- Instructions for UPSC Mains GS Paper-1
- GSM1-2016: Question paper in linear format
- Observations compared to past years
- Is expensive coaching and secret material required for Mains-2017?
- GSM1-Topicwise Questions since Pattern change in 2013
Instructions for UPSC Mains GS Paper-1
- UPSC conducted general studies paper 1 of civil services mains examination on 5th December 2016
- Duration: 3 hours; Maximum Marks: 250
- Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions:
- There are TWENTY questions printed both in HINDI and in ENGLISH. Each Question carries 12.5 marks.
- All the questions too compulsory.
- Answers must be written in the medium authorized in the Admission Certificate which must be stated clearly on the cover of this Question-cum-Answer (QC4) Booklet in the space provided.
- No marks will be given for answers written in a medium other than the authorized one.
- Word limit in questions, wherever specified should be adhered to.
- Any page or portion of the page left blank in the Question-cum-Answer Booklet must be clearly struck off.
GSM1-2016: Question paper in linear format incl. HINDI
Each Question is worth 12.5 marks and maximum word limit is 200. But content of the answer is more important than its length.
- Early Buddhist Stupa-art, while depicting folk motifs and narratives successfully expounds Buddhist ideals. Elucidate.
प्रारम्भिक बुद्धा स्तूप कला, लोक वर्ण्य-विषयो एवं कथानको को चित्रित करते हुए बुद्धा आदर्शो की सफलतापूर्वक व्याख्या करती है | विशदीकरण कीजिए | - Krishnadeva Raya, the King of Vijayanagar, was not only an accomplished scholar himself but was also a great patron of learning and literature. Discuss.
विजयनगर नरेश कृष्णदेव रॉय न केवल स्वयं एक कुशल विद्वान थे अपितु विधया एवं साहित्य के महान संरक्षक भी थे | विवेचना करिए | - Explain how the Uprising of 1857 constitutes an important watershed in the evolution of British policies towards colonial India.
यह स्पष्ट कीजिए कि 1857 का विप्लव किस प्रकार औपनिवेशिक भारत के प्रति ब्रिटिश नीतियों के विकासक्रम में एक महत्वपूर्ण एतिहासिक मोड है | - Discuss the role of women in the freedom struggle especially during the Gandhian phase.
स्वतन्त्रता संग्राम में, विशेष तौर पर गांधीवादी चरण के दौरान महिलाओं कि भूमिका का विवेचन कीजिए | - Highlight the differences in the approach of Subhash Chandra Bose and Mahatma Gandhi in the struggle for freedom.
स्वतन्त्रता के लिए संघर्ष में सुभाष चन्द्र बोस एवं महात्मा गांधी के मध्य दृष्टिकोण की भिन्नताओं पर प्रकाश डालिए | - Has the formation of linguistic States strengthened the cause of Indian Unity?
क्या भाषाइ राज्यों के गठन नें भारतीय एकता के उद्देश्य को मजबूती प्रदान की है ? - The anti-colonial struggles in West Africa were led by the new elite of Western-educated Africans. Examine.
पश्चिमी अफ्रीका में उपनिवेश-विरोधी संघर्षों को पाश्चात्य सिक्षित अफ़्रीकियों के नव संभ्रांत वर्ग के द्वारा नेत्रत्व प्रदान किया गया था | परीक्षण करिए | - To what extent globalization has influenced the core of cultural diversity in India? Explain.
वैश्वीकरण नें भारत में सांस्कृतिक विविधता के आंतरक (कोर) को किस सीमा तक प्रभावित किया है ? स्पष्ट कीजिए | - “An essential condition to eradicate poverty is to liberate the poor from deprivation.” Substantiate this statement with suitable examples. 7+5.5 marks
“ गरीबी उन्मूलन की एक अनिवार्य शर्त गरीबों को वंचितता के प्रक्रम से विमुक्त कर देना है |” उपयुक्त उदाहरण प्रस्तुत करते हुए इस कथन को पुष्ट कीजिए | - Why are the tribals in India referred to as the Scheduled Tribes? Indicate the major provisions enshrined in the Constitution of India for their upliftment. 4.5+8 marks
क्या कारण है कि भारत में जनजातियों को “अनुसूचित जनजातियाँ ” कहा जाता है ? भारत के संविधान में प्रतिष्ठापित उनके उत्थापन के लिए प्रावधानों को सूचित कीजिए | - With a brief background of quality of urban life in India, introduce the objectives and strategy of the ‘Smart City Programme’. 4.5+8 marks
भारत में नगरीय जीवन कि गुणता कि संक्षिप्त पृष्ठभूमि के साथ, ‘ स्मार्ट नगर कार्यक्रम ‘ के उद्देश्य और रणनीति बताइये ? - What is the basis of regionalism? Is it that unequal distribution of benefits of development on regional basis eventually promotes regionalism? Substantiate your answer. 3.5 + 9 marks
प्रादेशिकता का क्या आधार है ? क्या ऐसा प्रादेशिक स्तर पर विकास के लाभों के असमान वितरण से हुआ , जिसने कि अंतत: प्रादेशिकता को वढावा दिया ?अपने उत्तर को पुष्ट कीजिए | - Discuss the concept of air mass and explain its role in macro-climatic changes.
वायु संहति कि संकल्पना की विवेचना कीजिए तथा विस्तृत क्षेत्रीय जलवायवी परिवर्तनों में उसकी भूमिका को स्पष्ट कीजिए | - “The Himalayas are highly prone to landslides.” Discuss the causes and suggest suitable measures of mitigation.
“हिमालय भूस्खलन के प्रति अत्याधिक प्रवण है |” कारणो कि विवेचना कीजिए तथा अल्पीकरण के उपाय सुझाए | - The effective management of land and water resources will drastically reduce the human miseries. Explain
भूमि तथा जल संसाधनो का प्रभावी प्रबंधन मानव विपत्तियों को प्रबल रूप से कम कर देगा | स्पष्ट कीजिए | - South China Sea has assumed great geopolitical significance in the present context. Comment.
वर्तमान संदर्भ में दक्षिणी चीन सागर का भू-राजनीतिक महत्त्व बहुत बढ़ गया है | टिप्पणी कीजिए | - Major cities of India are becoming more vulnerable to flood conditions. Discuss.
भारत के प्रमुख नगर बाढ़ दशाओं से अधिक असुरक्षित होते जा रहे है | विवेचना कीजिए | - Present an account of the Indus Water Treaty and examine its ecological, economic and political implications in the context of changing bilateral relations.
सिंधु जल संधि का एक विवरण प्रस्तुत कीजिए तथा बदलते हुए द्विपक्षीय संबंधो के संदर्भ में उसके पारिस्थितिक आर्थिक एवं राजनीतिक निहितार्थों का परीक्षण कीजिए | - Enumerate the problems and prospects of inland water transport in India.
भारत में अंतर्देशीय जन परिवहन कि समस्याओं एवं संभावनाओ को गिनाइए ? - In what way micro-watershed Development projects help in water conservation in drought prone and semi-arid regions of India.
भारत में सूखा-प्रवण एवं अर्धशुष्क प्रदेशों में लघु जलसंभर विकास परियोजनाए किस प्रकार जल संरक्षण में सहायक है ?
Observations about Mains-2016 GS Paper-1

| 2013 to 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|
| Answer each question in max. 200 words and 12.5 marks | Same. Now internal breakup also given. E.g. 3.5 + 9 mark. In Question no.12 |
| In 2013- 2 out 3 culture Qs from South India. |
|
| So far they used to ask kingdoms’ Architecture e.g. Gandhara, Chola. | Now specific king asked – Krishnadeva Raya. |
|
This year, freedom struggle portion is:
First time 1857 revolt asked, since syllabus change. Thankfully nothing from medieval India, unlike 2014’s Panipat. |
| 2013: women in freedom struggle |
|
| Ideals of Gandhi vs Dr.Ambedkar (in social science) | Gandhi vs Subash (in Freedom Struggle) |
| Post Independent India- nothing asked after 2013. | Drought continues. (as such linguistic state question is part of Post-Independent history but the wording is such that I put it under Regionalism topic). |
| World History: easy questions on industrial revolution and role of Germany in WW. |
|
| 2015: 25 marks questions on “women issues” under Social science. |
|
| 2015: Dalit empowerment asked |
|
| 2013: regionalism to separate state demand asked |
|
| 2015: link between cultural diversity vs. national identity asked |
|
| 2015: Two questions from poverty, population, globalization |
|
| Nothing in physical geography- in 2015 | Finally asked – 2 things related to physical geo’s subtopic “disaster”
|
|
|
|
|
| 2015: why shortage of water? |
|
| 2015: smart city and pollution asked |
|
| 2015: nothing from industrial location | Same. |
Overall
- Just like essay-2016 paper was continuation of 2015’s essay paper. The GSM1-2016 seems to be a continuation of 2013’s paper! (be it landslides, women freedom fighters)
- While Geography had seen receding waters in the prelim-2016, it makes a “cloudburst” here with total 112.5 marks worth question (=45% of the GSM1 paper!) similar case for Laxmikanth (with tribal provision question)
- All in all- less difficult paper than earlier. Because ‘secret Material‘ or expensive coaching’ is NOT required to attend any of the question. Observe:
| Questions | Coverage | Price? | How much covered in Mrunal.org |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buddhist Stupa Art |
|
free | 12.5, Ishani’s lecture |
| Krishnadevraya |
|
free | – |
| Women in freedom struggle |
|
free | 12.5, article |
| Subhas vs Gandhi; | Sufficient points freedom struggle related books such as Rajiv Ahir or Bipan Chandra. | cheap | – |
| Revolt of 1857 | Pratik’s lecture HFS6/P3; Books on freedom struggle such as Rajiv Ahir, Bipan Chandra | Free, cheap | 12.5, lecture |
| Questions on regionalism, linguistic states | Sufficient points in IGNOU’s “Democracy and Development” booklet. | free | – |
| Tribal | Laxmikanth | Cheap | – |
| Urbanization | Both were covered in my lectures
|
free | 25, lecture |
| geography | Himalayan landslide cause (half of the answer) in this answer key for 2013 paper link | free | 7, article |
| geography | Airmass and its role: G6/P4 | free | 12.5, lecture |
| geography | Land and water resources: G7/P7 (water) and G8/P4 (land) | free | 12.5, lecture |
| geography | Indus water treaty (half of the answer in this article) | free | 7, article |
| geography | Watershed development: Lecture G7/P8 | Free | 12.5 lecture |
- Overall, 107/250 = ~43% of the paper covered in Mrunal.org
- Overall, 17 out of 20 questions, directly available in the either free or cheap sources.
- Q.E.D.: secret material, expensive coaching – unnecessary.

यानि की मेरे सारे पाप भी धुल गये…..
GSM1-Topicwise Questions since Pattern change in 2013
In 2013, UPSC changed the syllabus-pattern of Mains examination and the number of general studies papers were increased from two to four. Out of them, GS Paper-I deals with History, Culture, Society and Geography. Overall breakup looks like this
| Category | GS Mains Paper-1 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 |
| History | Culture | 20 | 40 | 25 | 25 |
| History | Freedom struggle | 30 | 30 | 25 | 37.5 |
| History | World History | 40 | 30 | 25 | 12.5 |
| History | Post-independence | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
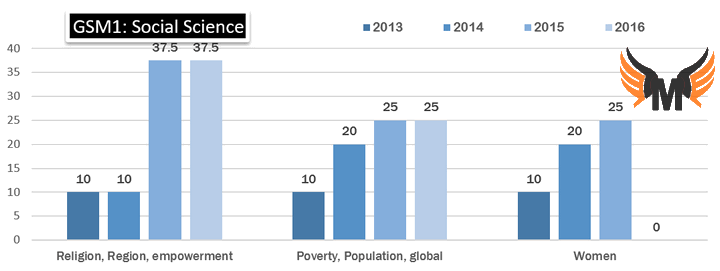
| Society | Religion, Region, empowerment. | 10 | 10 | 37.5 | 37.5 |
| Society | Poverty, Population, Development | 10 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| Society | Women | 10 | 20 | 25 | 0 |
| Geography | Climate | 10 | 30 | 25 | 12.5 |
| Geography | Resources | 20 | 20 | 37.5 | 62.5 |
| Geography | Urbanization | 10 | 0 | 25 | 25 |
| Geography | Physical | 30 | 20 | 0 | 12.5 |
| Geography | Industrial Location | 10 | 30 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 |
[Block-1] History

History: Art & Culture
GS1 Syllabus Topic: Salient aspects of Art, Architecture, literature from Ancient to Modern Times
| Early Buddhist Stupa-art, while depicting folk motifs and narratives successfully expounds Buddhist ideals. Elucidate. | 2016 |
| Krishnadeva Raya, the King of Vijayanagar, was not only an accomplished scholar himself but was also a great patron of learning and literature. Discuss. | 2016 |
| The ancient civilization in Indian sub-continent differed from those of Egypt, Mesopotamia and Greece in that its culture and traditions have been preserved without a breakdown to the present day. Comment. | 2015 |
| Mesolithic rock cut architecture of India not only reflects the cultural life of the times but also a tine aesthetic sense comparable to modem painting. Critically evaluate this comment. | 2015 |
| To what extent has the urban planning and culture of the Indus Valley Civilization provided inputs to the present day urbanization? Discuss. | 2014 |
| Gandhara sculpture owed as much to the Romans as to the Greeks. Explain. | 2014 |
| Taxila university was one of the oldest universities of the world with which were associated a number of renowned learned personalities of different disciplines. Its strategic location caused its fame to flourish, but unlike Nalanda, it is not considered as a university in the modern sense. Discuss. | 2014 |
| Sufis and medieval mystic saints failed to modify either the religious ideas and practices or the outward structure of Hindu / Muslim societies to any appreciable extent. Comment. | 2014 |
| Though not very useful from the point of view of a connected political history of South India, the Sangam literature portrays the social and economic conditions of its time with remarkable vividness. Comment. | 2013 |
| Discuss the Tandava dance as recorded in the early Indian inscriptions. | 2013 |
| Chola architecture represents a high watermark in the evolution of temple architecture. Discuss. | 2013 |
History: India before Independence
GS1 Syllabus Topic: Mid-18th century – Present (significant events, personalities, issues); Freedom Struggle (various stages, important contributors from different parts of the country)
| Explain how the Uprising of 1857 constitutes an important watershed in the evolution of British policies towards colonial India. | 2016 |
| Discuss the role of women in the freedom struggle especially during the Gandhian phase. | 2016 |
| Highlight the differences in the approach of Subhash Chandra Bose and Mahatma Gandhi in the struggle for freedom. | 2016 |
| How different would have been the achievement of Indian independence without Mahatma Gandhi? Discuss. | 2015 |
| It would have been difficult for the Constituent Assembly to complete its historic task of drafting the Constitution for Independent India in just three years but for the experience gained with the Government of India Act, 1935. Discuss. | 2015 |
| The third battle of Panipat was fought in 1761. Why were so many empire-shaking battles fought at Panipat? | 2014 |
| Examine critically the various facets of economic policies of the British in India from mid-eighteenth century till independence. | 2014 |
| In what ways did the naval mutiny prove to be the last nail in the coffin of British colonial aspirations in India? | 2014 |
| Defying the barriers of age, gender and religion, the Indian women became the torch bearer during the struggle for freedom in India. Discuss. | 2013 |
| Several foreigners made India their homeland and participated in various movements. Analyze their role in the Indian struggle for freedom. | 2013 |
| In many ways, Lord Dalhousie was the founder of modern India. Elaborate. | 2013 |
History: India After independence
GS1 Syllabus Topic: Post-Independence (consolidation and reorganisation within country)
| Critically discuss the objectives of Bhoodan and Gramdan movements initiated by Acharya Vinoba Bhave and their success. | 2013 |
| Write a critical note on the evolution and significance of the slogan “Jai Jawana Jai Kisan”. | 2013 |
| Discuss the contribution of Maulana Abul Kalam Azad to pre-and post-independent India. | 2013 |
| Analyze the circumstances that led to Tashkent Agreement in 1966. Discuss the highlights of the agreement. | 2013 |
| Critically examine the compulsions which prompted India to play a decisive roles in the emergence of Bangladesh. | 2013 |
History: world
GS1 Syllabus Topic: 18th century events (e.g. Industrial revolution, WWs, redrawn boundaries, colonisation, decolonisation); Political philosophies (e.g. communism, capitalism, socialism) and their effect on society
| The anti-colonial struggles in West Africa were led by the new elite of Western-educated Africans. Examine. | 2016 |
| Why did the industrial revolution first occur in England? Discuss the quality of life of the people there during the industrialization. How does it compare with that in India at present? | 2015 |
| To what extent can Germany be held responsible for causing the two World Wars? Discuss critically | 2015 |
| What were the major political, economic and social developments in the world which motivated the anti-colonial struggle in India? | 2014 |
| What were the events that led to the Suez Crisis in 1956? How did it deal a final blow to Britain’s self-image as a world power? | 2014 |
| The New Economic Policy – 1921 of Lenin had influenced the policies adopted by India soon after independence. Evaluate. | 2014 |
| “Latecomer” Industrial revolution in Japan involved certain factors that were markedly different from what west had experience. | 2013 |
| Africa was chopped into states artificially created by accident of European competition. Analyse. | 2013 |
| American Revolution was an economic revolt against mercantilism. Substantiate. | 2013 |
| What policy instruments were deployed to contain the great economic depression? | 2013 |
[Block-2] Social Science
Social Science: Caste, Religion, Region
GS1 Syllabus Topic: Communalism, Regionalism, Secularism; Social Empowerment
| Has the formation of linguistic States strengthened the cause of Indian Unity? | 2016 |
| Why are the tribals in India referred to as the Scheduled Tribes? Indicate the major provisions enshrined in the Constitution of India for their upliftment. | 2016 |
| What is the basis of regionalism? Is it that unequal distribution of benefits of development on regional basis eventually promotes regionalism? Substantiate your answer. | 2016 |
| Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, despite having divergent approaches and strategies, had a common goal of amelioration of the downtrodden. Elucidate. | 2015 |
| Describe any four cultural elements of diversity in India and rate their relative significance in building a national identity. | 2015 |
| Debate the issue of whether and how contemporary movements for assertion of Dalit identity work towards annihilation of caste. | 2015 |
| How do the Indian debates on secularism differ from the debates in the West? | 2014 |
| Growing feeling of regionalism is an important factor in the generation of demand for a separate state. Discuss. | 2013 |
Social Science: Poverty, Population, Globalization
- GS1 Syllabus Topic: Salient features of Indian Society; Diversity of India; Globalisation (effects on Indian society)
- GS1 Syllabus Topic: Poverty, Population; Development and associated issues
| “An essential condition to eradicate poverty is to liberate the poor from deprivation.” Substantiate this statement with suitable examples | 2016 |
| To what extent globalization has influenced the core of cultural diversity in India? Explain. | 2016 |
| Critically examine whether growing population is the cause of poverty OR poverty is the main cause of population increase in India. | 2015 |
| Discuss the changes in the trends of labour migration within and outside India in the last four decades. | 2015 |
| The life cycle of a joint family depends on economic factors rather than social values. Discuss. | 2014 |
| Critically examine the effects of globalization on the aged population in India. | 2013 |
Social Science: Women
- GS1 Syllabus Topic: Role of women and women’s organisation;
- Although some of the following questions fall under population-globalization categories, but if a person cultivates habit of noting down women related topics under one head, it’ll benefit in both GS1, GS2 and Essay.
| Discuss the positive and negative effects of globalization on women in India. (2013, Asked about Globalization effect on Elderly) | 2015 |
| How do you explain the statistics that show that the sex ratio in Tribes in India is more favourable to women than the sex ratio among Scheduled Castes? | 2015 |
| How does patriarchy impact the position of a middle class working woman in India? | 2014 |
| Discuss the various economic and socio-cultural forces that are driving increasing feminization of agriculture in India. | 2014 |
| Why do some of the most prosperous regions of India have an adverse sex ratio for women? Give your arguments. | 2014 |
| Male membership needs to be encouraged in order to make women’s organization free from gender bias. Comment. | 2013 |
[Block-3] Geography

Geography: Physical
GS1 Syllabus Topic: Salient Features of World Physical Geography; Important Geophysical phenomena (earthquakes, tsunami, volcanoes, cyclones); Geographical features and location;
| “The Himalayas are highly prone to landslides.” Discuss the causes and suggest suitable measures of mitigation. | 2016 |
| Explain the formation of thousands of islands in Indonesian and Philippines archipelagos. | 2014 |
| Why are the world’s fold mountain systems located along the margins of continents? Bring out the association between the global distribution of Fold Mountains and the earthquakes and volcanoes. | 2014 |
| What do you understand by the theory of continental drift? Discuss the prominent evidences in its support. | 2013 |
| There is no formation of deltas by rivers of the Western Ghat. Why? | 2013 |
| Major hot deserts in northern hemisphere are located between 20-30 degree north and on the western side of the continents. Why? | 2013 |
| Bring out the causes for more frequent landslides in the Himalayas than in Western Ghats | 2013 |
Geography: Climate, Disaster related
GS1 Syllabus Topic: Critical geographical features, flora, fauna (changes and effects thereof)
| Discuss the concept of air mass and explain its role in macro-climatic changes. | 2016 |
| Explain the factors responsible for the origin of ocean currents. How do they influence regional climates, fishing and navigation? | 2015 |
| How far do you agree that the behavior of the Indian monsoon has been changing due to humanizing landscapes? Discuss. | 2015 |
| Tropical cyclones are largely confined to South China Sea, Bay of Bengal and Gulf of Mexico. Why? | 2014 |
| Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree? | 2014 |
| Bring out the relationship between the shrinking Himalayan glaciers and the symptoms of climate change in the Indian sub-continent. | 2014 |
| The recent cyclone on the east coast of India was called “Phailin”. How are the tropical cyclones named across the world? | 2013 |
| Bring out the causes for the formation of heat islands in the urban habitat of the world. | 2013 |
| What do you understand by the phenomenon of temperature inversion in meteorology? How does it affect the weather and the habitants of the place? | 2013 |
Geography: Resources Distribution
GS1 Syllabus Topic: Distribution of key Natural Resources (world, S. Asia, Indian subcontinent)
| The effective management of land and water resources will drastically reduce the human miseries. Explain | 2016 |
| South China Sea has assumed great geopolitical significance in the present context. Comment. | 2016 |
| Present an account of the Indus Water Treaty and examine its ecological, economic and political implications in the context of changing bilateral relations. | 2016 |
| Enumerate the problems and prospects of inland water transport in India. | 2016 |
| In what way micro-watershed Development projects help in water conservation in drought prone and semi-arid regions of India. | 2016 |
| What are the economic significances of discovery of oil in Arctic Sea and its possible environmental consequences? | 2015 |
| India is well endowed with fresh water resources. Critically examine why it still suffers from water scarcity. | 2015 |
| The states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand arc reaching the limits of their ecological carrying capacity due to tourism. Critically evaluate. | 2015 |
| Critically evaluate the various resources of the oceans which can be harnessed to meet the resource crisis in the world. | 2014 |
| How does India see its place in the economic space of rising natural resource rich Africa? | 2014 |
| With growing scarcity of fossil fuels, the atomic energy is gaining more and more significance in India. Discuss the availability of raw material required for the generation of atomic energy in India and in the world. | 2013 |
| It is said the India has substantial reserves of shale oil and gas, which can feed the needs of country for quarter century. However, tapping of the resources doesn’t appear to be high on the agenda. Discuss critically the availability and issues involved. | 2013 |
Geography: factors affecting industrial locations
GS1 Syllabus Topic: Factors responsible for location of Industries (primary, secondary, tertiary; India, world)
| Whereas the British planters had developed tea gardens all along the Shivaliks and Lesser Himalayas from Assam to Himachal Pradesh, in effect they did not succeed beyond the Darjeeling area. Explain. | 2014 |
| Account for the change in the spatial pattern of the Iron and Steel industry in the world. | 2014 |
| Why did the Green Revolution in India virtually by-pass the eastern region despite fertile soil and good availability of water? | 2014 |
| Do you agree that there is a growing trend of opening new sugar mills in the Southern states of India? Discuss with justification | 2013 |
| Analyze the factors for highly decentralized cotton textile industry in India | 2013 |
Geography: Urbanization
GS1 Syllabus Topic: Urbanization: problems and remedies
| With a brief background of quality of urban life in India, introduce the objectives and strategy of the ‘Smart City Programme’. | 2016 |
| Major cities of India are becoming more vulnerable to flood conditions. Discuss. | 2016 |
| Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata are the three mega cities of the country but the air pollution is much more serious problem in Delhi as compared to the other two. Why is this so? | 2015 |
| Smart cities in India cannot sustain without smart villages. Discuss this statement in the backdrop of rural urban integration. | 2015 |
| Discussion the various social problems which originated out of the speedy process of urbanization in India. | 2013 |

![[Download] Topicwise UPSC GSM2-2023 Paper- polity, Governance international relations in Hindi and English with topic wise analysis](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/ana-gsm2-2023-mrunal79-500x383.png)
![[Download] Topicwise UPSC Mains General Studies Paper-1 (GSM1): History, Geography, Social Science](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/mains-answer-writing-d1-500x383.jpg)
Can You please write a article on “How to use mrunal.org site effectively. Ur wehsite has so many important things to study. I am a beginner and i have no idea how to use your site propperly.. please guide me through. ANYONE PLZZZ.
Are you doing coaching somewhere?
Can you please write in Hindi
how can i download topicwise discussion of mains gs1
Are you doing coaching somewher
no