- Prologue
- [Act 1] Infrastructure Corridors GK/theory
- [Act 2] Road infrastructure
- [Act 3] PPP & Infrastructure: challenges & reforms
Prologue
Economic Survey Ch11. Energy, Infrastructure and Communications. Total four subparts
- Energy & communication
- Roads, Industrial corridors, PPP, Infrastructure problems & reforms
- Shipping, aviation
- Railways infrastructure
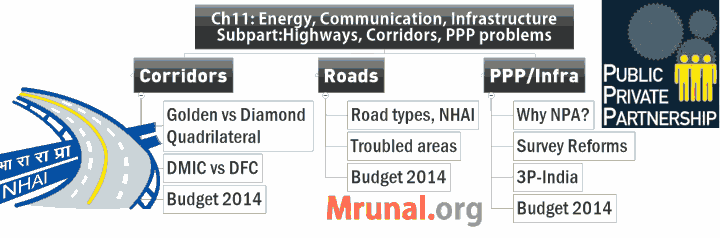
[Act 1] Infrastructure Corridors GK/theory
For stupid MCQs: list of rail and highway corridors:
C1: (Rail) Dedicated Freight Corridor Project

| Western | Eastern |
|---|---|
| ~1500km | ~1800km |
| Jawaharlal Nehru Port in Mumbai to Dadri near Delhi | from Dankuni near Kolkata to Ludhiana in Punjab |
| Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) | World bank funding |
| Starts: Dadri in UP | Ludhiana, Punjab |
|
|
| Ends: J.Nehru Port near Mumbai | Dankuni, W.Bengal |
- Total 3000+ kms. ~96% land acquired.
- Land compensation as per Railway Amendment Act’08
Benefits:
- Only electric trains =less greenhouse gases.
- More transportation capacity
- LESS unit costs of transportation
C2: (Road) Industrial corridors: DMIC

- 2006: MoU India and Japan
- 2008: DMIC Development Corporation as the implementing agency. (and NOT NHAI)
States covered under DMIC
|
|
- above six states list, as per PIB-April 2007. and in July 2007, Commerce ministry elaborated that it’ll pass through Madhya Pradesh as well.
- Total length: 1483 kms
- Railways designing (Western) Dedicated rail freight corridor to extract maximum leverage with DMIC.
C3: Other industrial corridors

| Industrial corridor | States | Funding |
| Chennai-Bengaluru-Chitradurga | KarnatakaAndhra PradeshTamil Nadu | Japan |
| Bengaluru-Mumbai Economic Corridor (BMEC) | Maharashtra, Karnataka | United Kingdom |
| East Coast Economic Corridor (ECEC) | linking Kolkata-Chennai-Tuticorin | ADB |
| Vizag-Chennai Industrial Corridor (VCIC) | Andhra Pradesh and Tamilnadu | ADB |
| Amritsar-Kolkata Industrial Corridor (AKIC), 2014 | 150-200 km band on either side of the Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (EDFC) in a phased manner. 7 states:
|
Govt.ofIndia |
C4: Golden vs. Diamond Quadrilateral
| Golden Quadrilateral | Diamond quadrilateral |
|---|---|
| 1999 | 2014 |
| under NHAI | under Rail budget |
| To connect four main cities of India Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai. ~6000km length | To connect major metros through High Speed Rails. |
(length wise, longest to shortest)
|
Proposed routes
|
C5: (Road) North South, East West corridor
| North | Srinagar (Kashmir) |
| South | Cochin (Kerala), Kanyakumari + Salem (TN) |
| East | Silchar (Assam) |
| West | Porbandar (Gujarat) |
Budget 2014: industrial corridor announcements
National Industrial Corridor Authority
- to coordinate the development of the industrial corridors,
- with smart cities
- linked them all using transport connectivity
- HQ Pune. (100 cr allotted)
Additionally: Three new smart cities in the Chennai-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor region:
| Ponneri | Tamil Nadu |
| Krishnapatnam | Andhra Pradesh |
| Tumkur | Karnataka |
- Amritsar Kolkata Industrial master planning will be started.
- Bengaluru Mumbai Economic corridor (BMEC) and Vizag-Chennai will be developed.
[Act 2] Road infrastructure
| Name | Responsibility of | Connects |
|---|---|---|
| National Highways | Union Government | State capitals |
| State highways | State Government | State Capital to District HQ |
| district roads | Zila Parishad | District HQ to tehsil and Blocks |
| village roads | Gram Panchayat | Villages to neighboring towns |
| other roads | >46 lakh kms |
| state highways | 1.4 lakh kms |
| national highways / expressways | ~93,000 kms |
R1: National highway authority of India (NHAI)
- Statutory body under ministry of road transport and highways
- it’s responsible for national highways’ development, maintenance and management
- Three main projects
- National Highway developmental Project (NHDP)
- Golden quadrilateral
- north-south + East-west corridors
- NHDP phase 6 started from 2013.
R2: NHAI: Where do they get cash?
- 1999: Government imposes CESS on petrol and (high speed) diesel.
- Rate: 2 Rupees per litre
- This FUEL CESS money goes to Central Road Fund (CRF) [in public accounts and NOT in consolidated fund of India].
- from CRF, money goes to four places:
- state highways
- rural roads
- rail over bridges
- NHAI’s national highway Development Program. (0.50 paisa from every two rupee)
- NHAI also borrows fund by issuing bonds in Debt market.
- World bank, ADB, JICA also gives them fund, mostly used for LWE areas.
R3: Highways in troubled areas
| SARDP-NE |
|
| 2004 |
|
| 2009 |
|
| PBJY | FDI and tax reliefs |
|---|---|
|
|
R4: Budget 2014: Highways related announcement
- Expressways in parallel to Industrial Corridors. This will help faster transport of goods across country.
- more funds for NHAI (>37k.cr) and North East road Development(3k.cr)
- Will built 8500 km highway in FY2014
[Act 3] PPP & Infrastructure: challenges & reforms
from the points given in Economic Survey:
P1: Why infrastructure important?
- Population + Economic growth= heavy pressure on Transport + Energy + communications.
- So, if these 3 not improved = GDP bottleneck + poverty rise + costly essential services.
- Without environmentally sustainable infrastructure= No inclusive growth
- Lack of infrastructure = Poor GDP growth rate
P2: Government role in Infra Development?

Government role in infra = three angles: planning, contracting, and regulating.
State#1: Planning
- Planning = the decision to build an element of infrastructure.
- Requires inter-relationships between multiple elements: e.g. where there is a port, there will be a requirement for railway lines and roads
- Political considerations inevitable in the planning process.
- As an example, political authorities may decide that it is important to build transportation infrastructure in backward states, or in states with greater law and order problems, even when their economic viability is lower.
Stage#2: Contracting
- The task of giving contract to a private producer for building infrastructure.
- survey recommends creating a new agency for drawing the complex PPP contracts, and prevent future litigations.
Stage#3: Regulating
Once an asset is working, autonomous body must regulate the infrastructure Usages and service charges
- to prevent market failure
- to prevent monopoly of any private/public company
- to provide level playing field between public and private sector companies
P3: PPP Challenges
- 1300 projects worth ~7 lakh crore by the end of March 2014
- These projects are at different stages of implementation, i.e. bidding, construction, and operational.
| PPP worldwide | PPP in India |
|---|---|
|
|

- In India, Initial PPP projects were successful (early 2000s), because private companies finished within deadline. Many highways, ports, airports successfully working.
- With booming Indian economy (before sub-prime crisis), the private companies started “overleverage” i.e. creating assets on borrowed money beyond a sustainable level. Even companies with modest balance sheets started bidding for big PPP projects beyond their “aukaat”.
- They had hoped, the booming economy would ‘reward’ their risk taking ability e.g. lot of highway traffic = we’ll mint crores via toll collection.
- They had hoped even in worst case scenario, Government would redraw the PPP contracts – extending deadlines or allowing them to collect more toll charges.
- But with subprime crisis, global economic slowdown, these companies couldn’t finish projects on time, OR sustain the losses (because expected traffic did not come.)
- They couldn’t raise fresh loan / equity /capital / finance because of the slowdown.
- Government did not help them. In fact Government aggravated the problem by stalling environment clearance, policy paralysis, corruption, rent seeking etc.
- Even when PPP contracts were redrawn, matter was stuck in courts because of corruption allegations.
- Result= #epicfail, bank NPA increased.
More problems in PPP
- No integrated planning: ports that lack railway lines or power plants that lack coal supplies
- Corporate bond market is not developed. Companies rely on banks for finance. higher interest rate = more chances of NPA
P4: PPP reforms: Economic Survey points
- for future highway PPP contracts do following:

| Traffic trigger | re-equilibrium discount |
|---|---|
|
|
- overleveraged companies can’t finish highway projects, so
- simplify corporate debt market regulation, to help them get fresh capital
- Allow them to “EXIT”, let new player takeover the project.
- Highway tolls should have correlation between
- reasonable profit for the private player
- users’ capacity to pay
- Setup a Separate institute for designing PPP contracts. (Budget 2014 implemented this)
- Division of work
- infrastructure construction work should be handed over to giant companies having expertise in construction
- After the asset is built, the operation work / toll collection work should be given to another company having expertise in “operation part”.
P5: 3P India: Jaitley’s solution to PPP problems
What was the problem?
- PPP projects often run into time and cost over runs
- then private players want more share from profit/revenue
- PPP contract doesn’t provide that
This problem leads to
- private player compromises service quality
- private player goes for court litigation
- Government demands bribes to rework the PPP contract to help the distressed private company
Budget 2014 Solution?
- Budget 2014 announced new institution called 3P India (500 cr provided)
- 3P India will ensures proper PPP contract-making with proper grievance redressal mechanism
- 3P India will not provide funding / finance to any PPP projects.
P6: Infrastructure Financing
- 12th FYP projections: ~1 trillion USD investment necessary for infra. Development. 50% of that expected to come from private sector.
- To achieve this, Government has taken following initiatives
| Bank loans | flow rank: power > roads > Telecom |
| FDI | flow rank: Telecom > Power > Renewable energy |
| IDF | infrastructure debt fundFor long term loans to infra. projectsIDF can be setup either as an NBFC (2 exist); or a Mutual fund (5 exist) |
| IIFCL |
|
| IIPDF | India Infrastructure Project Development Fund (IIPDF) under Economic Affairs department. |
| InvITsREITs | Discussed under chapter 13=> rural and urban infrastructure segment. |
| Municipal bonds | Government has simplified municipal bond norms, to help’em raise funds for urban infra. Development |
| Tax free bonds | 2013: Government allowed the PSUs to issue tax free bonds worth 50,000 cr. for infra. Development |
| PPP training |
|

![[Win23] Economy Pill4ABC: Sectors: Agri, Mfg, Services, EoD, IPR related annual current updates for UPSC by Mrunal Patel](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/win234b-500x383.jpeg)

![[Economy] BOT-PPP Model for Highways, Right to Repair, WTO & Foodgrains Exports- Weekly Mrunal Digest from Jul week1-2022 (WMD)](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/ppp-bot-500x383.jpg)
marvellous
dear sir, i am unable to understand the meaning of 100percent FDI in railway. Actually, i am not acquainted with the basic concept of the FDI. Could u help me please ?
Mrunal bhai. PIB article (http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=106267) says DMIC spans through Madhya Pradesh also. It does not mention Delhi like you have. What is your source of info?
here it says Delhi: http://pib.nic.in/newsite/erelease.aspx?relid=26890
Mrunal sir….. You work is really commendable ! Seriously.