan | 75 |
Maximum grant: Rs.15 crore per project.
Ten slaughterhouse projects ongoing:
|
|
So, these three were the main schemes of Food processing ministry.
- mega food park
- cold chain infra
- slaughterhouse modernization.
Now let’s look @some chillar schemes of this MoFPI (Ministry of food processing industries)
MoFPI: Misc. Schemes
| North East |
|
| HRD | #1 InstitutesMoFPI has two institutes to offer B.Tech, M.Tech, Ph.D level programs in food processing
#2 Grant to Other universities
|
| Quality | To export in developed countries, your food processing plant would require HACCP, GMP, GHP certificates. Ministry gives financial assistance for it. |
| testing labs | scheme for Setting up/Upgradation of Food Testing Laboratories |
Enough of Food processing Ministry. Let’s look at the schemes by other departments/ministries. (Here, I’m only focusing on schemes related to post-harvest management, storage, food processing and Agro-export, otherwise there are dozens of schemes related to agriculture, public procurements etc. but they’re ignored here.) First the food grains
National Policy on Handling and Storage of Foodgrains
Launched in 2000.
- To Minimize storage and transit losses in foodgrain.
- Declaration of foodgrains storage as “infrastructure” (meaning it can get various tax benefits for investment)
- Encourage mechanical harvesting, cleaning and drying at farm and market level
- transport of grains from farm to silos by specially designed trucks
- Construct chain silos.
- private sector participation via Build-Own-Operate (BOO)
- encourage private sector to
- building storage capacities in which grains procured by Government agencies would be stored on payment of storage charge
- create infrastructure for the integrated bulk handling, storage and transportation of foodgrains
PEG scheme
- By Whom? = Department of Food & Public Distribution (DFPD)
- In recent times, Government has increased the Minimum Support Price (MSP) for wheat and rice. Result? high procurement but FCI’s storage capacity =limited=rotten grains.
- In 2008, new scheme was made “Private Entrepreneurs Godowns (PEG-2008).
- To increase grain storage capacity with help of Private sector.
| Government |
|
| FCI |
|
FCI reforms
Initiates to prevent rotten grain in godowns, FCI will be doing following:
- Dunnage materials: wooden crates, bamboo mats, polythene sheets to prevent moisture from floor to the foodgrains.
- fumigation, insecticides to control pests and rats.
- Regular periodic inspections of the stocks/godowns by senior officers.
- The principle of “First in First Out” (FIFO) to avoid longer storage of foodgrains in godowns.
- To avoid damage during transit:
- Only covered rail wagons will be used to transporting grain
- use of tarpaulins (waterproof canvas) on trucks during road movement.
Gramin Bhandaran Yojana
By Department of Agriculture & Cooperation
- Create scientific storage capacity and allied facilities in rural areas
- grading, standardization and quality control of agricultural produce to improve their marketability;
- Provide pledge finance and marketing credit to farmers, so they don’t have to distress sale immediately after harvest.
National Horticulture Mission (NHM)
- By Whom? = Department of Agriculture and Cooperation
- To increase production of all horticultural products (Fruits, Vegetables, Flowers, Plantation crops, Spices, Medicinal Aromatic plants) in the states.
- Provides funding for various activities (R&D, nurseries etc) including funds for post-harvest management, supply chain infrastructure, cold storages.
Terminal market complexes (TMC)
- scheme is being implemented under National Horticulture Mission
- These Terminal market complexes will establish forward linkages with wholesalers, distribution centres, retail cash and carry stores, processing units and exporters.
- via PPP model under 12th Five year plan.
- Maximum subsidy Rs. 50 crore to the Projects based on competitive bidding.
Some Terminal market complexs (TMC) projects:
|
|
National Horticulture Board (NHB)
- Autonomous society (falls under Department of Agriculture & Co-operation, Ministry of Agriculture)
- For food processing, NHB runs following schemes
| Commercial Horti |
|
| Tech Dvlp | Technology Development and Transfer for promotion of Horticulture
|
| market information | nation-wide communication network for speedy collection and dissemination of market information including:
then NHB issues farmers’ advisory using above reports. |
| Horticulture Promotion Service |
|
National Centre for Cold Chain Development (NCCD)
Setup during 11th FYP, under Societies Registration Act, to do following
- Create an enabling environment for the cold chain sector
- help private sector involvement in cold chain sector
- Financial assistance upto 90% to State Governments to setup/modernize/expand cold storages and ice plants via cooperatives.
- establish standards and protocols related to cold chain testing, verification, certification and accreditation as per international standards
- Provide technical assistance to Financial Institutions, Government Departments/ agencies, and industry for selecting cold chain component e.g. refrigeration units, refrigerated transport equipment, display cabinets, milk tanker etc.
- HRD and technical advisory.
Scheme for Agri Market
Full name: Scheme for Development/Strengthening of Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure, Grading and Standardization (Again too bad no fancy abbreviation.)
By Ministry of Agriculture.
- To Develop and Strengthen agricultural marketing infrastructure.
- Facilitate private and cooperative sector investments in marketing infrastructure.
- Provide additional agricultural marketing infrastructure to agriculture, dairy, poultry, fishery, livestock and minor forest produce.
- facilities for grading, standardization and quality certification of agricultural produce so farmers can get money commensurate with the quality of their produce;
- Introduce Negotiable warehousing receipt system
- promote forward and future markets
- To create general awareness and provide education and training to farmers, entrepreneurs and market functionaries.
Agmarknet
- Agricultural marketing information network (http://agmarknet.nic.in/)
- by Directorate of Marketing & Inspection (DMI) under Agro ministry.
- it is an online portal that provides information on following
| Prices | daily prices of various commodities |
| Movement | information on the type of goods that have arrived across the various wholesale markets Commodity |
| Farmers’ Advisory |
|
| Weather |
|
| Commodity Exchange | information on various commodity exchanges in India and abroad along with |
| Research | higher institutes for agricultural research, international agencies like the Food and Agriculture Organization |
ok so far we saw the schemes associated with Agro+Horti+Marketing. Now moving to Dairy
Dairy Schemes
By Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries
They run following schemes:
- install Bulk Milk Coolers at village level close to the area of milk production
- for installation of bulk milk cooler
| Intensive Dairy Development Scheme (IDDS) |
|
| Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme (DEDS) |
|
National Dairy Plan (NDP)
by National dairy development board (NDDB), with support from International Development Association (IDA)
- Phase-1 (2012-17) was launched at Anand, Gujarat.
- Scheme will run in 14 states – Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Orissa and Kerala.
- ^These states collectively account for over 90% of country’s milk production.
National Dairy plan will do following:
- Breed improvement + animal nutrition=> increase milk production, reduce methane emission.
- Strengthen of village based milk procurement system= Rural milk producers to get greater access to the organized dairy sector.
- HRD, management, knowledge sharing, R&D and other fancy stuff
Funding pattern
| ca$h comes from |
|
| to | NDDB: National Dairy Development Board (a statutory body) |
| ultimately to | End Implementing Agencies (EIAs):
|
^Exactly 159 words. Again aukaat of National dairy plan cannot be beyond 12-15 marks from UPSC point of view, hence not going into further details. Besides, we’ll look more into Dairy sector in separate article later. Time to move on to Agro-Export related schemes
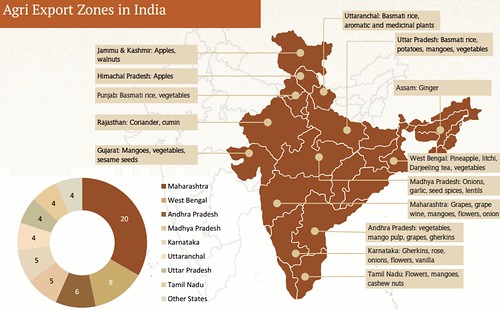
Agri Export zones (AEZ)
- In 2001, By Commerce Ministry.
- Total 60 AEZs in 20 states.
- To converge the efforts of central and state governments to increase agro-exports
- AEZ concentrates on a particular produce/ product located in a geographically contiguous area (e.g. Mango in Chittur District of Andhra) and coordinates the ongoing Central-State schemes to cover the entire value chain from farm to the foreign consumer, including sorting, grading, packaging, processing, exporting.
AEZ: Problems
- Government Agencies don’t take ownership or responsibility.
- Villagers and field officers are unaware about the scheme and its conceptual framework
- The Design of AEZ itself doesn’t have project orientation.
- Lack of coordination/ monitoring system in AEZs
- The investment made by central and state government have not materialized into real-useful assets on the ground.
- Indiscreet proliferation of AEZs in certain states. WB, Maharashtra have multiple Agro export zones while Odisha barely got one AEZ and that too in 2013= More than a decade after the scheme was launched in 2001!
Export credit schemes
|
get duty credit for exporting food products |
|
Export to Europe, Latin America block, African block, or Commonwealth Independent States (CIS) block are entitled for duty credit. |
|
duty credit for exports to countries NOT included in above FMS list e.g. Thailand, Taiwan and the Czech Republic. (ok then when next: another scheme for countries not included in MLFPS list?) |
|
duty credit for exporting following
|
Doubt: what is duty credit?
Without going into all technical correctness:
- You exported xyz worth Rs.100 then Director General of Foreign trade will give you a scrip (piece of paper) worth Rs. 2 to 5 (or whatever % credit is decided in the scheme)
- When you import capital goods, you’ve to pay custom duty. But you can use these credit scrip to pay for that custom duty.
Another doubt: Why does or why should government give duty credit?
Ans. Because other (stupid) schemes have failed to improve the rural infrastructure, hence it is difficult to transport/market these products from India to abroad. Therefore duty credit is given to offset infrastructure inefficiencies and other associated costs involved in marketing of these products.
Misc. Bodies
List is not exhaustive (and that is the criticism: too many bodies=lack of coordination.)
Export related
| APEDA |
|
| MFEDA |
|
| EIC |
|
Boards
|
|
| Grapes |
|
| Nddb |
|
| Meat + Poultry |
|
Research/Education related
| ICAR |
|
| CFTRI |
|
| Crop processing |
|
| NIFTEM |
|
| Nutrition |
|
| Horticulture research |
|
Next article, we see the nuisance of middlemen, APMC Acts, direct cooperative markets (Rythu bazar etc).

![[Win23] Economy Pill4ABC: Sectors: Agri, Mfg, Services, EoD, IPR related annual current updates for UPSC by Mrunal Patel](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/win234b-500x383.jpeg)

![[Economy] BOT-PPP Model for Highways, Right to Repair, WTO & Foodgrains Exports- Weekly Mrunal Digest from Jul week1-2022 (WMD)](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/ppp-bot-500x383.jpg)
thanks a lot sir
Thankyou sir….its very helpful
thank you very much sir. Very neatly analysed.
Dear Sir,
Please write some notes on PDS and subsidy.
thanks
Respected Sir,
Thanks for this owesome article series.
Mrunal Sir,
Do u know the best thing associated with your article
“It brings a unique happiness inside whenever u released some new articles. It’s an awesome feeling something like what one get’s from his loved one’s (parents, siblings, teachers) that they deeply care for him”
Keep shining our hearts….
thank you mrunal … please keep posting !
Dear sir
Kindly guide suggest me about the notes for gs and geography(for mains) for quick preparation.
whose notes are the best and where i can get it.
sir plz do smthg regarding invest models and that farm subsidy topic of paper 3
Excellent article.Well explained and easy to understand.Thank you.
i can see ur hard work sr………… thanks a lot
really outstanding article
sir,
your articles are awesome.find it very useful.
thanks for your efforts.
Hello sir,
what is the use of establishing the cold chains when we will not be able to provide them with 24×7 power. Anyways the products will rot and will lead to another scam….cold chain scam:-)
Extremely helpful article, presented in a very lucid manner..
Thanks , sir..
VERY INFORMATIVE SIR THANK YOU.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rtS6KwxcE7w A film on Mega food parks by MOFPI.
thanx… good clip….
im playing the devil’s advocate here but why does the govt need to set up food parks… isnt it enuf that it has deregulated de licensed the industry… let the mncs (kellogs, nestle) and cooperatives set up their own infra… so that it focuses more on consolidating legislation s and setting standards and labs etc…. any one??
You have an amazing sense of humour.. Handled in your articles excellently…Reading that in between the lines really reduces the stresslevel..Keep it up ..
i have to make big plant nursaries near tirupati please sugest me
your articles very impressive. please mail your new articles to me
thanking you
g.babu
Sir , thank you, send me for Gujarat farmer mega food park or send me your cell
Sir, I am interested in opening a food testing lab also for which the ICAR and MOFPI is giving financial assistance. Plz help me how to apply and whom should I contact regarding this. Is there any consultant or any kind person Who can help me
Respected sir I need full information to set up a commercial processing juice industry by using sweet lime and acid lime and tomato in one unit seasonally. Please provide me project proposals with all budjet details.
bahut sahi aur satik shabdo ka prayok :)
What type of questions can we expect from this section of the syllabus (Food processing industry) in the UPSC Mains GS3 ?
Why the govt is confusing us with lot of schemes………..