Prologue
- “Reproduction” related Current affairs topics in news 1) injectable contraceptive 2) three parent baby.
- And since UPSC combined the preliminary exam of both civil services and forest services- agriculture / plant reproduction related things also need to be prepared.
- इसलिए भगवान का नाम लेके let’s take a look at both theory and current of “reproduction”.
Reproduction: Two Types
| Asexual | Sexual |
|---|---|
| Faster | Slower, because gestation period involved |
|
|
| Plants and lower organisms can do it. | Plants and higher organisms do it. |
Asexual reproduction: Subtypes
| Fission |
|
|---|---|
| Budding | bulb-like projection or outgrowth arises from the parent body and makes new baby. Eg. Hydra, yeast, bryophyllum. |
| Regeneration or Fragmentation | an individual breaks up into two or more parts and each part develops into a complete individual. Examples: Spirogyra, Planaria. |
| Spore formation | Protoplast of the cell divides to form 4–8 spores/ zoospores. E.g. Fungi, Chlamydomonas, Moss, fern, rhizopus. |
| Vegetative propagation or reproduction |
any vegetative part of the plant body like leaf, stem or root develops into a complete new plant. This can happen either naturally or artificially:
|
Q. What are the characteristics of vegetative propagation?
- All plants produced are genetically similar to the parent plant to have all its characteristics
- It’s possible to replicate plants that have lost capacity to product seeds e.g. banana, orange, rose and jasmine.
- Such reproduced plants bear fruits and flowers faster than the ‘naturally’ cross-pollinated plants.
- All of above.
Sexual reproduction in plants
Pollen
- Spherical. Produced in male part of flower, and sent to female part.
- Considered to increase performance of athletes and race horses. Hence pollent tablets used as “food supplements” in first world.
- Can cause allergy. e.g. carrot grass (Parthenium) in imported wheat. [given in class-12 NCERT, hence needs to be remembered]
Pollinating Agents: Two Types
| Abiotic |
|
|---|---|
| Biotic |
|
Pollination: Two types
| Self-pollination / autogamy |
|
|---|---|
| Cross pollination / allogamy |
|
In either method: male + female fusion -> fertilization -> Zygote -> endosperm->embryo-> mature ovary-> fruit -> seed.
Fruits: Types of
| False fruit | They are born from parts other than ovaries. E.g. Apple, strawberry, cashew, jackfruit, pineapple. |
| True fruit | They are born only from ovaries. Mango, Maize, Grape |
| Parthenocarpic fruit | Fruits develop without fertilization e.g. Banana, seedless grape-orange-watermelons. This is done via growth hormones and the resultant fruit is seedless. |
Seed dispersing agents
Seed is the final product of sexual reproduction in angiosperms.
| Wind | Drumstick, maple, aak (Madar), sunflower. Their seeds get blown by wind to faraway places |
| Water | Coconuts because they’ve floating ability. |
| Animals | Xanthium and Urena: they’ve hooks that attach to fur of sheep / goat. |
Q. Seed dispersal helps the plants to
- prevent overcrowding
- avoid competition for sunlight, water and minerals
- invade new habitats.
- All of above
Sexual reproduction in Animals
| In vitro fertilization |
|
| Internal fertilization / in-vivo |
|
| External fertilization |
|
| Viviparous |
|
| Oviparous |
|
Family planning Methods Classification
| Preventive methods |
|
| Contraception methods |
Methods prevent of fertilization and conception. Three types
|
| Corrective methods |
If preventive or contraceptive method not used or fails, then fetus destroyed using these methods. Also known as Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
|
Current Affairs: Injectable contraceptives
- Injection of Deoxymedroxy progesterone acetate (DMPA).
- Given to the arm or buttock muscle every 3 months.
- It blocks Luteinizing Hormone (LH) –> hence Ovulation doesn’t take place -> egg doesn’t goto ovary -> sperm and egg can’t meet.
- Why in News? Health ministry told parliament that it’ll be given free to Government hospitals and primary health centres (PHC)
Q. Injectable contraceptive contains ___ hormone?
- Luteinizing hormone
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
- None of the above
Current Affairs: Three Parent Baby
Old topic from 2013-14. But again in NEWs because one such baby born in Q3-2016.
Background: Mitochondria
- Mitochondria crucial to the energy supply of cells.
- Defective Mitochondria will disrupt energy supply to muscles, heart, liver and brain.
- In Britain alone, around one in 6,500 children is born annually with a severe mitochondrial disease like muscular dystrophy.
- Mitochondrial diseases are incurable.
- Current methods can only reduce but not eliminate the risk; no treatment is available either.
Solution: mitochondrial transfer/ 3-Parent IVF

| Mom | gives egg but her DNA material has defective genes for Mitochondria. So that part related to Mitochondria is removed. |
| Dad | Sperm |
| donor (female) | gives DNA that has right ‘codes’ for healthy Mitochondria. |
- Thus, with help of genetic material from ^three people, an IVF baby is created. Embryo transferd to mother and baby is born without any disease related to mitochondria.
- UK government allowed doctor to use this method.
Arguments in favour and against 3-Parent Baby
| Favour | Against 3-parent baby |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Twin Babies- Theory
Happens when either:
- One than 1 egg fertilized by more than 1 sperm. OR
- After fertilization, ovum divides into two or more cells.
| Identical twins | When a fertilized egg divides into two independent sets of cells-> two identical embryos products from same egg. |
| Non-identical or fraternal twins | When two eggs are produced at the same time and a different sperm fertilizes each egg, non-identical or fraternal twins are produced. |
Cloning- Theory
- A clone is a cell or an organism that is produced asexually from an ancestor. (=without sperm meeting egg)
- A Clone cell genetically identical to its ancestor.
- Thus the clone of Lennon, produced today, will be genetically the same John Lennon of the 70s.
Dolly Sheep Cloning (Scotland, 1996)
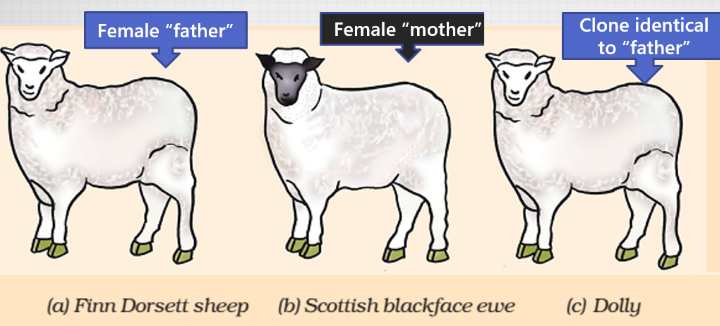
| Polly (Black face) | they removed genetic material from her egg-cell. Thus her egg remained only an empty reaction vessel. |
| Molly (White face) | they took cells from her udder, extracted genetic material out of it, and planted in Dolly’s empty egg cell. Thus an embrayo created. |
| Holly | they planted above embryo in Holly’s womb. Thus holly served as a surrogate mother. |
Result: Dolly sheep was born. White faced, inherited the genes from Molly only. The only male DNA of Dolly came from Molly’s father’s DNA contained in her somatic cells.
- A Man does not live by body alone. What goes into the brain is interaction with the external world. Culture is not coded in our DNA. Experience, education, environment — all these matter.
- If Cloned Mohandas Gandhi isn’t thrown out of a train going to Pretoria (or face similar racial discrimination), he may not become “Mahatma”.
- Cloned John Lennon will not be an equally good singer-musician like original John Lennon, Cloned Adolph Hitler will not be a mass-murderer, IF they don’t live through similar circumstances like their “fathers”.
Surrogacy: theory
- Husband has healthy sperms and Wife has healthy eggs
- but Wife cannot carry a baby to its full term. For example, Aamir Khan’s wife Kiran Rao suffered a miscarriage earlier and had uterine medical problems so the couple opted for surrogacy.
- In surrogacy: Wife’s egg is fertilized with husband’s sperm through in-vitro fertilization (IVF) and an embryo is created. (In Vitro=outside body. In-vivo=inside body.)
- This embryo is implanted in the womb of a “surrogate mother”, she will carry It for nine months and deliver the baby.
- Baby thus produced, will have genetic make-up of the husband and wife (and not that of surrogate mother.)
- Ethical Merits and demerits are given here

![[Science WMD] ISRO POEM, NASA CAPSTONE, GEMCOVAC-19, Doctors Day, Weekly Mrunal Digest from Jun week4-2022](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/isro-poem-scaled-500x383.jpg)
![[Revision] Agriculture Chemistry: Mineral Nutrition, Plant Growth Regulators, Ethylene, Hydroponics, Photoperiodism, Vernalisation](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/c-nitro-cycle-500x383.jpg)
![[Revision] Chemistry Part-2: Metal, Non-Metal, Metalloid, Liquid, Surface tension, Viscosity, Gas Laws, Periodic Table](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/c-elementbl-500x383.gif)
Thanks Mrunal sir…
Sir did this appear in hindu or pib moreover if i wish to ask u something how can i contact
Thanks sir….I have some of suggestions.
1. Plz complete Economic survey and Budget at least one month before prelims (last year didn’t get sufficient time to revise)
2.Plz provide ppts on World history (it is not uploaded in Download section)
3. Its good if you provide monthly current affairs
sir, is there any plan of video lectures on ancient hostory of India on youtube?
Sir please discuss monthly current affairs also
Very informative article. One stop solution of all doubts. Thank you Sir. This series of science should be continued.
Sir please provide monthly current affairs consistently and keep posting important articles like this one.
how can we download such a best effort made by your team….
Its really very nice and helpful info.
nice
Please complete economic survey before one month of prelims 2017
sir please discuss current affairs monthaly.it will helpfull student like us
sir can you do mppsc special something please
Hi friends, I have one doubt regarding ‘protected forests’. What is a protected forest? And what are the activities allowed in that? Like grazing,taking headloads of wood,collecting forest produce for their own use etc ?? Please clarify me thanking you
Hi friends, I have one doubt regarding, hardest bone and hardest muscle in our body. Please clarify me.
Bone— femur
Muscle—Jaw muscle( masseter)
good to see your mail after so long
Great job done….murnal sir
Superb,Great job done….murnal sir
Your defination of cross pollination is wrong. Pollination between different flowers of same plant is self pollination not cross pollination.
Thank u sir,,,its really very helpful…….reproductive biology revised in a very short time……
THANK YOU MURNAL SIR
Mrunal sir it’s my humble request to u provide at least 25 practice test series for pre-2017
dmpa stands for depomedroxy progesterone acetate and not Deoxymedroxy progesterone acetate (DMPA
sir,
please make different section of science so that we can easily revise during prelims
Very informative, thank you very much
Great sir