Ozone layer recovering thanks to Montreal
- Ozone gas in stratosphere prevents 99.5% entry of UV radiation (255nm) on earth.
- Chlorofluorocarbons / freons: non-reactive, non-flammable, non-toxic. Used in Refrigerators, spray cans, insulation foam and propellant.
- Once they’re released in atmosphere, they reach stratosphere=> react with UV=> release Chlorine free radicals => Ozone broken.
- 1980s: Scientists realized Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) reach had damaged Ozone layer above Antarctica. Result?
- Skin cancer, Cataract, Sunburns
- Phytoplanktons die=> fish population declines.
- Soil Moisutre content declines, plant proteins are mutated=> plant growth affected.
- Fibers and Wall paints fade faster.
- Late 80s: Montreal Protocol signed, to cut down use of
- chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) / freons
- Halons in fire-extinguishers
- 2014: CFC has declined by 90%, Ozone layer showing signs of recovery- as per United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
- This will also prevented 2 million skin cancer cases per year.
- 2050: Ozone Layer will recover near mid-latitudes
- 2075: Ozone layer will recover near Antarctic.
Challenges:
- CFCs are replaced with HFCs (Hydroflurocarbons). Although HFCs don’t deplete Ozone layer but they’re greenhouse gases, hence contribute to global warming.
- Researchers found Carbon tetrachloride increased in atmosphere. This is a banned ozone-depleting carcinogenic solvent.
- Meaning, some companies in the third world countries are still using it illegally, as a cheaper alternative to HFCs.
IPCC 5th Assessment report
| Assessment Report (AR) | Year |
| 1st | 1990 |
| 2nd | 1995 |
| 3rd | 2001 |
| 4th | 2007 |
| 5th | Yet To Publish Entirely. (Only 2/3 Parts Published) |
IPCC 5th Assessment Report (AR5)
Three groups working to prepare this report
| group No. | working on | Published? |
| 1 | On physical science and climate change | September, 2013 |
| 2 | Adaption measures [“Impact, Adaption and vulnerability”] | March 2014 (hence in news during April 2014) |
| 3 | Mitigation measures | yet to be published |
So now we come to the report that is making news=> Report on “Adaptation measures” under 5th assessment report. Since this is only a small part of the big report yet to come => so, don’t waste time doing lot of Ph.D majoori (labour) in this report.
Overall it says following:
- Soil moisture will decline globally => dry regions will become even more drier => global drought =>food shortage.
- Temperature has risen 0.2 cel since Industrial revolution.
- Climate change is inevitable challenge, but if we understand the challenge correctly then we can better tackle it.
- But, Science can help in adaptation and risk reduction. for example:
| Problem | SCIENTIFIC SOLUTION |
|---|---|
| Sea Level Rise | Build coastal barriers and plant mangroves |
| Agriculture | climate resilient seeds and agri-technology |
| Water | Water-conservation, desalination. |
| Natural Disaster | Invest in technology for early detection of cyclones, flood and droughts=> training of personnel, take precautionary measures. |
Impact on India?
- The poor and developing countries of tropical regions are the most vulnerable of the climate change.
- Small island countries of Indian Ocean, like, Maldives, Mauritius and Shri Lanka, will migrate to India as climate refugee. (India has made such agreements with these countries)
- Indian coastal cities will face danger of submergence.
- Erratic Rainfall, melting of Himalayan glaciers, frequent flooding, draughts, storms and cyclones.
- Food insecurity for large population.
- New diseases and weather patterns.
Sahara Dust Storm in London
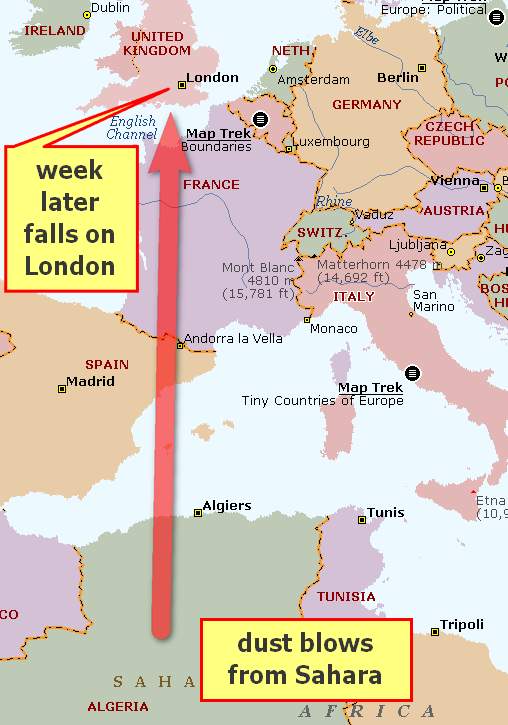
Sahara Desert dust brings smog to UK
- During summer, the Sahara desert undergoes low pressure depression => dust lifted upwards and flies towards Europe and America
- locally this is called “Simoom” or poison wind, because it causes heat strokes.
- In April 2014: a large mass of this dust storm fell over London, hence in news.
| good | bad |
|---|---|
| Provides phosphate nutrients to Amazon soil. | Continuous and large scale dust storm decreases total soil fertility=forcing villagers to migrate to cities. This happened in USA during 40s, more than 2.5 million people migrated to California. |
| Provides nutrients to plankton in Mediterranean sea. |
|
| reduces the surface temperature sea and lowers the possibilities of hurricane |
|
| Harmattan wind carries this dust in Niger- brining soil nutrients K, Mg and Ca. |
|
| dust particles directly reflect sunlight backinto space, thus reducing amount of heat coming to Earth’s surface- this has both positive and negative impacts on long term climate. |
|

![[Environment] Mangrove Species Conocarpus banned in Gujarat & Telangana](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/edp-conocarpus-500x383.png)
![[Environment] Floating Solar Farms, Banni Grassland, Nairobi flies & more Weekly Mrunal Digest from Jul week1-2022 (WMD)](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/Floating-Solar-Farm-500x383.webp)
![[Environment WMD] Single use plastic ban, ESZ, Surya Nutan Cooker, & more from Jun week3-2022](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/single-use-plastic-main-500x383.jpg)
![[T25] UPSC Mock Round#43: Environment & Geography Practice Questions- Global Climate Risk Index 2020, Bog wetland and More](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/c-t25-taimur-500x383.jpg)
do u have any notes in hindi ?
Superb
nicely covered all aspects
mrunal sir… u hv given studyplan for SBIPO general awareness… reasoning and english… but not on DI …. plzz give a study plan for DI so tht i can practice it for upcoming sbipo 2014 exam
Sir thank u for ur valuable info. sir, one request please give me some idea how to study from indian culture specrum book
Should i read the entire book
Awesome article as awx……thnx alloott sirr……..
Thanks very much for your invaluable articles.
Sometimes you really scare me that whether I am on the right track. or not
I have missed most of the news you publish and will happen in future as well.
Please let us know how to collect the current affairs. I want to develop the skills you do so that I can get the confidence that I am an UPSC aspirant.
This is humble request.
really gud matter
nice work sir .. specially for hindi medium student who get to complete one hindu new paper for a 4 hrs in a day to undrsatnd only article page .its good work sir ji u r god
Ty mrunal
please put in Hindi ………….if possible
thanx to mrunal sir
pls any one tell me how to qualifie in upsc compulsory english paper i have written 4 times upsc mains but unluckly 3 times not qualifie in english
The IUCN status of Olive Ridley Sea Turtle is “Vulnerable” and not “Endangered”.
Though it is vulnerable but All the species of sea turtles in the coastal water of Orissa are listed as “endangered” as per IUCN Red Data Book.
Dig-Boy-1901-Indian Oil company(from Assam Oil company ltd.)
Refinery is in loss cuz of lack of Raw material, i.e, Production not sufficient. Technologically, Refinery is top notch (within India)…the solution is to bring in more raw material from surrounding production fields of N.E
Creation of Hydro electric plants is not a mutually exclusive event, as it will be covered by a body similar to “SJVN” of Assam(Don’t know the exact body).
Besides, if refinery is closed, there is nothing else running this town’s economy, although from a business perspective it’s not IOC’s head ache(apna kaam banta, bhar mein jai janta)
Mahendraparvata and http://www.un.org/apps/news/story.asp?NewsID=46461&Cr=court+of+justice&Cr1=#.U9JzZfmSxPo
Shiva and Dravidian
Hi mrunal, I was reading about euro norms, in Wikipedia it is written that it does not consider carbon dioxide. It considers NOx, THC, NMHC, CO and PM. Please clarify.
Phenomenon work…Great…thanks a lot,sir.
If the Gir Lions have to be relocated to MP, what uttar pradesh and Akhilesh has got to do with it?
thanks mrunal
Mrunal, the working groups III report of IPCC is out. check this
http://www.downtoearth.org.in/content/latest-ipcc-report-reeks-northern-agenda
well done keep it up
hello Mrunal sir,
You have mentioned that Angorvat temple architecture is of Kalinga style, but in wikipedia it is mentioned that it is of Dravidian style.
Please clear this doubt.
Sorry I got confused with the wiki page of Dravidian Architecture.
hi mrunal, can you list out the important hydroelectricity projects
“Gir has been traditional habitat of lions since centuries.”
Asiatic Lions spread from Mediterranean to N.E India http://www.planetwildlife.com/information/species/asiatic-lion
There natural habitat was rather large…why wasting time in trivial thing? Cuz once UPSC asked such question on Rhino
sir when upsc will declare the result of CSAT Pre 2014 ?
Sir I want to know that when upsc will declare the result of CSAT PRE 2014.
One more part under 5th Assessment Report: Synthesis Report (Nov 2014). The summary of this report (might be helpful):
1. Burning of fossil fuels, has been the dominant cause of global warming over the past several decades (In previous reports it had said humans were very likely the cause of climate change. In this it says more strongly that humans + fossil fuels are the very cause)
2. Warming by the end of the 21st century will lead to high to very high risk of severe, widespread, and irreversible impacts globally (Ex: West Antarctic Ice Sheet will melt totally forever, ocean level rise + flooding)
3. Reiterated previous report point – sea-level rise, shrinking glaciers, decreasing snow and ice cover, warmer oceans and more frequent and intense extreme weather events, such as heat waves
4. More delay in phasing out the fossil fuel more costly it is going to be
stretdgy for civil services…how can studty best