- Prologue
- [Act 1] Fertilizers: Botany /Chemistry angle (NCERT)
- [Act 2] Subsidies: Where is it counted in budget?
- [Act 3] What is Nutrient Based subsidy (NBS)?
- [Act 4] Budget-2014 on Agriculture
- Appendix:
Prologue
Economic Survey Chapter 8: Agriculture and Food Management. SIX subparts:
- Fertilizer subsidy & schemes, Budget-2014 announcement
- Minimum support pricing, Sugar pricing, Procurement reforms
- National food security act (NFSA)
- WTO Bali Summit
- APMC reforms, National market for agriculture, NSEL crisis
- El Nino and its impact on Indian monsoon
[Act 1] Fertilizers: Botany /Chemistry angle (NCERT)
- Source: NCERT Biology Class11, Ch.12
Essential elements classified into two parts:
| Macro nutrients | Micro Nutrients |
|---|---|
|
Iron, manganese, copper, molybdenum, zinc, boron, chlorine and nickel. |
| present in large amount in the tissue | Needed in very small amount |
| Nutrient | Symptoms visible in | Why? |
|---|---|---|
|
olderleaves |
|
|
youngerleaves |
|
if soil is deficient in any nutrient, we’ve to artificially fill it up with fertilizer or manure.
| Fertilizer | Manure |
|---|---|
| Inorganic salt | Natural substance from decomposition of organic waste. |
| doesn’t provide humus to soil | yes, provides |
| rich in nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium (depending on composition) | less rich |
| prepared in factories | prepared in fields |
| Fertilizer | Ratio* | source |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (Urea) | 4 |
|
| Phosphorous | 2 | 80-85% via import |
| Potash | 1 | 100% via import |
*Ideal ratio for Indian soil
[Act 2] Subsidies: Where is it counted in budget?

Budget type: revenue vs. capital
| revenue part | capital part | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| receipt | Expenditure | receipt | Expenditure |
|
subsidy counted here | ||
Budget type: plan vs Non-plan
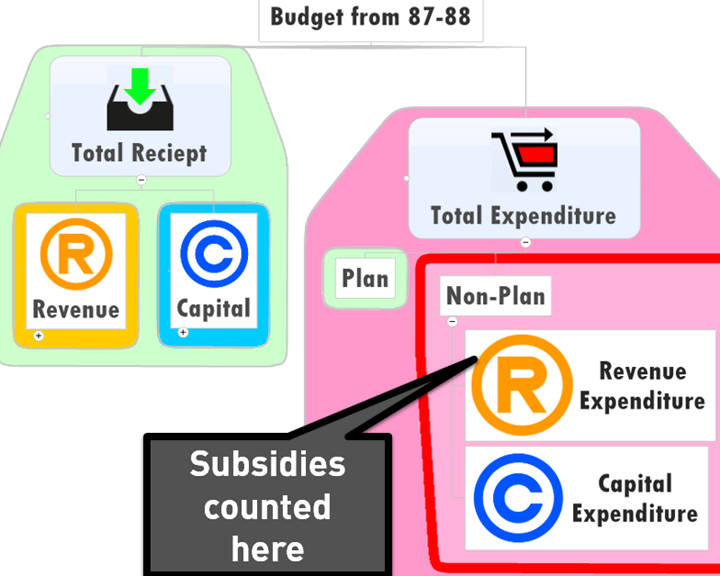
| Total Receipts | Total Expenditure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| revenuereceipts | capitalreceipts | plan Expenditure | non plan Expenditure | |
| revenueExpenditure | capitalExpenditure | |||
| subsidies counter here | ||||
Ranking of Subsidies

| Ranking 2013 | Food > Petroleum > fertilizer |
| Ranking 2014 | Food > Fertilizer > Petroleum |
Amount of Subsidies (Cr.)
| Subsidycomponent | RE-2013 | Jaitley fullBE-2014 |
| Food | 92000 | 115000 (same as Chindu interim) |
| Fertilizer | 67971 | 72970(increased over Chindu interim) |
| Petroleum* | 85480 | 63427(same as Chindu interim) |
* given to state-run oil companies for selling fuel, LPG and kerosene below cost price.
Fertilizer subsidy internal ranking
| Jaitley budget 2014 | Rs. Crore |
|
36000 |
|
25000 |
|
12300 |
Ranking: Domestic urea >> (P,K) >> Imported Urea
[Act 3] What is Nutrient Based subsidy (NBS)?
- Launched in 2010. Before that, we had “product based subsidy”.
- Under NBS, govt. gives subsidy based on weight of the different Macro/micro nutrient in the fertilizer.
- In this way, fertilizers companies can make new product mixes with micro-nutrients, according to soil requirement in each region.
- And farmers can afford to buy these tailor-made fertilizers because government gives subsidy to keep them cheap.
Disadvantages of NBS?
- Urea not covered in this scheme.
- Delay in NBS subsidy payments.
- Therefore Fertilizer companies focus more on Urea more than other fertilizers.
- Result: shortage of (Cheap) non-urea fertilizers.
- So, farmers also overuse Urea. ideal ratio of NPK disrupted
| Nutrient Ratio in soil | Ideal | real |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | 4 | 8.2 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 2 | 3.2 |
| Potassium (K) | 1 | 1 |
- Result? Ground water pollution, Soil fertility declined, especially in Punjab and Haryana
- Additional nitrogen doesn’t improve crop yield beyond a point.
- Farmer doesn’t move to specialized fruits, vegetable, horticulture cropping- because they require special non-Urea fertilizers, which are not easily available at cheap rates.
- So, one hand, tax payers pay for subsidies (and MSP), yet consumers still suffer from food inflation due to low production.
- Shortage of coal and natural gas has decreased Urea production. Government has to import from abroad.
Urea smuggling
| UP, Bihar | urea smuggled to Bangladesh and Nepal |
| Maharashtra, Gujarat and Haryana | Urea smuggled to chemical industries- especially in dyeing, inks, coatings, plastics and paints. |
- Result: nearly 3 million tonnes of Urea, doesn’t reach farmers.
- And since Government gives Rs.5360 subsidy PER tonne to urea companies so imagine the loss of public money!
- Thus fertilizer subsidy hurts everyone: farmers, firms, taxpayers, and consumers
Economic Survey reforms:
- Add Urea in the NBS regime.
- Pay fertilizer subsidy directly to farmer (i.e. by bank transfer) as per Nilekani Task force recommendations.
- Then, fertilizer companies & their middlemen will have no benefit in smuggling.
- Encourage Indian companies to setup joint ventures with foreign fertilizer companies.
- Enter in long term fertilizer supply agreement with foreign countries.
[Act 4] Budget-2014 on Agriculture
Soil Health card
- Mission mode project (100 crores)
- For all farm lands
- 100 Mobile Soil Testing Laboratories to be Set up
- A computerized system will facilitate local agriculture science centres to keep details of ‘soil test’ results of their area.
- The system will give allot a unique number to ‘Soil Health Card’ of each soil sample.
- The card will carry crop-wise recommendations of nutrients and fertilizers
- This way, any change in ownership of the farm lands will not create any problem in updating the information
Gujarat’s soil health card projects
- 2006: Gujarat becomes the first state to launch Soil health card scheme.
- First the soil properties tested-mineral composition, water retaining capacity etc.
- Then farmer gets a soil health cards containing information on what kind of pesticides, fertilisers, seeds and how much water should be used, to get MAXIMUM productivity from his land.
National market & Food security
| National market | Food security |
|---|---|
|
|
AGRO Finance
| Bhoomi Heen Kisan |
|
| PSU Banks |
|
| Interest subvention |
|
| RIDF |
|
AGRO Funds
| National Adaptation Fund100 cr |
|
| Price Stabilization Fund.500 cr |
|
| Warehouse Infrastructure Fund (5k cr.) |
|
| PRODUCE200 cr |
|
| Long Term Rural Credit Fund (5k) | NABARD To provide refinance to cooperative and RRBs |
| Short Term Cooperative Rural Credit (50k cr.) |
|
AGRO R&D support
| Research |
|
| Teaching | Agro universities @Andhra + Rajasthan |
| Horticulture | Universities @Telangana + Haryana |
| Soil testing labs | 100 mobile labs across country |
| blue revolution in inland fisheries | 50 crore |
| Kisan TV |
|
| Indigenous cattle breed | 50 crore |
Appendix:
- This appendix contains the topics, scheme discussed in Economic Survey.
- Beyond that, remaining (truckload of schemes), FDI conditions already under the [Food processing] Article series. click me.
Indigenous cattle breed
| World average | 2238 kg/year |
| India | 1538 kg/year |
- This is mainly due to low genetic potential of indigenous cattle breed, shortage of fodder and prevalence of diseases.
- There 37 recognised indigenous cattle breed in India- Gir, rathi, Sahiwal, Kasaragod Dwarf, Kankrej etc.
- 2013: Animal Husbandry Department launched a project to conserve indigenous breeds.
- Indigenous cattle breeds are better than exotic cattle breed due to following reasons:
- resistant to climate change and diseases
- need less fodder
- suitable for drought work
- Although they give less milk but its quality better than that of hybrid or cross breed cattle.
Existing Agriculture extension services
| Technology |
|
| helpline |
|
| ICAR |
|
| weather |
|
| seeds |
2013: launched Seed rolling plan to identify good domestic seed varieties & improve their production, preservation. (expires in 2016-17) |
| Nutrifarms |
|
National Food Security Mission (NFSM):
Do not confuse between “ACT” and “MISSION”.
| National food security | who? |
| Act(for giving cheap grains to junta) | Dept. of Food and public distribution under consumer affairs ministry |
| mission(for increasing agro production) | Ministry of agriculture (discussed below) |
Food security mission has FIVE components:
- Rice
- Wheat
- Pulses
- Millets (coarse cereals)
- Commercial crops- cotton, sugarcane and Jute
+cotton development program added recently
| Targets @end of 12th FYP | Million tonnes |
|---|---|
| Foodgrains | 25 |
| Rice | 10 |
| Wheat | 8 |
| Pulses | 4 |
| Coarse cereals | 3 |
Related: Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY)
Stupid statistics
| Agriculture growth rateincluding fishing and forestry | 4.7% |
| contribution to GDP |
|
| Contribution to employment | Agro > Services > industries (Ref. Survey box 1.2) |
| Contribution to total inputs in economy | Industries > Services > Agro (Ref. Survey box 1.3) |
| Assertion | in recent years, the real farm wages have increased |
| Reason | there has been a shift from farm to non-farm employment |
| Correct answer | both right and R explains A, because Economic Survey says so |
| 75% | Of annual rainfall comes from south-west monsoon (from June to September). During El Nino, it’ll decline to 70% |
| 60% | Of total foodcrop & oilseed grown in kharif season |
| 35% | Of areable area is being irrigated |
| 45% | of net cropped area, is irrigated. |

![[Win23] Economy Pill4ABC: Sectors: Agri, Mfg, Services, EoD, IPR related annual current updates for UPSC by Mrunal Patel](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/win234b-500x383.jpeg)

![[Economy] BOT-PPP Model for Highways, Right to Repair, WTO & Foodgrains Exports- Weekly Mrunal Digest from Jul week1-2022 (WMD)](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/ppp-bot-500x383.jpg)
thank u sir
Thank u very very much sir
Delhi high court to listen plea againiat upsc decision http://m.economictimes.com/news/politics-and-nation/delhi-high-court-to-hear-plea-against-upsc-decision-not-to-evaluate-questions-on-english/articleshow/40425175.cms
Sir, thanks for your great work. considering very short time left for pre, will you able to provide matter on initial chapters , which seems more important.
Amit refer to the powerpoints and videos for inital chapters. it’s not possible to release their articles before prelims.
A setback for the guys who uses limited data pack of 3G…was hoping +vely
Sir how many article is left before prelim?
awesome
Thank you sir for your effort.Sir,please create one thread after prelims for the search of hostels in old rajendhernagar, karolbagh, mukerjeenagar etc., It will save time,money,energy of so many aspirants.Thank you very much.
mrunal.org for the guys who are doing self prep. and its the step to make upsc aspirants to prepare efficiently NOT for coaching institutes…
sir plz explain how to do that “graph” question in csat ?
every year upsc asks a single question on it
plz throw some light if possible…
Hi. Mrunal
Can we get the copies of our CSE mains answer sheet by using RTI.if yes,then kindly tell me the procedure for it.
Regards
Vinay
Where do the farmers sell their produce, when not selling to the government?
Lord Dufferin, farmers can sell grains at the APMC mandi. If they’re not getting good price, they can opt for Government’s MSP.
Just wanted to confirm something. El Nino officially didn’t arrive this year right? Because monsoon was late but nevertheless, it arrived and fed most regions well.
Nevermind. Read the El Nino article by Mrunal.
A and B start from the same point and in the same direction at 7 a.m to walk around a rectangle field 400*300 m, AandB walk at the rate of 3 km/hr and 2.5km/hr respctvly. how many times shall they cross each other if they continue to walk till 12:30 p.m
@Sakshi
In these type of questions always proceed with concept of relative speed
Speed of A – 3 km/hr
Speed of B – 2.5 km/hr
relative speed in advantage of A = 3.0 – 2.5 = 0.5 km/hr
when you take this concept you assume that one is stationary (in this case B) and only A is moving (since it has advantage in relative speed)
So B stays at starting point and A moves around a rectangular field 0f perimeter = 2 * (400+300) = 1400 mts = 1.4 km
So it means to pass B , A has to cover distance of 1.4 Km
so Distance = 1.4 km
Speed ( in this case relative speed) = 0.5 km/hr
hence time taken to pass B by A – 1.4 / 0.5 = 2.8 hr = 168 minutes
Means, A takes 168 minutes to pass B When they walk relatively
So in 5 hrs and 30 min = 330 minutes
A will cross B only once as 168*2 = 336 min but that is greater than 330 min
Hence it will cross B only once.
( if any problem do tell where you did not get it )
OK CONCEPT CLEAR THANKS LOT :-)
nicely explained. thanks.
In these types of question take the ratio of the speeds as in this case 3:2.5 => 30:25, now reduce this ratio to the lowest form like 6:5 and then take difference 6-5 = 1. So they will meet only once.
if they are moving in opposite direction then u have to add them 6+5 = 11
I have another question..plz attempt this as well..
28 steps – A is at 1st step and 28th step..with A taking 1 step at a time, and B taking 2 steps at a time.Both start simultaneously..at which step do they meet.
Plz help me, how to go abt such questions..lot of confusion..
@Hriti
Assumption : both A and B start simultaneously and at same speed
A takes one step at a time; this he does say “X” times
So after X time he will be on step no = 1+X
At the same time B takes 2 steps downwards at a time and B also does this “X” times as A has done “X” times
So after “X” times , B will be at step = 28 – (2*X)
So if they meet both equations have to be equal
1+X = 28 – (2*X)
X = 9
Meaning they do it 9 times
This implies that they are at ( if you take A’s equation ) = 1+X = 1+9 = 10th step
OR if you take B’s equation = 28 – (2*X) = 28 – (2*9) = 10th step
So answer : 10th step
So to meet them both have to be equated
thanks Maharaj, i got ur logic towards the approach. But one doubt –
for A u have X+1(X steps + 1 to indicate he was there at step 1) , but for B, 28 – 2X (not considering the step on which B is) ?
@Hriti
Do not get confused
Look at equation 1 of A : 1 + X ( the step on which A is + how many times does he does this act of climbing 1 step at a time)
now take a look at equation of B : 28 – (2*X) [ the step on which B is – no of times he does his act of coming down 2 steps at a time { here 2*X because X is the activity of climbing 1 stairs upwards or coming 1 step downwards}]
So in both cases of the equation i have takes the step at which presently A and B are.
Hope ur crystal clear now
nice explanation Maharaj , my approach is a bit different though
initially the distance between them is of 26 steps and after each stride taken by both of them distance reduces by three steps so an AP generates 26,23,20,17 and so on the term which will be zero or the first term before negative term will be the step where they will meet
@Nikhil
Every question has multiple ways of solving
Many short cuts, but my aim here is to kill the beast itself ” Even if you do not have a short cut or encounter a never before done question, still you re able to do them and that too correctly”
As i am always guided by one motto ” Never feed a fish to hungry. Teach him to catch fish himself and by doing this you have you have quenched his hunger for lifetime”
i was just telling my approach , you are doing a commendable job and olready appreciated your explanation in previous comment :)
thanks to both Nikhil and Maharaj.
@ I got it this time. Lemme apply it to some questions to get hands on. Thanks once again..
I guess I read ur guiding motto somewhere…i think at ICICI CSR adv..
See this solution !
Since A and B are coming towards each other so relative velocity(not speed) of A w.r.t B = 3 steps per second so 28 steps will be covered in 9.33 seconds take it as a 9 seconds so A travelled for 9 seconds and in 9 seconds steps covered = 9 + 1( on which A was originally at) hence ans = 10th step
Whenever 2 bodies move relative to each other use the concept of relative velocity with it u can give ans in seconds (without using pen) + it doesnot use equations or A.P which are error prone..
Can anybody share the trick of solving question like “if there is storm light will not blink. Only if light blink flight take off”..
https://mrunalmanage.wpcomstaging.com/2013/04/reasoning-logical-connectives-if-unless-either-or-for-csat-cat-shortcuts-formulas-approach-explained.html
Hello! Mrunal I am done with all my previous 4 attempts. I am 26 years old and fall in general category. If I don’t give my attempt this year so can I appear next year. Because someone was saying that we have to give exam this year otherwise we are not eligible for attempting upsc exam next year.
Anybody please clear the status of my question..its urgent.
If u gave exam in 2011,you will get another attempt in 2015….first point..
Such restrictions are not mentioned in notification….
@Neha
Since as per your age u are eligible as per UPSC’s notification.
However anything about continuation or candidates can take break from giving exam has not been clarified by upsc and most probably it will clarify in 2015.
Visit this page of mrunal to solve all ur queries
https://mrunalmanage.wpcomstaging.com/2014/03/dopt-clarifies-ageattempt-relaxation-upsc-civil-service-exam-gen-32-year-6-attempt-obc-35-9-attempt-scst-37unlimited-ph-42-47.html#1
And if you were asking about an extra attempt for those who appeared in 2011 , i personally do not know
As Mr jitendra Singh’s statement “Candidates who appeared in Civil Services examination 2011 may be given one more attempt in 2015” here mentions may…up till now no conditions applied that you have to give 2014 exam to be eligible for 2015..
can someone plz tell me the meaning of 5/25. mentioned in union budget 2014……
Banks can give loans to real estate firm and can fix the amortization period for say 25 years with periodic refinance facilities in say 5 years. Meaning real estate firm can pay loan (principal and interest) amount via installments in 25 years and can also get refinance facilities in 5 years. It will be good for real estate sector as most of the projects take longer time to complete and become commercially viable.
I hope it is clear enough.
Thank u very much
Thanks for everything sir……you helped us a lot…and we r getting tensed when ubr uploading new articles……sir we are trying very hard to read but those r not getting to mind …so i think no more new updates frm u and once again thank alot ….
vidyanagar,karad
sir can u give some info about rajasthan five year’s plan in hindi …….. many many thanks in advance……
Nice and helpful info.
sir, why was urea not covered in nutrient based subsidy earlier when others where included? on what basis was urea subsidised previously?
please include a downward arrow as you include upward
yes Saurabh, I was thinking about the same.
And an option to “Print” at the start of article only.
msp and cacp what the meaning
Q. If Urea is also subsidised but not under NBS then how does it encourage the companies to produce more urea than any other fertilizers ?
Economics was never so lucid.. (y)
i am prepare cse exa my optional agriculuture sir i read basic books ad well as preparation
Sir,Please rectify the soil health card scheme.It is originally started by PM narndra modi at Rajasthan and punjab is the 1st state to implement this soil health card scheme..Please rectify it..You are mentioned that Gujurat….
Hi colleagues, good piece of writing and good urging
commented at this place, I am truly enjoying by these.
As I website owner I think the subject matter here is rattling
excellent, thanks for your efforts.