- Timeline: Vehicle emission control in India
- What is Bharat emission standards?
- Alternative Fuels
- Suggestions to reduce tailpipe pollution
- Mock Questions:
- Correct answers
| 1991 | Vehicle emission norms introduced in India |
| 1999 | SC order government to introduce Euro norms like pollution control regime. |
| 2000 onwards | Bharat State emission standard I introduced. |
| 2003 |
|
| 2005 |
|
| 2010 |
|
| Dec 2012 |
|
| 2014, May | Saumitra Chaudhri gave recommendations. Hence in news. |
What are Bharat emission standards?
- Euro norms define the maximum limit of pollutant that a vehicle can emit. (CO2, nitrogen oxide, sulfur and suspended particulate matter)
- If vehicle emits more than this limit, it cannot be sold in Europe.
- In India, we follow Euro norms under the label “Bharat stage” norms. we are gradually implementing them in more and more cities

| Euro normBharat Stage | limit of RSPM* | India implements from |
|---|---|---|
| I (1) | 0.14 | 2000: nation wide |
| II (2) | 0.08 | 2005: nation wide |
| III (3) | 0.05 | 2010: nation wide |
| IV (4) | 0.025 |
|
| V (5) | 0.005 | 2022 (All India)# |
| VI (6) | 0.0025 | after 2024 (All India)# |
- #as per Saumitra Committee recommendation.
- *Respirable suspended particulate matter (RSPM)

Sulfur lead content vs Bharat norms:
- To reduce emission from vehicle, we’ve to fit “catalytic converter”, “particulate filter”, & other fancy devices in its exhaustion system.
- But the chemical catalysts in such devices get immobilized in presence of lead/sulphur.
- Therefore, fuel should have minimal quantity of lead and sulfur. Else, you’ll have to replace those fancy devices too often.
- Lead: we are already selling lead-free petrol. Since year 2000 only lead free petrol sold in India.
- sulfur: the Bharat norms give following limits:
| year | particles per million (ppm) in diesel |
|---|---|
| present (BS3) | 350 |
| 2017 (BS4) | 50 (already done in BS4 cities) |
| 2020 (BS5) | 10 |
Why additional Levy on petrol/diesel?
To implement Bharat norms, we’ve to do two things:
| To Vehicle manufacturers | To Oil refineries |
|---|---|
| You’ve fit “catalytic converter”, “particulate filter” & other fancy gadgets in the engine. This will decrease soot & pollutants. | You produce fuel with less sulfur, olefin & other impurities. (especially for Bharat stage 5) |
| ok, Not a problem because these companies already fitting such equipment’s in engine, before exporting vehicles to Europe. (due to higher level Euro standards) | Problem because refiners have to buy machines and technology worth Rs.~80,000 crore. |
- Government can arrange cash for refineries, by imposing 75 Paise “special fuel upgradation cess” on Petrol and Diesel. (says Sumitra Committee)
- Send this cash to Oil Industry Development Board (OIDB)
- Then, OIDB will upgrade the refineries to Bharat stage 4 and 5.
- Previously, recall Famous lawyer Harish Salve reported to supreme court and asked for 30% cess on private diesel vehicles. and that money should be used for implementing Bharat stage 5 and 6.
Taxation: Misc. recommendations
- Import duty should be 0% on both LNG and crude oil.
- States VAT should be reduced on CNG sale (to promote CNG vehicles)
Bharat Standards: limitations
- Four refineries in the North East- Guwahati, Digboi, Numaligarh and Bongaigaon- their equipment outdated, cannot produce BS4, BS5 quality fuels.
- Government designated only a few cities under BS-4 standards. BS-4 vehicles more expensive than BS3. Hence public buys BS3 vehicles from peripheral towns to evade registration taxes.
- BS3 fuel is cheaper than BS4 fuel.
- On older vehicles, we need to fit “catalytic after-treatment devices” to reduce their emission. But government & public not pursuing this project enthusiastically.
- Our diesel to petrol usage ratio is almost (4.5): 1 hence more pollution. This ratio is low in USA, Europe and Japan.
Flash point in Diesel
- It is the lowest temperature at which a fuel starts turning into vapor (which will later ignite)
- Flash point of diesel is set at 35 degree C. (under both BS3 and BS4.)
- Some journalist argue that 35 degree is too dangerous. Because in India, temperature often above 40 degree celcius (Even EU has flash point limit 55 C, despite having cold climate.)
- Sumitra rejects this hypothesis, because even tropical countries like Brazil and Argentina have lower flash points. The temperature in and around the engine of the vehicle is well over 100 C – much above the highest flash point prescribed anywhere in the world. Hence 35 degree flash point doesn’t automatically mean explosion.
Misc. terms from his report
| Olefin | These are unsaturated alkanes. We need to reduce their quantity in fuel, to reduce pollution. |
| Cetane number | It is a measure of diesel quality. Lower the cetane number, diesel will produce more smoke. |
Alternative Fuels
Overall, Saumitra report is three things
- Bharat norms: implementing next stage
- taxation issues
- Alternative fuels- for reducing petrol and diesel consumption. Here, he give pros and cons of each alternative.
#1: Methanol
| Good points | Bad points |
|---|---|
|
|
Mrunal notes: Additional pros, cons and facts can be gathered for each “alternative fuel” via google books, Britannica etc. but then article will become 5 miles long and will take another five days to finish. And yet there is no guarantee that it’ll have sufficient facts to solve a possible UPSC MCQ! Therefore, I’ve confined myself only to the facts mentioned in Saumitra report, nothing beyond that. But you’re free to dig through all angles.
#2: Ethanol
- is an organic solvent
- Ethanol itself burns cleaner and burns more completely than petrol.
- Ethanol can be derived from Sugar cane juice and molasses.
- Molasses is the byproduct when sugar cane juice converted to sugar.
| 2001 | Government permitted adding Ethanol in petrol. Pilot project in Uttar Pradesh. |
| 2006 | 5% Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) began in most states, except JK and North East. |
| 2008 |
|
| 2017 | Sumitra Committee proposed 20% ethanol blending by 2017 |
Case study: Brazil’s ethanol blending program
- Started in mid-70s
- Their car-engines designed such way, they use even upto 18% ethanol blending. (Exact figures not important but for MCQ the examiner may twist statement saying “car engine cannot run properly if ethanol blending more than 10%“…then you should know it is an incorrect statement.)
#3: Hydrogen fuel
Bad points:
- Cost of hydrogen pipeline is 15x times more expensive than a CNG/LPG pipeline.
- Hence, only few areas of USA have hydrogen pipeline.
- In the entire world hardly 200 hydrogen refiling stations by 2013. (rank: N.America > Asia > South America)
- Hydrogen burns with colorless odorless flame, hence hard to detect leakage.
Hydrogen Vision 2020 – (GIFT)
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE)’s Green Initiatives for Future Transport (GIFT)
- It has vision 2020 for Hydrogen.
- Aim: sell Hydrogen at cost of 60-70 per kg
- Build pipelines and refilling stations for hydrogen fuel.
- Get at least 1 lakh hydrogen vehicles on Indian road
- Safety regulation, laws and codes.
#4: CNG: Compressed Natural gas
| Favor | Against |
|---|---|
|
Public not ready to buy CNG kits/vehicles because
|
#5: LPG-Liquefied Petroleum gas
- LPG is predominantly propane and butane. Propane constitutes 30-99%.
- LPG can be derived from.
- refining crude oil
- natural gas
- Hence no risk of “single source dependence”
- LPG is globally surplus because of Natural Gas production.
- In some countries, LPG is called “Auto-Gas” and used in taxis e.g. Korea, Turkey, Russia, Poland and Italy.
| Good points | bad points |
|---|---|
|
|
#6: Hybrid and electric vehicles (HEV)
- HEVs have both internal combustion (running on petrol) and electricity.
- Both USA and China planning to add 1-5 million new HEV vehicles by 2020.
- India should also work on this. More details in old article click me
Suggestions to reduce tailpipe pollution
List not exhaustive. I’ve lifted only a few non-technical, easy to memorize points from his report.
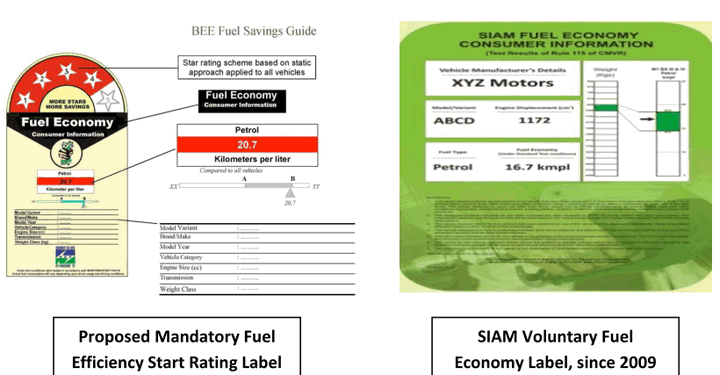
- BEE (Bureau of energy efficiency) labels on vehicles to show their fuel efficiency.
- We need to replace the existing PUC system to a more reliable computerized system.
- We need to link vehicle insurance with pollution. (i.e. higher pollution vehicle should be ordered to pay higher premium for same coverage)
- Give subsidy, tax-benefit to vehicle owners to retrofit their engines with newly emission control devices
- Impose higher taxes on old vehicles, because they emit more gases.
- More tax on diesel guzzling SUV cars.
- Less tax on hybrid cars, CNG vehicles.
- Use chemical markers to detect adulteration of diesel/petrol with kerosene. Make oil companies responsible for fuel quality at their station.
Mock Questions:
Correct statements
Q1. Petroleum ministry had setup Saumitra Chaudhari Committee for ___.
- Diesel subsidy pricing in India
- Petrol taxation in India
- Implementation of Bharat stage 4 norms.
- Auto fuel vision policy 2025
Q2. Suppose two cars are of identical size and body. One produced India and another in Europe. Which of the following is/are correct:
- Euro IV car causes less pollution than Bharat V car.
- Euro III car causes more pollution than Bharat III car.
- Both A and B
- Neither A nor B
Q3. At present, every city of India is under ___ norm.
- Bharat stage VI or higher
- Bharat stage II of higher
- Bharat stage III or higher
- Bharat stage IV or higher
Q4. To comply with higher level Bharat norms, oil refineries need to produce diesel with less sulphur content because
- It is an air pollutant
- It deactivates the catalysts in particulate filter & other emission reduction devices fitted in the vehicles.
- Both A and B
- Neither A nor B
Q5. Consider following statements about flashpoint:
- Flashpoint is the temperature at which fuel catches fire.
- Indian diesel has flashpoint of 35 degree celcius.
- Higher the flashpoint, less dangerous the fuel.
Correct statement
- Only 1 and 2
- Only 2 and 3
- Only 1 and 3
- None of them
Q6. Consider following statements
- To improve the quality of petrol and diesel, refineries will have to add Olefin into them from Bharat stage IV onwards.
- Diesel with higher Cetane number is considered to be of lower quality.
- National biofuel policy 2008 requires Oil refineries to blend at least 5% ethanol with petrol.
Incorrect statements are
- Only 1 and 2
- Only 2 and 3
- Only 1 and 3
- None of them
Q7. Consider following statements about Methanol
- Pure Methanol can be used in treatment of retinal glaucoma
- Methanol is biodegradable in aerobic environment but not in anaerobic environment.
- In many countries, methanol is used as a fuel in race cars, including China.
Incorrect statements are
- Only 1 and 2
- Only 2 and 3
- Only 1 and 3
- None of them
Q8. Consider following statements
- CNG is not a safe fuel because contains traces of carcinogens such as Benzene in vapor form.
- In the whole world, North America has highest number of Hydrogen refilling stations
- Pure hydrogen fuel burns with blue flame hence provides highest amount of energy per kg, than any other fuel.
Incorrect statements are
- Only 1 and 2
- Only 2 and 3
- Only 1 and 3
- None of them
Mains
General Studies Mains paper 3 Syllabus topic: Environmental Pollution.
- Write a note on the salient recommendations of Saumitra Chaudhary Committee on auto fuels (200 words).
- What is India’s Hydrogen Vision 2020? (100 words)
- What are alternative fuels? Why is it impractical to adopt most of them in India? (200 words).
- What is Bharat Stage emission standards? Discuss the challenges in their implementation. (200 words).
- “To minimize vehicular pollution, Bharat norms alone are not sufficient.” Comment. (200 words).
Correct answers
- C-auto fuel vision policy
- D neither correct. Because Both Euro and Bharat norms are same. And higher stage means less pollution.
- C-Bharat Stage 3 or higher
- C both reasons correct
- B only 2 and 3 correct.
- A- 1 and 2 wrong. Olefin causes more pollution. Higher cetane is better quality.
- A- 1 and 2 wrong. Methanol itself can cause blindness even in minute quantity, how can you treat glaucoma with it! Second statement is also wrong.
- C- 1 and 3 wrong. CNG doesn’t have benzene and hydrogen flame colorless.

![[Environment] Mangrove Species Conocarpus banned in Gujarat & Telangana](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/edp-conocarpus-500x383.png)
![[Environment] Floating Solar Farms, Banni Grassland, Nairobi flies & more Weekly Mrunal Digest from Jul week1-2022 (WMD)](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/Floating-Solar-Farm-500x383.webp)
![[Environment WMD] Single use plastic ban, ESZ, Surya Nutan Cooker, & more from Jun week3-2022](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/single-use-plastic-main-500x383.jpg)
![[T25] UPSC Mock Round#43: Environment & Geography Practice Questions- Global Climate Risk Index 2020, Bog wetland and More](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/c-t25-taimur-500x383.jpg)
Diesel
Petrol
Uses In diesel engines, heating systems In petrol engines
Made from Petroleum/ Crude oil Petroleum/ Crude Oil
Energy content 38.6 MJ/litre 34.6 MJ/litre
Made by Fractional distillation Fractional distillation
Torque (for 10L engine) 1000 Nm @ 2000 rpm 300Nm @ 4000 rpm
Power (for 10L engine) 490Hp @ 3500 rpm 600Hp @ 5500 rpm
Power = torque*RPM More torque at low speeds Runs at higher RPM
Auto-ignition temperature 210°C 246°C
CO2 emission More than gasoline(petrol). Diesel fuel produces approximately 13% more CO2 gas per gallon of fuel burned, compared to gas (petrol) engines. Lower than diesel.
Viscosity increase at lower temperatures No change
US Consumption (2006) 50 Billion gallons 148 Billion gallons
Types of ignition Direct ( by compression ) Spark
Since 2000, India started following European emission and fuel regulations for four-wheeler heavy duty and light duty vehicle. India’s own emission regulations are implemented on two and three wheeled vehicles.
Each stage of the emission norms represents a specific limit on the pollutants released, which is controlled by the type of fuel made by the companies and the up-gradations and modifications made by the auto firms to the vehicle to control pollution.
https://askopinion.com/bharat-stage-emission-norms-in-india