- Food Chain
- Food Web
- DDT and Biomagnification
- Biotic Potential.
- Carrying Capacity
- Interspecies relations
- Predation vs Parasitism
- Free download IGNOU Material
- Mock questions
Food Chain
- For example, plants are eaten by insects, who are eaten by frogs, these frogs are eaten by fish, who are eaten by human beings.
- Plant > insect > frog > fish > human.
- This sequence is known as Food chain.
What is Trophic Level?
- Each step in the food chain is called a “Trophic level”.
- In this food chain: Plant > Insect > Frog > Fish > human= five steps.
- The trophic level to which an organism belongs, indicates how far it is away from plants in the food chain.
- green plants (producers)= trophic level I
- herbivores (primary consumers)= trophic level II
- carnivores (secondary consumers)=trophic level III
- top carnivores (tertiary consumers)= trophic level IV
- Herbivores (deer, cow etc.) are always @second trophic level.
- Higher trophic levels are made up of carnivores.
- An organism cannot always be assigned to one specific trophic level.
- E.g. man (omnivore), so he is both a herbivore (@2nd trophic level) and as a carnivore he can be (@>2nd trophic level)
*Detrius = dry leaves, dead plant, animal remains, dead skin cells, other organic waste (urine, excreta).
Ecological Pyramids
- You already know about the food chain: grass –> Grasshoppers –>birds –>hawk.
- Each step or level is known as Trophic level.
- If we draw these trophic levels in a verticle fashion, a pyramid is created. This pyramid is known as Ecological pyramid.
- The Autotrophs (green plants) = base of the pyramid
- The top carnivores (lion tigers) = tip (apex) of this pyramid.
Types of Pyramids
- Pyramid of numbers,
- Pyramid of biomass
- Pyramid of energy or productivity

Food Web
- Food Chain:–> Grass> grasshopper >frog > fish > man
- Food chain assume the isolated linear line. But in real life, frog could be eating other insects apart from grasshopper. Fish could be eating smaller fishes apart from frog. So there exists an interconnected Network of (Food Chain + Food Chain + Food chain…).
- This interconnected network of food chains = food web.
Why is Food web important?
- Suppose in a jungle, the deer species is wiped out due to some human poaching/ diseases / natural disaster.
- Then its predators (lion,tiger) can feed on other animals such as fox, wolf, crane, peacock etc. until deer population grows again.
- Thus, food web= help living organism survive in case of minor or major setbacks in their food chain.
- food web=provides stability to the ecosystem.
Energy Flow in the Ecosystem
- So far you know what is food chain and what is food web.
- You also know what is Trophic level. (each step in a food chain).
- When energy is passed from one tropic level to next trophic level, some part of energy is wasted. So energy declines as we move up in the chain/ web / pyramid.
Why?
- Because some energy is wasted as body heat.
- No herbivore (deer, cow) can entirely digest and absorb the plant nutrients.
- Some energy is wasted while capturing the prey. (e.g. Tiger chasing a deer.)
- Some energy remains trapped e.g. Tiger only eats the flash of a deer. He doesn’t eat the skin, hair, bone and teeth of a deer.
- So the energy stored in the skin, hair, bone and teeth of a deer =not moved up in the food chain.
- However this energy is later utilized when scavenger (hyena) comes into picture. Because Hyena’s stomach acid is so powerful, it can digest the skin, hair, bone, teeth and other remnants of a deer corpse.
2nd law of themodynamics

- When energy changes from one form to another, some of the energy is Lost. Suppose a jungle receives 1000 calories worth Sunlight everyday.
- Most of the sunlight is not absorbed; some is reflected back to space.
- Out of the sunlight that is absorbed, only a small portion is utilized by green plants
- Out of which the plant uses up some for respiration, therefore only 100 calories are stored as energy rich materials.
- Now a deer, eats the green plant containing 100 cal of food energy.
- The deer uses some of it for its own metabolism and stores only 10 cal as food energy.
- A tiger eats the deer gets an even smaller amount of energy.
- Thus usable energy decreases from sunlight to producer(green plant) to herbivore(deer) to carnivore(tiger).
- Therefore, the energy pyramid will always be upright.
Connection: Trophic level vs Energy flow
- The loss of energy (explained in previous para) limits the number of trophic levels in the ecosystem.
- Hence trophic levels are seldom more than five.
- This also explains why the steps in a food chain are limited to four or five.
Energy=Unidirectional
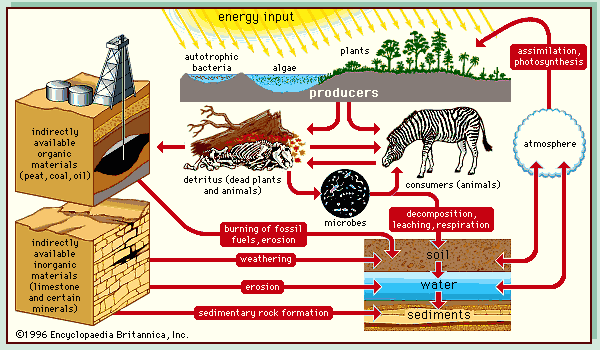
- Movement of Energy is Unidirectional (one-way).
- Because initial Solar energy trapped by an autotroph (plant) does not go back to Sun.
- Similarly, energy that passes from herbivore (deer) to carnivore (lion) does not pass back to herbivore (deer).
- This unidirectional (one-way) and continuous energy flow=prevents the collapse of Ecosystem.
- (otherwise, if lion ate deer and another rabbit ate lion then what will happen hahaha!)
Nutrients/Material=Cyclic
- The Movement of nutrients/materials is cyclic.
- e.g. grasshopper eats grass and dies.
- Its body is decomposed and again absorbed by some other plant/grass.
- In other words: The Decomposers break down the fecal matter, excretory products and dead bodies of all plants and animals into inorganic materials.
- And this inorganic material is again reused by autotrophs (green plants).
- Ok here is a question? If you want to make the movement of nutrients unidirectional then what should be done? Ans. Eliminate the decomposers.
Entry of DDT and other pesticides, damages this smooth cycle of nutrient movement. Let’s check how:
DDT and Biomagnification
- DDT=dichloro-diphenyl trichloroethane.
- It is a “broad” spectrum pesticide (meaning it can kill variety of insects, not just one or two.)
- It lasts for a relatively long time (nearly 20 years) after one application.
- DDT is cheap to produce, been extensively used across world.
- Problem: DDT cannot be metabolized (digested) by any living organism.

- Suppose DDT was sprayed on water.
- There are millions of planktons in the water. Each of them absorbed 5ppm of DDT. Since they cannot digest DDT, it remains unprocessed in their body.
- A fish eats 8 such planktons, so it gets 8 x 5 =40 ppm of DDT in its body.
- A bird eats 50 such fishes, so bird gets 40 x 50 =2000 ppm of DDT in its body.
- So the amount of DDT keeps increasing as we move up in the food chain. This phenomenon is known as bio magnification.
- Bio magnification is bad because it produces variety of diseases in the species + its offsprings (babies) via teratogenesis.
- Teratogenesis = formation of defective embryo.
To sumup
- Biomagnification is a man-induced process.
- Biomagnification occurs with non-degradable chemicals/substances/pollutants only.
- For example Pesticides, anti-knocking agents used in internal combustion engines, paints, artificial perfumes etc.
- Biomagnification doesn’t occur with degradable chemicals/substances for example sugar, tea, cheese, milk etc. because they can be digested by (some) living organisms.
Biotic Potential.
- Unlimited food + ideal environmental conditions =a species can produce offspring @ maximum rate. This is known as Biotic potential.
- It can be high or low, depending on how many offspring (children) can a species produce in ideal conditions.
| Biotic potential | Example | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| High | Bacteria, insects, mice, rabbits | produce a large number of offspring in a short time. |
| low | larger species like elephants, tigers and humans | Gestation period is long. So they produce only a few offspring species during their lifetime, even if ideal food and environment conditions are given. |
Carrying Capacity
- It means the maximum population that an environment can support and sustain.
- When the carrying capacity is reached, birth rates equal death rates and the population should maintain a steady state equilibrium.
Interspecies relations
| Interaction | Species A | Species B | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Enjoys | Enjoys | Bees and flowers (pollination) |
|
Enjoys | Neutral | Orchid plant growing on a mango tree. |
|
Enjoys | Harmed | Tiger eating deer. |
|
Enjoys | Harmed | Tapeworm in human digestive tract. |
|
Harmed | Harmed | Jungle Deers vs domestic goats grazing in same area. |
|
Neutral | Harmed | bread mold Penicillium secretes penicillin and it destroys other bacteria. |
Btw, what’s the difference between
Predation vs Parasitism
Predation |
Parasitism |
| Tiger killing deer. | Tapeworm in human digestive tract. |
| done only for food. | Done for food + shelter. |
| Prey (deer) killed immediately | Host not killed immediately |
| Predator is (usually) big in size. | Smaller. |
| Predator’s biotic potential is usually very low. (tiger, lion etc.) | Parasite’s biotic potential is usually higher. |
Free Download IGNOU EnB Material
This article is based on the first four chapter of IGNOU’s Certificate course in Environmental Studies: Click me to download (Size 30MB)
You already have NIOS material on EnB. This IGNOU set has lot of overlapping with its coverage, but still a good read nonetheless.
Mock questions
[columnize]
Q1. Correct statements about Bio magnification
- It is a natural phenomenon occurring since stone-age.
- It is associated with biodegradable chemicals.
- Bio Magnification protects biodiversity.
- Only 1 and 2
- Only 2 and 3
- Only 1 and 3
- None.
Q2. Correct statements
In an ecosystem,
- The flow of energy is cyclic
- The flow of nutrients is unidirectional
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both
- None
Q3. Correct Statements about Trophic levels:
- Each step in a food chain is called a “Trophic level”.
- Carnivores always occupy trophic level 1 or 2.
- Herbivores always occupy trophic level 3 or above.
- Every species can be assigned a single unique trophic level.
- Only 1 and 2
- Only 1 and 3
- Only 1, 2 and 3
- Only 1
Q4. Which among the following is/are example(s) of bio magnification?
- Tiger kills a cow. A (Human) poacher poisons the corpse of cow. Tiger comes back and eats it. Tiger dies.
- A factory discharges untreated chemical affluent into a pond. A Man regularly eats fishes caught from the pond. Man gets cancer after some years.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both
- None
Q5. An ecosystem would collapse:
- If flow of energy is not unidirectional.
- If flow of nutrient is not cyclic.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both
- None
Q6. The usable energy decreases as we move up in the food chain. Which among the following explains this phenomenon?
- Newton’s third law of motion.
- Einstein’s law of general relativity.
- Second law of thermodynamics.
- None of above.
Q7. When an ecosystem has reached its carrying capacity It means.
- Birth rate = death rate
- Birth rate < death rate
- Birth rate > death rate
- Birth rate greater than or less than death rate
Q8. Which among the following is/are example(s) of commensalism?
- An orchid growing on a eucalyptus tree
- Tapeworm in the intestinal tract of a child.
- Plasmodium in Human blood.
- Bees drinking nectar of a flower.
- Only 2 and 3
- Only 1 and 4
- Only 1, 2 and 4
- Only 1
Q9. Correct statement:
- Biotic potential of tigers is higher than rabbits.
- Biotic potential of rabbits is higher than tigers.
- Both equal
- None of above.
Q10. If one species benefits by harming another species. It may be
- Parasitism
- Predation
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Either 1 or 2
- None.
[/columnize]

![[Environment] Mangrove Species Conocarpus banned in Gujarat & Telangana](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/edp-conocarpus-500x383.png)
![[Environment] Floating Solar Farms, Banni Grassland, Nairobi flies & more Weekly Mrunal Digest from Jul week1-2022 (WMD)](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/Floating-Solar-Farm-500x383.webp)
![[Environment WMD] Single use plastic ban, ESZ, Surya Nutan Cooker, & more from Jun week3-2022](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/single-use-plastic-main-500x383.jpg)
![[T25] UPSC Mock Round#43: Environment & Geography Practice Questions- Global Climate Risk Index 2020, Bog wetland and More](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/c-t25-taimur-500x383.jpg)
amzing inf
thanks sir.
1. d
2. d
3. d
4. c
5. c
6. c
7. a
8. b
9. b
10. c
*8. D
1.d
2.d
3.d
4.b
5.c
6.c
7.a
8.d
9.b
10.c
Plz correct me…if I m wrong..
D rite choice.
Thanks Mrunal…………….!!!!!
1. D
2. D
3. D
4. C
5. C
6. C
7. A
8. D
9. B
10. C
d,d,d,b,c,c,c,d,b,c
1. D
2. D
3. D
4. D
5. C
6. C
7. A
8. D
9. B
10. C
mrunal sirs wats answer for 4th question…only 2 or both??
I think its only 2, because this process starts with trophic level 1 or 2 and then gets magnified.
ur right
Option 2 in 4th question says “chemical effluent”. It doenot mention whether its biodegradable or not.
So I believe answer should be None..
Nitesh sir u r right…..chemicals may be biodegradable…..
I do not think so, cow is on 2nd level so its got magnified and also its dependent on the quantity of persistent in the the level which pass it on. So can be both.
Yup i misunderstood the case as it does not pass onto the next level by natural phenomena , its just human intervention. So cannot be a biological mag its just a special case.
Tiger death=no bio-magnification.
Untreated affluent= yes.
bio-magnification means increase in concentraion of substance involved in the foodchain,so i think the concentraion increases in tiger as compare to cow.
and thus answer is both please correct if am wrong.
Tiger death is not due to bio magnification but due to poison.
For that, tiger will need to eat many poisoned cows for many months.
1.d
2.d
3.d
4.b
5.c
6.c
7.a
8.d
9.b
10.c
I differ for the answers posted above.
4. b
5. b (Confusion)
8. d
Sir, please help us with correct answer key.
1. D
2. D
3. D
4. B
5. C
6. C
7. A
8. D
9. B
10.C
1.D
2.D
3.D
4.B
5.C
6.C
7.A
8.D
9.B
10.C
Almost all are correct.
mrunal can you plz explain me about share capital,authorized capital and issued capital?
today i read amended RRB’s act.in that act,the authorized capital of each RRB is 5cr and the issued capital is maximum 1cr
1.d
2.d.
3.d
4.b// In the first case only Tiger died of the poisoning, there ends the story. No further magnification
5.c
6.c
7.a
8.d
9.b
10.c
d
d
d
b
c
c
a
d
b
c
d d d c c c a d b c
mrunal sir ,,u hv mentiond about energy pyramid always upright but in ponds and lake it is up side down….how is it? can u xplian…thanks
upsc website is showing old notice in new, colorful letters.
why?????
dont know
It could be a reminder that notification will be out by Saturday.
Agree with you.
I guess- many aspirants must have been calling at UPSC office to enquire, so probably that’s why they highlighted the notice in red,big and bold letters :D, so that people do not bother them much.
Sir PRINT OUT IS NOT WORKING….. Please help…
Sir,
could you please write an article explaining demat accounts..
I read the term today in newspaper, regarding the sahara case, but could not ‘really’ understand the meaning, though i tried reading from wikipedia also.
go through this
https://mrunalmanage.wpcomstaging.com/2013/01/economy-sebi-sahara-ofcd-case-optionally-fully-convertible-debentures-meaning-explained.html
search in mrunal search b4 asking option.you will get answer there,.
Demat account-
When you purchase shares, you don’t get paper certificates, but those shares get electronically transferred to your demat account in the Depositary. Meaning your shares are not in physical paper (material) form but electronic format. De-materializied= De-mat. No fear of theft, misplacement, delay in transfer etc. Something like having a caller-tune in your mobile. You own the tune but don’t actually have to have it in your phone’s memory card.
not able to down lode the IGNOU material you provided for environment
Sir, the google docs download limit is getting exceeded for the IGNOU file download,the error displayed is [Sorry, you can’t view or download this file at this time.
Too many users have viewed or downloaded this file recently. Please try accessing the file again later. If the file you are trying to access is particularly large or is shared with many people, it may take up to 24 hours to be able to view or download the file. If you still can’t access a file after 24 hours, contact your domain administrator]
Kindly provide another link if possible. Thank You
try this download link:
http://files.secureserver.net/3s9Yz8T5rTkosv
sir,
can you provide total no of national parks and tiger reserves with name and states and year of establishment.
regards.
@srivastava,
He has already gave tiger reserves list in his tiger tourism article: https://mrunalmanage.wpcomstaging.com/enb
besides you can also find this sort of information easily on google search.
1. D
2. D
3. D
4. B
5. B
6. C
7. A
8. B
9. B
10. C
:-) =D
1 D
2 D
3 D
4 C
5 C
6 C
7 A
8 D
9 B
10C
if nutrient flow is cyclic does it imply it’s not uni-directional? I think nutrient flow follows enery flow except in last stage of decomposers making nutrient flow cyclic…thus nutrient flow is uni directional and cyclic(?)
thankyou.., sir.
Excellent article mate. Just one thing & sorry if I have understood it wrong or if i am making a wrong argument or even if i’m just being a brat!
In question 7 you ask
Carrying capacity means & people have answered with (a) death=birth.
But carrying capacity does not “means” this. It only means the amount of life/organisms that environment can support. Ex: Civic(car) carrying capacity=5 person=equilibrium
more than 5=unstable(may topple)
less than 5=under utilized
Now in order to maintain that delicate equilibrium, the death rate “should” be equal to birth rate, cause if the birth rate further increases, the ecology gets unstable, & if the death rate increases, then the resources are under utilized.
the upsc !@#$ use these minor details to catch the candidates
Agree with u. Saturation of carrying capacity by itself does not tweet the birth rate and death rates. If this were the case then the we would not have been worrying much about sustainability and population explosion. Anyways , salute to Mrunal for this wonderful peace . Keep up the gud work.
D
D
D
B
B
C
A
A
B
C….
PLEASE PROVIDE THE KEYS
1-d
2-d
3-d
4-b
5-c
6-c
7-a
8-d
9-b
10-c