- UPSC Mains General Studies Paper-3: 2017 (Linear Format)
- Answer Sources for GSM3-2017 Paper
- Bookie-Mentality #FAIL?
- How is 2017 vs. 2016?
- GS3: Topicwise Papers since Syllabus Change
- [Block #1] Economy
- [Block#2] Agriculture
- [Block #3] Science
- [Block#4] Security
UPSC Mains General Studies Paper-3: 2017 (Linear Format)
Total marks 250. Total duration: 3 hours. Date: 31/10/2017.
Answer following questions each in 150 words x 10 marks.
- Among several factors for India’s potential growth, savings rate is the most effective one. Do you agree? What are the other factors available for growth potential?
- Account for the failure of manufacturing sector in achieving the goal of labour-intensive exports rather than capital-intensive exports. Suggest measures for more labour-intensive rather than capital-intensive exports.
- Examine the developments of Airports in India through Joint Ventures under Public-Private Partnership(PPP) model. What are the challenges faced by the authorities in this regard.
- Explain various types of revolutions, took place in Agriculture after Independence in India. How these revolutions have helped in poverty alleviation and food security in India?
- What are the reasons for poor acceptance of cost effective small processing unit? How the food processing unit will be helpful to uplift the socio-economic status of poor farmers?
- Stem cell therapy is gaining popularity in India to treat a wide variety of medical conditions including Leukaemia, Thalassemia, damaged cornea and several burns. Describe briefly what stem cell therapy is and what advantages it has over other treatments?
- India has achieved remarkable successes in unmanned space missions including the Chandrayaan and Mars Orbitter Mission, but has not ventured into manned space mission, both in terms of technology and logistics? Explain critically.
- Not many years ago, river linking was a concept but it is becoming reality in the country. Discuss the advantages of river linking and its possible impact on the environment.
- Discuss the potential threats of Cyber attack and the security framework to prevent it.
- The north-eastern region of India has been infested with insurgency for a very long time. Analyze the major reasons for the survival of armed insurgency in this region.
Answer following questions each in 250 words x 15 marks.
- One of the intended objectives of Union Budget 2017-18 is to ‘transform, energize and clean India’. Analyse the measures proposed in the Budget 2017-18 to achieve the objective.
- “Industrial growth rate has lagged behind in the overall growth of Gross-Domestic-Product(GDP) in the post-reform period” Give reasons. How far the recent changes in Industrial Policy are capable of increasing the industrial growth rate?
- What are the salient features of ‘inclusive growth’? Has India been experiencing such a growth process? Analyze and suggest measures for inclusive growth.
- What are the major reasons for declining rice and wheat yield in the cropping system? How crop diversification is helpful to stabilize the yield of the crop in the system?
- How do subsidies affect the cropping pattern, crop diversity and economy of farmers? What is the significance of crop insurance, minimum support price and food processing for small and marginal farmers?
- Give an account of the growth and development of nuclear science and technology in India. What is the advantage of fast breeder reactor programme in India?
- ‘Climate Change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change?
- On December 2004, tsumani brought havoc on 14 countries including India. Discuss the factors responsible for occurrence of Tsunami and its effects on life and economy. In the light of guidelines of NDMA (2010) describe the mechanisms for preparedness to reduce the risk during such events.
- Mob violence is emerging as a serious law and order problem in India. By giving suitable examples, analyze the causes and consequences of such violence.
- The scourge of terrorism is a grave challenge to national security. What solutions do you suggest to curb this growing menace? What are the major sources of terrorist funding?
Answer Sources for GSM3-2017 Paper
- If large chunk of answer is available at a single standard reference source, then I’ll count material availability as yes.
- If answer is scattered across multiple less-known / less used sources, then I’ll count as “no*”. It doesn’t mean that given question is unsolvable, it only means that it requires much more effort.
| Question | Answer | Available |
|---|---|---|
| 1.factors affecting growth potential apart from savings rate |
|
Yes |
| 2. Suggest measures for more labour-intensive rather than capital-intensive exports. | Economic survey has been highlighting this since last three years.
|
Yes |
| 3.JV model in Airport PPP |
|
partially |
| 4.how Agri. revolutions have helped in poverty alleviation and food security in India? | Verbatim answer given in Kurkshetra 2016 March PDF page 5 onwards in Sandip Das’s article. Alternatively NCERT class11-Indian Economy:
Plus, lot of points spread around my [food processing] article series. |
yes |
| 5.why poor acceptance of cost effective small processing unit? How the food processing uplift poor farmers? |
|
partially |
| 6. what stem cell therapy is and what advantages it has over other treatments? |
|
yes |
| 7.India has not ventured into manned space mission? Explain critically. |
|
no |
| 8. advantages of river linking and its possible impact on the environment. |
|
Yes |
| 9. Cyber-attack and the security framework in India? |
|
Yes |
| 10.The north-eastern insurgency? |
|
Yes |
| 11. ‘transform, energize and clean India’ agenda in Budget-2017 |
|
Yes |
| 12 Recent changes in Industrial Policy are capable of increasing the industrial growth rate? |
|
No |
| 13.inclusive growth in India |
|
Yes |
| 14.why declining rice and wheat yield in the cropping system? How crop diversification can help? |
|
Yes |
| 15. subsidies affect the cropping pattern, crop diversity and economy of farmers? | This is a running theme in last three years’ economic surveys, and even in the latest NITI3yr. Matter is sufficiently covered in my lecture and articles. | yes |
| 16. nuclear science and technology in India. |
|
Yes |
| 17.‘Climate Change’ on Himalayan and coastal states of India |
|
Yes |
| 18.Tsunami management |
|
yes |
| 19.Mob violence |
|
Yes |
| 20.terrorism? | 2nd ARC 8th Report.
|
Yes |
Conclusion?
- 16 out of 20 = 80% of the questions directly covered in standard sources.
- And 2 questions: partially available in standard sources. So total 90% of the paper is fully or partially covered in sources that are either free or very cheap. And majority of them from Economic Survey, Yojana, Kurukshetra and 2nd ARC : all freely available on internet.
- Only 2 questions are not directly available. [(1) manned mission and (2) industrial policy change]
- Therefore, expensive coaching and study material is not necessary for success. Mains Success primarily depends on your ability to write less mediocre answer than others, in given time limit.
- So, before scavenging for “Secret” material and compilations for 24/7 basis on telegram groups, you should first finish these standard reference sources.
Now coming to the analysis part….
Bookie-Mentality #FAIL?
UPSC usually doesn’t ask questions from hot-current affairs of the given year. Astrologers, Bookies and Coaching classes use this unwritten rule to predict the questions. In GSM2-2017, Examiner blatantly violated this rule. Whether GST or right to privacy- they’ve asked hot topics. However, in GSM3-2017, he has by and large avoided hot current affairs from 2016-17. For example:
- Nothing from artificial intelligence, drones or robots this time, even though they were hot topics in science-tech in GSM3.
- Nothing from black money, although it was a hot topic in the aftermath of demonetization and passing of new bills related to black money.
- Nothing from NPA, TBS problem.
- Instead of asking “funding to Kashmiri stone-pelters” specifically, they asked about “funding to terrorism” in general.
- Nothing from D.B. Shekatkar committee report on defense reforms or Dokhlam crisis. Senior players were expecting question in ‘security forces / border areas’.
- Nothing from GST (but in fairness, it was asked in GSM2-2017).
- Nothing from N.K.Singh’s FRBM Review panel in the Budgeting topic. (but in fairness, asked full-scale topic essay-2017 paper.)
Examiner’s Fear for jobless and non-inclusive growth continues
| Previously | Mains-2017 |
|---|---|
|
|
|
What are the salient features of ‘inclusive growth’? Has India been experiencing such a growth process? Analyze and suggest measures for inclusive growth. |
As you can see, their pipudi (small-flute) is stuck at the same things since last three years.
Fear ABOUT industrial sector continues
| Previously | Mains-2017 |
|---|---|
| 2014: What are the reasons for the huge growth of services vis-a-vis industry in the country? Can India become a developed country without a strong industrial base? | “Industrial growth rate has lagged behind in the overall growth of Gross-Domestic-Product(GDP) in the post-reform period” Give reasons. How far the recent changes in Industrial Policy are capable of increasing the industrial growth rate? |
Pingpongs between GSM1 & GSM3
| GSM1 | GSM3 |
|---|---|
| 2014: Bring out the relationship between the shrinking Himalayan glaciers and the symptoms of climate change in the Indian sub-continent. | 2017: ‘Climate Change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (even though given the wording of this question, it is more suitable for asking in GSM1.) |
| 2017: In what way can flood be converted into a sustainable source of irrigation and all-weather inland navigation in India? (here you’ve to write about river interlinking) | 2017: Discuss the advantages of river linking and its possible impact on the environment. |
| 2016: Major cities of India are becoming more vulnerable to flood conditions. Discuss. | 2016: Discussing the reasons for urban floods. highlight the mechanisms for preparedness to reduce the risk during such events. |
| 2016: The basis of providing urban amenities in rural areas (PURA) is rooted in establishing connectivity. Comment. | 2017: What are ‘Smart Cities? Examine their relevance for urban development in India. Will it increase rural-urban differences? Give arguments for Smart Villages’ in the light of PURA and RURBAN Mission. |
Pingpong between general to specific
| Previously | Mains-2017 |
|---|---|
|
|
| 2013: specific question about “Pink Revolution” in food industry. | 2017: asked “general” question about all agriculture revolutions that occurred since independence. |
| 2013: general question on subsidies to farmers @national and state level, and how do they create distortions? | 2017: asked subsidies’ impact on specific things: How do subsidies affect the cropping pattern, crop diversity and economy of farmers? |
|
|
| 2015: India’s preparedness against Earthquakes. (specific) | 2017: India’s preparedness against Tsunamis (earthquakes in oceans). Again specific. |
| In 2016 asked about allelopathy (extremely technical agro topic meant for perhaps IFoS and Agriculture optional). Thankfully no crazyness this time. |
How is 2017’s Paper compared to 2016?
| Subjectwise Breakup | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|
| Economy | 75 | 75 |
| Agriculture | 50 | 50 |
| Sci. Env. | 75 | 75 |
| Security | 50 | 50 |
| Total | 250 | 250 |
No change in weightage to each subject:
| Area | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|
| Theory | 62.5 | 20 |
| Current | 75 | 40 |
| Contemporary | 112.5 | 190 |
| Total Marks | 250 | 250 |
- In both 2016 and 2017, majority of the questions came from contemporary issues i.e. topics older than one year. But in 2017, there is heavy focus on contemporary issues, over 75% questions from this area only.
- 2017 has just two theory questions: 1) factors affecting growth potential (2) principles & benefits of stem cell therapy. In every other question – at least partially they’ve asked some contemporary issue e.g. crop-diversification benefits is “theory” but simultenously they asked in the same question “why rice-wheat yields declining (in recent times)?
- Implications: rather than doing haay-haay for ‘next’ current affairs, one should look back at what has been happening in last 3-5-7-10 years in contemporary perspective.
Opinion / Assessment Type Questions
| Type of Question | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|
|
62.5 | 95 |
|
187.5 | 155 |
| Total Marks | 250 | 250 |
In 2017, there is slight increase in the ‘opinion / assessment’ type questions.
| 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|
| 20 questions: all have to be answered in 200 words |
|
| Total 4000 words. | Total 4000 words. |
Length wise there is no difference, but paper is tougher because this time more ‘contemporary, opinion, analysis’ type questions where you’ve to pause, think, arrange points in logical sequence and then answer.
GS3 Topicwise Papers since Syllabus Change
In 2013, UPSC changed the syllabus-pattern of Mains examination and the number of general studies (GS) papers were increased from two to four. Out of them, GS Paper-3 deals with Economy, Agriculture, Environment, Disaster management, science technology and security. Here are the topicwise sorted questions since the pattern change:
| Block | GSM3 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1: Economy | Growth | 10 | 25 | 37.5 | 25 | 35 |
| Budget | 30 | 0 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 15 | |
| Liberlization | 20 | 25 | 0 | 12.5 | 15 | |
| Infra, Invest | 10 | 37.5 | 12.5 | 25 | 10 | |
| 2: Food | land Reform | 10 | 0 | 0 | 12.5 | 0 |
| Cropping | 0 | 0 | 0 | 37.5 | 15 | |
| MSP-PDS | 20 | 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 15 | |
| E-Tech in aid | 0 | 0 | 12.5 | 0 | 10 | |
| Food Processing | 10 | 12.5 | 37.5 | 0 | 10 | |
| 3: Science | Sci.Tech | 40 | 12.5 | 25 | 0 | 10 |
| Sci.Tech (Indian) | 0 | 25 | 12.5 | 25 | 25 | |
| Environment | 35 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |
| Disaster | 10 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 25 | 15 | |
| 4: Crime | Develop vs Exterm. | 10 | 0 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 40 |
| Border | 10 | 62.5 | 25 | 25 | 0 | |
| Cyber Security | 25 | 0 | 25 | 12.5 | 10 | |
| Money Laundering | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 |
[Block #1] Economy
Topics related to economy, infrastructure, investment

Growth and Resource mobilization
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Indian Economy (issues re: planning, mobilisation of resources, growth, development, employment); Inclusive growth and issues therein
| Among several factors for India’s potential growth, savings rate is the most effective one. Do you agree? What are the other factors available for growth potential? | 2017 |
| Account for the failure of manufacturing sector in achieving the goal of labour-intensive exports rather than capital-intensive exports. Suggest measures for more labour-intensive rather than capital-intensive exports. | 2017 |
| What are the salient features of ‘inclusive growth’? Has India been experiencing such a growth process? Analyze and suggest measures for inclusive growth. | 2017 |
| Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is necessary for bringing unbanked to the institutional finance fold. Do you agree with this for financial inclusion of the poorer section of the Indian society? Give arguments to justify your opinion. | 2016 |
| Comment on the challenges for inclusive growth which include careless and useless manpower in the Indian context. Suggest measures to be taken for facing these challenges. | 2016 |
| The nature of economic growth in India in described as jobless growth. Do you agree with this view? Give arguments in favour of your answer. | 2015 |
| Craze for gold in Indians have led to a surge in import of gold in recent years and put pressure on balance of payments and external value of rupee. In view of this, examine the merits of Gold Monetization Scheme. | 2015 |
| Capitalism has guided the world economy to unprecedented prosperity. However, it often encourages shortsightedness and contributes to wide disparities between the rich and the poor. In this light, would it be correct to believe and adopt capitalism driving inclusive growth in India? Discuss. | 2014 |
| With a consideration towards the strategy of inclusive growth, the new companies bill, 2013 has indirectly made CSR a mandatory obligation. Discuss the challenges expected in its implementation in right earnest. Also discuss other provisions in the bill and their implications. | 2013 |
| “Success of ‘Make in India’ programme depends on the success of ‘Skill India’ programme and radical labour reforms.” Discuss with logical arguments. | 2015 |
| While we found India’s demographic dividend, we ignore the dropping rates of employability. What are we missing while doing so? Where will the jobs that India desperately needs come from? Explain. | 2014 |
Economy: Budget
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Government Budgeting
| One of the intended objectives of Union Budget 2017-18 is to ‘transform, energize and clean India’. Analyse the measures proposed in the Budget 2017-18 to achieve the objective. | 2017 |
| Women empowerment in India needs gender budgeting. What are the requirements and status of gender budgeting in the Indian context? | 2016 |
| In what way could replacement of price subsidy with Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) change the scenario of subsidies in India? Discuss. | 2015 |
| What are the reasons for introduction of Fiscal responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) act, 2003? Discuss critically its salient features and their effectiveness. | 2013 |
| What is meaning of the term tax-expenditure? Taking housing sector as an example, discuss how it influences budgetary policies of the government. | 2013 |
| Discussion the rationale for introducing Good and services tax in India. Bring out critically the reasons for delay in roll out for its regime. | 2013 |
Economy: Investment and Infrastructure
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Infrastructure (energy, ports, roads, airports, railways); Investment models
| Examine the developments of Airports in India through Joint Ventures under Public-Private Partnership(PPP) model. What are the challenges faced by the authorities in this regard. | 2017 |
| What are ‘Smart Cities? Examine their relevance for urban development in India. Will it increase rural-urban differences? Give arguments for Smart Villages’ in the light of PURA and RURBAN Mission. | 2016 |
| Justify the need for FDI for the development of the Indian economy. Why there is gap between MOUs signed and actual FDIs? Suggest remedial steps to be taken for increasing actual FDIs in India. | 2016 |
| There is a clear acknowledgement that Special Economic Zones (SEZs) are a tool of industrial development, manufacturing and exports. Recognizing this potential, the whole instrumentality of SEZs requires augmentation. Discuss the issues plaguing the success of SEZs with respect to taxation, governing laws and administration. | 2015 |
| The right to fair compensation and transparency land acquisition, rehabilitation and resettlement act, 2013 has come into effect from 1 January 2014. What implication would it have on industrialisation and agriculture in India? | 2014 |
| National urban transport policy emphasizes on moving people instead of moving vehicles. Discuss critically the success of various strategies of the government in this regard. | 2014 |
| Explain how private public partnership agreements, in longer gestation infrastructure projects, can transfer unsuitable liabilities to the future. What arrangements need to be put in place to ensure that successive generations’ capacities are not compromised? | 2014 |
| Adaptation of PPP model for infrastructure development of the country has not been free from criticism. Critically discuss the pros and cons of the model. | 2013 |
Economy: Liberalization
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Effects of Liberalisation on the economy; Changes in Industrial policy & their effects on industrial growth
| “Industrial growth rate has lagged behind in the overall growth of Gross-Domestic-Product(GDP) in the post-reform period” Give reasons. How far the recent changes in Industrial Policy are capable of increasing the industrial growth rate? | 2017 |
| How globalization has led to the reduction of employment in the formal sector of the Indian economy? Is increased informalization detrimental to the development of the country? | 2016 |
| Normally countries shift from agriculture to industry and then later to services, but India shifted directly from agriculture to services. What are the reasons for the huge growth of services vis-a-vis industry in the country? Can India become a developed country without a strong industrial base? | 2014 |
| Foreign direct investment in the defence sector is now said to be liberalised. What influence this is expected to have on Indian defence and economy in the short and long run? | 2014 |
| Examine the impact of liberalization on companies owned by Indian. Are the competing with the MNCs satisfactorily? | 2013 |
| Discuss the impact of FDI entry into multi-trade retail sector on supply chain management in commodity trade pattern of the economy. | 2013 |
| Though India allowed foreign direct investment (FDI) in what is called multi brand retail through joint venture route in September 2012, the FDI even after a year, has not picket up. Discuss the reasons. | 2013 |
[Block#2] Agriculture
Topics related to farming, food processing and food security
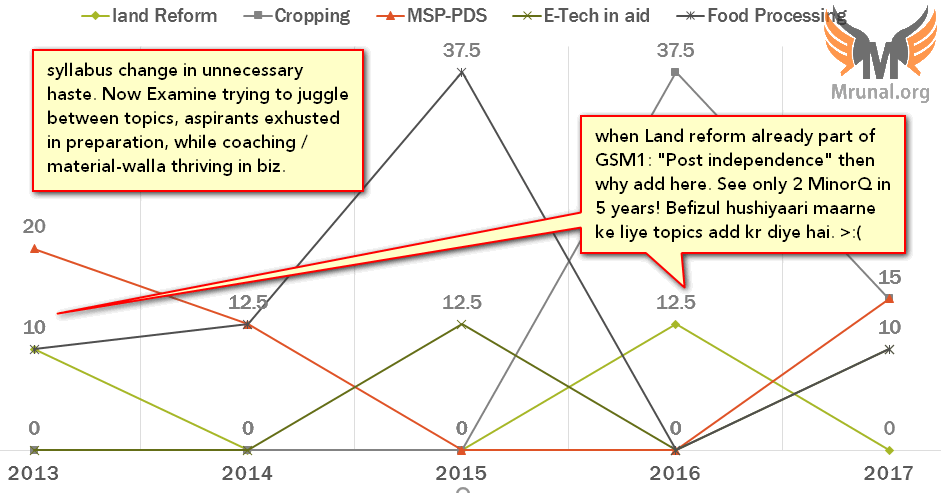
Food: Cropping-irrigation
| What are the major reasons for declining rice and wheat yield in the cropping system? How crop diversification is helpful to stabilize the yield of the crop in the system? | 2017 |
| What is water-use efficiency? Describe the role of micro-irrigation in increasing the water-use efficiency. | 2016 |
| What is allelopathy? Discuss its role in major cropping systems of irrigated agriculture. | 2016 |
| Given the vulnerability of Indian agriculture to vagaries of nature, discuss the need for crop insurance and bring out the salient features of the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) | 2016 |
Food: Tech. in aid of farmers
GS3 Syllabus Topic: e-technology to aid farmers, Technology missions;
| Explain various types of revolutions, took place in Agriculture after Independence in India. How these revolutions have helped in poverty alleviation and food security in India? | 2017 |
| How can the ‘Digital India’ programme help farmers to improve farm productivity and income? What steps has the Government taken in this regards? | 2015 |
Food: Food processing industry
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Food processing and related industries in India (scope & significance, location, upstream-downstream requirements, supply chain management); storage, transport & marketing of agro-produce and related issues & constraints; Economics of animal-rearing
| What are the reasons for poor acceptance of cost effective small processing unit? How the food processing unit will be helpful to uplift the socio-economic status of poor farmers? | 2017 |
| Livestock rearing has a big potential for providing non-farm employment and income in rural areas. Discuss suggesting suitable measures to promote this sectors in India | 2015 |
| In view of the declining average size of land holdings in India which has made agriculture non-viable for a majority of farmers, should contract farming and land leasing be promoted in agriculture? Critically evaluate the pros and cons. | 2015 |
| What are the impediments in marketing and supply chain management in industry in India? Can e-commerce help in overcoming these bottlenecks? | 2015 |
| There is also a point of view that agriculture produce market committees (APMCs) set up under the state acts have not only impeded the development of agriculture but also have been the cause of food inflation in India. Critically examine. | 2014 |
| India needs to strengthen measures to promote the pink revolution in food industry for better nutrition and health. Critically elucidate the statement. | 2013 |
Food: Land reforms
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Land Reforms in India
| Discuss the role of land reforms in agricultural development. Identify the factors that were responsible for the success of land reforms in India. | 2016 |
| Establish the relationship between land reform, agriculture productivity and elimination of poverty in Indian Economy. Discussion the difficulty in designing and implementation of the agriculture friendly land reforms in India. | 2013 |
Food: MSP
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Farm subsidies and MSP and issues therein (direct and indirect); PDS (objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping, issues of buffer stocks & food security)
| How do subsidies affect the cropping pattern, crop diversity and economy of farmers? What is the significance of crop insurance, minimum support price and food processing for small and marginal farmers? | 2017 |
| “In the villages itself no form of credit organisation will be suitable except the cooperative society.” – All Indian rural credit survey. Discuss this statement in the background of agriculture finance in India. What constrain and challenges do financial institutions supplying agricultural finances? How can technology be used to better reach and serve rural clients? | 2014 |
| Food security bill is expected to eliminate hunger and malnutrition in India. Critically discuss various apprehensions in its effective implementation along with the concerns it has generated in WTO | 2013 |
| What are the different types of agriculture subsidies given to farmers at the national and state levels? Critically analyze the agriculture subsidy regime with the reference to the distortions created by it. | 2013 |
[Block #3] Science
Topics related to environment, science-tech and disaster management

Disaster Management
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Disasters & Disaster Management
| On December 2004, tsumani brought havoc on 14 countries including India. Discuss the factors responsible for occurrence of Tsunami and its effects on life and economy. In the light of guidelines of NDMA (2010) describe the mechanisms for preparedness to reduce the risk during such events. | 2017 |
| The frequency of urban floods due to high intensity rainfall is increasing over the years. Discussing the reasons for urban floods. highlight the mechanisms for preparedness to reduce the risk during such events. | 2016 |
| With reference to National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) guidelines, discuss the measures to be adopted to mitigate the impact of the recent incidents of cloudbursts in many places of Uttarakhand. | 2016 |
| The frequency of earthquakes appears to have increased in the Indian subcontinent. However, India’s preparedness for mitigating their impact has significant gaps. Discuss various aspects. | 2015 |
| Drought has been recognised as a disaster in view of its party expense, temporal duration, slow onset and lasting effect on various vulnerable sections. With a focus on the September 2010 guidelines from the National disaster management authority, discuss the mechanism for preparedness to deal with the El Nino and La Nina fallouts in India. | 2014 |
| How important are vulnerability and risk assessment for pre-disaster management. As an administrator ,what are key areas that you would focus in a disaster management | 2013 |
Environment and Pollution Control
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Environmental conservation; Environmental pollution and degradation; Environmental Impact Assessment
| Theme | Question | Year |
| EIA | ‘Climate Change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? | 2017 |
| EIA | Rehabilitation of human settlements is one of the important environmental impacts which always attracts controversy while planning major projects. Discuss the measures suggested for mitigation of this impact while proposing major developmental projects. | 2016 |
| Energy-Thermal | What are the consequences of illegal mining? Discuss the ministry of environment and forests’ concept of “GO AND NO GO” zones for coal mining. | 2013 |
| Energy- RNW | Give an account of the current status and the targets to be achieved pertaining to renewable energy sources in the country. Discuss in brief the importance of National Programme on Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). | 2016 |
| Energy- RNW | To what factors can the recent dramatic fall in equipment costs and tariff of solar energy be attributed? What implications does the trend have for the thermal power producers and the related industry? | 2015 |
| Energy- RNW | Should the pursuit of carbon credit and clean development mechanism set up under UNFCCC be maintained even through there has been a massive slide in the value of carbon credit? Discuss with respect to India’s energy needs for economic growth. | 2014 |
| Thermal energy | Environmental impact assessment studies are increasingly undertaken before project is cleared by the government. Discuss the environmental impacts of coal-fired thermal plants located at Pitheads. | 2014 |
| Thermal energy | Write a note on India’s green energy corridor to alleviate the problems of conventional energy. | 2013 |
| River | Not many years ago, river linking was a concept but it is becoming reality in the country. Discuss the advantages of river linking and its possible impact on the environment. | 2017 |
| River | What do you understand by run of the river hydroelectricity project? How is it different from any other hydroelectricity project? | 2013 |
| River | The Namami Gange and National mission for clean Ganga (NMCG) programmes and causes of mixed results from the previous schemes. What quantum leaps can help preserve the river Ganga better than incremental inputs? | 2015 |
| River | Enumerate the National Water Policy of India. Taking river Ganges as an example, discuss the strategies which may be adopted for river water pollution control and management. What are the legal provisions for management and handling of hazardous wastes in India? | 2013 |
Science-Tech: Awareness
GS3 Syllabus Topic: S&T developments and everyday applications & effects; Awareness in fields of IT, Space, Computers, Robotics, Nanotech, Biotech, IPR issues
| Stem cell therapy is gaining popularity in India to treat a wide variety of medical conditions including Leukaemia, Thalassemia, damaged cornea and several burns. Describe briefly what stem cell therapy is and what advantages it has over other treatments? | 2017 |
| India’s Traditional Knowledge Digital Library (TKDL) which has a database containing formatted information on more than 2 million medicinal formulations is proving a powerful weapon in the country’s fight against erroneous patents. Discuss the pros and cons making this database publicly available under open-source licensing | 2015 |
| What are the areas of prohibitive labour that can be sustainably managed by robots? Discuss the initiatives that can propel research in premier research institutes for substantive and gainful innovation. | 2015 |
| In a globalised world, intellectual property rights assume significance and are a source of litigation. Broadly distinguish between the terms – copyrights, patents and trade secrets. | 2014 |
| What do you understand by Umpire decision review in cricket? Discuss its various components. Explain how silicon tape on the edge of a bat may fool the system? | 2013 |
| What is an FRP composite material? How are they manufactured? Discuss their applications in aviation and automobile industry | 2013 |
| Bring out the circumstances in 2005 which forced amendment to section 3(d) in the India n Patent Law, 1970. Discuss how it has been utilized by Supreme court in its judgment rejecting Novartis patent application for “Glivec”. Discuss briefly the pros and cons of the decision. | 2013 |
| How does the 3D printing technology work? List out the advantages and disadvantages of the technology. | 2013 |
| What do you understand by fixed dose drug combinations (FDCs)? Discuss their merits and demerits. | 2013 |
Science-Tech: Indians
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Achievements of Indians in S&T; Indigenisation of technology & development of new technology
| India has achieved remarkable successes in unmanned space missions including the Chandrayaan and Mars Orbitter Mission, but has not ventured into manned space mission, both in terms of technology and logistics? Explain critically. | 2017 |
| Give an account of the growth and development of nuclear science and technology in India. What is the advantage of fast breeder reactor programme in India? | 2017 |
| Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology has helped India in its socio-economic development? | 2016 |
| Why is nanotechnology one of the key technologies of the 21st century? Describe the salient features of Indian Government’s Mission on Nanoscience and Technology and the scope of its application in the development process of the country. | 2016 |
| What do you understand by ‘Standard Positioning Systems’ and ‘Protection Positioning Systems’ in the GPS era? Discuss the advantages India perceives from its ambitious IRNSS programme employing just seven satellites. | 2015 |
| Scientific research in Indian universities is declining, because a career in science is not as attractive as our business operations, engineering or administration, and the universities are becoming consumer oriented. Critically comment. | 2014 |
| Can overuse and the availability of antibiotics without doctor’s prescription, the contributors to the emergence of drug-resistant diseases in India? What are the available mechanisms for monitoring and control? Critically discuss the various issues involved. | 2014 |
[Block#4] Security
Topics related to security, crime, extremism

यदि काले धन के बारे में पूछना ही नही तो सिलेबस में रख्खा क्यों है?
Security: Terrorism, Extremists (LWE, NE)
GS3 Syllabus Topic:
- Linkages between Development & spread of Extremism;
- Linkages of Organized crime and Terrorism
- Linkages of Pakistan and Terrorism
| Mob violence is emerging as a serious law and order problem in India. By giving suitable examples, analyze the causes and consequences of such violence. | 2017 |
| The scourge of terrorism is a grave challenge to national security. What solutions do you suggest to curb this growing menace? What are the major sources of terrorist funding? | 2017 |
| The north-eastern region of India has been infested with insurgency for a very long time. Analyze the major reasons for the survival of armed insurgency in this region. | 2017 |
| “Terrorism is emerging as a competitive industry over the last few decades.” Analyse the above statement. | 2016 |
| The persisting drives of the government for development of large industries in backward areas have resulted in isolating the tribal population and the farmers who face multiple displacements with Malkangiri and Naxalbari foci, discuss the corrective strategies needed to win the left wing extremism (LWE) doctrine affected citizens back into the mainstream of social and economic growth. | 2015 |
| Religious indoctrination via digital media has resulted in Indian youth joining the ISIS. What is ISIS and its mission? How can ISIS be dangerous for the internal security of our country? | 2015 |
| Article 244 of Indian Constitution relates to Administration of Scheduled areas and tribal areas. Analyze the impact of non-implementation of the provisions of fifth schedule on the growth of Left Wing Extremism. | 2013 |
Security: Cross border
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Border Areas (security challenges and management thereof); Security forces & agencies (mandate); Role of External State & Non-State actors in creating internal security challenges
| The terms ‘Hot Pursuit’ and ‘Surgical Strikes’ are often used in connection with armed action against terrorist attacks. Discuss the strategic impact of such actions. | 2016 |
| Border management is a complex task due to difficult terrain and hostile relations with some countries. Elucidate the challenges and strategies for effective border management. | 2016 |
| International civil aviation laws provide all countries complete and exclusive sovereignty over the airspace above the territory. What do you understand by airspace? What are the implications of these laws on the space above this airspace? Discuss the challenges which this poses and suggests ways to contain the threat. | 2014 |
| The diverse nature of India as a multireligious and multi-ethnic society is not immune to the impact of radicalism which has been in her neighbourhood. Discuss along with the strategies to be adopted to counter this environment. | 2014 |
| How illegal transborder migration does pose a threat to India’s security? Discuss the strategies to curb this, bring out the factors which give impetus to such migration. | 2014 |
| In 2012, the longitudinal marking of the high-risk areas for piracy was moved from 65° East to 78° east in the Arabian Sea by International Maritime organisation. What impact does this have on India’s maritime security concerns? | 2014 |
| China and Pakistan have entered into an agreement for development of an economic corridor. What thread does it dispose for India’s security? Critically examine. | 2014 |
| How far are India’s internal security challenges linked with border management, particularly in view of the long porous borders with most countries of South Asia and Myanmar? | 2013 |
Security: org. crime & money laundering
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Money laundering & Prevention
| Money laundering poses a serious threat to country’s economic sovereignty. What is its significance for India and what steps are required to be taken to control this menace? | 2013 |
Security: Cyber security and social media
GS3 Syllabus Topic: Basics of Cyber Security; Role of media and social-networking sites in internal security challenges; Internal security challenges through communication networks
| Discuss the potential threats of Cyber attack and the security framework to prevent it. | 2017 |
| Use of Internet and social media by non-state actors for subversive activities is a major concern. How have these have misused in the recent past? Suggest effective guidelines to curb the above threat. | 2016 |
| Discuss the advantage and security implications of cloud hosting of server vis-a-vis in-house machine-based hosting for government businesses. | 2015 |
| Considering the threats cyberspace poses for the country, India needs a “Digital Armed Force” to prevent crimes. Critically evaluate the National Cyber Security Policy, 2013 outlining the challenges perceived in its effective implementation. | 2015 |
| What is digital signature? What does its authentication mean? Giver various salient built in features of a digital signature. | 2013 |
| What are social networking site and what security implications do these sites present? | 2013 |
| Cyber warfare is considered by some defense analysts to be a larger threat than even Al Qaeda or terrorism. What do you understand by Cyber warfare? Outline the cyber threats which India is vulnerable to and bring out the state of the country’s preparedness to deal with the same. | 2013 |
Security- Security forces
| Human rights activists constantly highlight the view that the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act, 1958 (AFSPA) is a draconian act leading to cases of human rights abuses by the security forces. What sections of AFSPA are opposed by the activists? Critically evaluate the requirement with reference to the view held by the Apex Court. | 2015 |

![[Download] Topicwise UPSC GSM2-2023 Paper- polity, Governance international relations in Hindi and English with topic wise analysis](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/ana-gsm2-2023-mrunal79-500x383.png)
![[Download] Topicwise UPSC Mains General Studies Paper-1 (GSM1): History, Geography, Social Science](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/mains-answer-writing-d1-500x383.jpg)
Great Sir…good analysis..its very helpful all upsc aspirant
Excellent analysis.. bery useful one.
The question is….factors available for growth potential…not affecting growth potential
What is DL?
Thank you very much sir
thank you sir
Execellent sir.Thank you very much sir
Thank you Sir
thanks!
Sir you are the hope for poor students…. Don’t leave this great work… One day u will be rewarded by God
Thank You So much, Sir, Your analysis is always eye opener :)
DL = download
Brilliant ! Thank you Sir, for such a detailed and comprehensive analysis. This is immensely helpful for students like us it helps us know about the nuances of exam.
thankks sir grt job
Thanks sir for analysis these difficult fectors.
beyond words,,,indebted,,,thank you _/\_
Great analysis….thanks alot
This analysis is very useful for every aspirant of upsc
How can i download five years topic wise question papers?
this analytic thinking process is helping us a lot for maximum return and saving us from unfruitful sleepless nights. this is “vardan” for us. preparing from home without coaching.