- Instructions for UPSC Mains 2016 GS Paper-2
- GSM2-2016: Question paper in linear format incl. Hindi
- Observation / Analysis of GS Paper-2
- Toughness of the paper
- Relevance of Mrunal.org/ Bogus marketing propaganda
- GS2 Mains-Topicwise Questions since Syllabus change
- [Block-1] Polity
- [Block-2] Policies for sectors, services
- [Block-3] Governance & groups
- [Block-4] IR Diplomacy
Instructions for UPSC Mains 2016 GS Paper-2
- UPSC conducted general studies paper 1 of civil services mains examination on 5th December 2016
- Duration: 3 hours; Maximum Marks: 250
- Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions:
- There are TWENTY questions printed both in HINDI and in ENGLISH. Each Question carries 12.5 marks.
- All the questions too compulsory.
- Answers must be written in the medium authorized in the Admission Certificate which must be stated clearly on the cover of this Question-cum-Answer (QC4) Booklet in the space provided.
- No marks will be given for answers written in a medium other than the authorized one.
- Word limit in questions, wherever specified should be adhered to.
- Any page or portion of the page left blank in the Question-cum-Answer Booklet must be clearly struck off.
GSM2-2016: Question paper in linear format incl. Hindi
Answer all the questions in NOT MORE THAN 200 words each. Content is more important than its length. All questions carry equal marks.
- Discuss the essentials of the 69th Constitutional Amendment Act and anomalies, if any that have led to recent reported conflicts between the elected representatives and the institution of the Lieutenant Governor in the administration of Delhi. Do you think that this will give rise to a new trend in the functioning of the Indian federal politics?
69वे संविधानं संशोधन अधिनियम के उन अत्यावश्यक तत्वों और विषमताओं , यदि कोई हो, पर चर्चा कीजिए , जिन्होंने दिल्ली के प्रशासन में निर्वाचित प्रतिनिधियों और उप-राज्यपाल के बीच हाल में समाचारों में आये मतभेदों को पैदा कर दिया है | क्या आपके विचार में इससे भारतीय परिसंधीय राजनीती के प्रकार्यण में एक नई प्रवत्ति का उदय होगा ? - To what extent is Article 370 of the Indian Constitution, bearing marginal note “Temporary provision with respect to the State of Jammu and Kashmir”, temporary? Discuss the future prospects of this provision in the context of Indian polity.
भारतीय संविधान का अनुच्छेद 370, जिसके साथ हाशिया नोट “जम्मू- कश्मीर राज्य के सम्बन्ध में अस्थाई उपबंध ” लगा हुआ है , किस सीमा तक अस्थाई है ? भारतीय राज्य- व्यवस्था के सन्दर्भ में इस उपबंध की भावी सम्भावनाओ पर चर्चा कीजिए| - The Indian party system is passing through a phase of transition which looks to be full of contradictions and paradoxes.” Discuss.
“भारतीय राजनीतिक पार्टी प्रणाली परिवर्तन के ऐसे दौर से गुजर रही है , जो अंतरविरोधो और विरोधाभास से भरा प्रतीत होता है |”चर्चा कीजिए| - Exercise of CAC’s powers in relation to the accounts of the Union and the States is derived from Article 149 of the Indian Constitution. Discuss whether audit of the Government’s Policy implementation could amount to overstepping its own (CAG) jurisdiction.
संघ और राज्यों के लेखाओं के संबध में, नियंत्रक और महालेखापरीक्षक की शक्तिओं का प्रयोग भारतीय संविधान के अनुच्छेद 149 से व्युत्पन्न है |चर्चा कीजिए कि क्या सरकार की नीति कार्यान्वयन की लेखापरीक्षा करना अपने स्वयं (नियंत्रक और महालेखापरीक्षक) की अधिकारिता का अतिक्रमण करना होगा या कि नहीं | - Discuss each adjective attached to the word ‘Republic’ in the preamble. Are they defendable in the present circumstances stances?
‘उद्देशिका (प्रस्तावना) में शब्द ‘गणराज्य’ के साथ जुड़े प्रत्येक विशेषण पर चर्चा कीजिए| क्या वर्तमान परिस्थितियों में वे प्रतिरक्षणीय है ? - What was held in the Coelho case? In this context, can you say that judicial review is of key importance amongst the basic features of the Constitution?
कोहिलो केस में क्या अभिनिर्धारित किया गया था ? इस सन्दर्भ में, क्या आप कह सकते है की न्यायिक पुनर्विलोकन संविधान के बुनियादी अभिलक्षणों में प्रमुख महत्त्व का है ? - Did the Government of India Act, 1935 lay down a federal constitution? Discuss.
क्या भारत सरकार अधिनियम, 1935 ने एक परिसंघीय संविधान निर्धारित कर दिया था ? चर्चा कीजिए| - What is a quasi-judicial body? Explain with the help of concrete examples.
अर्ध-न्यायिक (न्यायिकवत) निकाय से क्या तात्पर्य है ? ठोस उदहारणों की सहायता से स्पष्ट कीजिए| - Professor Amartya Sen has advocated important reforms in the realms of primary education and primary health care. What are your suggestions to improve their status and performance?
प्रोफेसर अमृत्य सेन ने प्राथमिक शिक्षा तथा प्राथमिक स्वास्थ्य देखभाल के क्षेत्रो में महत्वपूर्ण सुधारों की वकालत की है | उनकी स्थिति और कार्य-निष्पादन में सुधार हेतु आपके क्या सुझाव है ? - “In the Indian governance system, the role of non-state actors has been only marginal.” Critically examine this statement.
” भारतीय शासकीय तंत्र में, गैर-राजकीय कर्ताओं की भूमिका सीमित ही रही है |” इस कथन का समालोचनात्मक परीक्षण कीजिए| - “Effectiveness of the goverment system at various levels and people’s participation in the governance system are inter-dependent.” Discuss their relationship with each other in context of India.
” विभिन्न स्तरों पर सरकारी तंत्र की प्रभाविता तथा शासकीय तंत्र में जन-सहभागिता अन्योन्याश्रित होती है |” भारत के सन्दर्भ में इनके बीच संबध पर चर्चा कीजिए| - In the integrity index of Transparency International, India stands very low. Discuss briefly the legal, political, economic, social and cultural factors that have caused the decline of public morality in India.
“ट्रांसपेरेंसी इंटरनेशनल ” के ईमानदारी सूचकांक में , भारत काफी नीचे के पायदान पर है | संक्षेप में उन विधिक, राजनीतिक , आर्थिक , सामाजिक तथा सांस्कृतिक कारकों पर चर्चा कीजिए, जिनके कारण भारत में सार्वजानिक नैतिकता का ह्रास हुआ है | - Has the Indian governmental system responded adequately to the demands of Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization started in 1991? What can the government do to be responsive to this important change?
क्या भारतीय सरकारी तंत्र ने 1991 में शुरू हुए उदारीकरण , निजीकरण और वैश्वीकरण की माँगो के प्रति पर्याप्त रूप से अनुक्रिया की है ? इस महत्त्वपूर्ण परिवर्तन के प्रति अनुक्रियाशील होने के लिए सरकार क्या कर सकती है ? - “Traditional bureaucratic structure and culture have hampered the process of socio-economic development in India.” Comment.
“पारंपरिक अधिकारीतंत्रीय संरचना और संस्कृति ने भारत में सामाजिक-आर्थिक विकास की प्रक्रिया में बाधा डाली है | ” टिप्पणी कीजिए| - Examine the main provisions of the National Child Policy and throw light on the status of its implementation.
भारतीय बाल नीति के प्रमुख प्रावधानो का परीक्षण कीजिए तथा इसके क्रियान्वयन की प्रस्थिति पर प्रकाश डालिए | - “Demographic Dividend in India will remain only theoretical unless our manpower becomes more educated, aware, skilled and creative.” What measures have been taken by the government to enhance the capacity of our population to be more productive and employable?
“भारत में जनानकिकीय लाभांश तब तक सैद्धांतिक ही बना रहेगा जब तक कि हमारी जनशक्ति अधिक शिक्षित, जागरूक , कुशल और सृजनशील नहीं हो जाती | ” सरकार नें हमे जनसंख्या को अधिक उत्पादानशील और रोजगार-योग्य बनने की क्षमता में वृद्धि के लिए कौन कौन से उपाय किये है ? - “The broader aims and objectives of WTO are to manage and promote international trade in the era of globalization. But the Doha round of negotiations seem doomed due to differences between the developed and the developing countries.” Discuss in the Indian perspective.
विश्व व्यापार संगठन (डब्लू.टी.ओं) के अधिक व्यापक लक्ष्य और उद्देश्य वैश्वीकरण के युग में अंतर-राष्ट्रीय व्यापार का प्रबंधन और प्रोन्नति करना है | परन्तु (संधि) वार्ताओं की दोहा परिधि म्रत्योंमुखी प्रतीत होती है , जिसका कारण विकसित और विकासशील देशो के बीच मतभेद है |” भारतीय परिपेक्ष में, इस पर चर्चा कीजिए| - Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario.
शीतयुद्धोत्तर अंतर-राष्ट्रीय परिद्रश्य के सन्दर्भ में, भारत की पूर्वोन्मुखी नीति के आर्थिक और सामरिक आयामों का मूल्यांकन कीजिए| - “Increasing cross-border terrorist attacks in India and growing interference in the internal affairs of several member-states by Pakistan are not conducive for the future of SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation).” Explain with suitable>
“भारत के बढ़ते हुए सीमापारीय आतंकी हमले और अनेक सदस्य-राज्यों के आंतरिक मामलों में पाकिस्तान द्वारा बढ़ता हुआ हस्तक्षेप सार्क (दक्षिणी एशियाई क्षेत्रीय सहयोग संगठन ) के भविष्य के लिए सहायक नहीं है | ” उपयुक्त उदहारण के साथ स्पष्ट कीजिए| - What are the aims and objectives of the McBride Commission of the UNESCO? What is India’s position on these?
यूनेस्को (संयुक्त राष्ट्र शैक्षिक, वैज्ञानिक एवं सांस्कृतिक संगठन ) के मैक्ब्राइड आयोग के लक्ष्य और उद्देश्य क्या क्या है ? इनमे भारत की क्या स्थिति है ?
Observations / Analysis of GS Paper-2

| 2013 to 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|
2015:
|
|
| 2015: UCC asked |
|
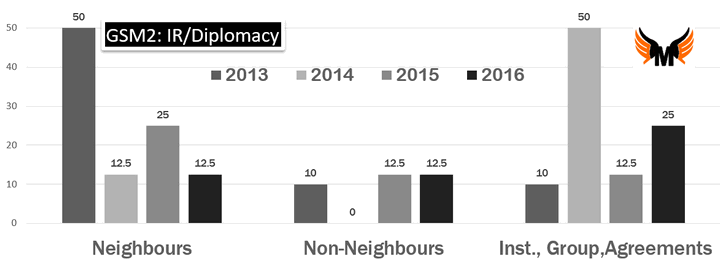
| 2013: federalism- 3 question | Repeat of the trend. 3 questions on federalism and this time from current issues- involving Delhi Lt. Governor and J&K’s Art.377. |
| Since 2013, each year one question always asked on separation of powers. | Continued the trend with Coelho Case. Albeit bit difficult than previous years questions on separation of powers. But overall theme remains the same i.e. “Supreme court” vs law making/ordinance making. |
| Each year, minimum two questions from “bodies” | Continued. |
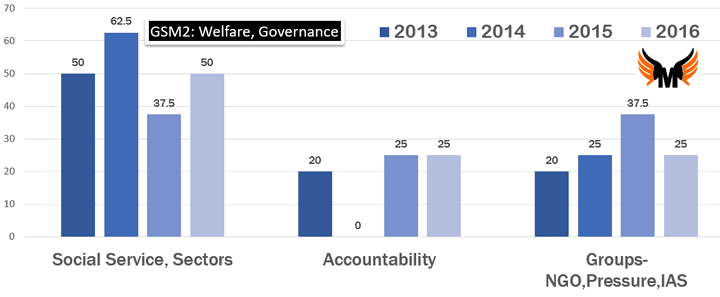
| Since 2013’s syllabus change, each year they’d ask exactly two questions from “social services”. | Examiner’s concern about social services has increased even further! 3 questions this time- Child policy, dem. Dividend and Amrtya Sen. |
| 2014: FDI in media channels. | 25th anniversary of BoP crisis. They did ask a question on LPG. |
| 2015: specific dimensions of transparency asked e.g. Satyam Scandal, Corporate governance, Whistleblower. | Broad question asked in the context of declining public morality in India. Although wording makes it more appropriate for GSM4 than for GSM2. |
| Last year’s analysis, I had talked about “exchange program” between syllabus topics of GS1, 2 and 3. | Same here- public morality (GSM4) and Act of 1935 (GSM1) are being asked in GSM2. |
| Since 2013, nothing from e-governance although it’s specifically mentioned in syllabus. | El-Nino Examiner induced Draught continues on E-governance topic. No question this year either. |
| First time asked specifically about “governance”, since the syllabus change in 2013. | |
| They’ve to ask some random low profile bill or court case or Constitutional amendment each year. | Continued – with Coelho case. |
|
|
Relevance of Last two Economic surveys:
|
Toughness of the paper
While there are some easy and directly from the book questions- such as Act of 1935 or quasi-judicial body. But overall, it is tough paper. And GSM2 has always been like that since inception of new syllabus in 2013.Let’s look at some of the question asked this time:
| Q | Comment |
|---|---|
| Adjectives to ‘republic’- can we defend? |
|
|
|
| Decay of public morality | Difficult to shift gear of brain into 4th gear (Ethics) while having spent previous night mugging up GSM1 and 2. If not difficult, at least time consuming. |
| Coelho case (2007): |
|
| McBride commission of UNESCO. |
|
- Anyways, no point in crying over spilled milk or criticizing UPSC examiner lest we also become theHindu columnists.
- But this type of papers are also a challenge in reaping India’s demographic dividend and internet bandwidth because youth has to spent precious time chasing/mugging up such feeble topics for next year’s preparation.
Difficult to come up with any reliable strategy.
- Because even in the topics where you definitely know something will be asked each year (such as separation of powers, bodies, social services)- the nature of questions remain such that in actual exam 1) unable to recall 2) lot of time spent brainstorming.
- So what to do then? …Ccontinue preparation in traditional fashion, keep reading and collecting points from Laxmikanth and other books, Economic survey and other reports, newspaper-columns to ensure there is enough ‘maal’ to beat around the bush whenever you don’t know the answer.
Relevance of Mrunal.org/ Bogus marketing propaganda

doesn’t matter if not much is asked in Paper-II, For my sins are already washed with urban floods
| Question | Covered | Credit claimed |
|---|---|---|
| Act of 1935 | HFS10P6 and P7 | 12.5 |
| Government’s responsiveness to LPG reforms | ML16-Rao | 12.5 |
| Primary health and education reforms | ML2/P3; ML3/P1 | 12.5 |
| Dem.dividend- what has Government done to make junta employable? | L5/P5; BES164/P4 | 12.5 |
| Bureaucracy as obstacle to socio-eco Development | ML5/P1 | 6-because not all aspects covered. |
| Total | 56 marks = 22% of the paper. |
As such, I had covered various Polity topics in this year’s revision series. Be it- referendum, direct mayor, refugees or Parliamentary Secretary- with hopes that something will come. But overall scene is हाथ आया पर मुंह न लगा...e.g. Delhi’s parliament Secretary not asked but Lt.Governor asked. Referendum not asked but Art.370 asked. A lesson in humility. Anyways, let’s see how events unfold in Paper-3 and 4 tomorrow.
GS2 Mains-Topicwise Questions since Syllabus change
In 2013, UPSC changed the syllabus-pattern of Mains examination and the number of general studies (GS) papers were increased from two to four. Out of them, GS Paper-2 deals with Polity, Governance, Welfare and International-Relations (IR)
| Category | GSM-2 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polity | Basic Str. | 10 | 12.5 | 37.5 | 12.5 |
| Polity | Executive | 10 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Polity | Legislature | 10 | 12.5 | 0 | 12.5 |
| Polity | Power Sep. | 10 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 |
| Polity | Fed-Local | 30 | 12.5 | 25 | 37.5 |
| Polity | Bodies | 20 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Welfare | Social Service, Sectors | 50 | 62.5 | 37.5 | 50 |
| Governance | Accountability | 20 | 0 | 25 | 25 |
| Governance | Groups-NGO,Pressure,IAS | 20 | 25 | 37.5 | 25 |
| IR | Neighbours | 50 | 12.5 | 25 | 12.5 |
| IR | Non-Neighbours | 10 | 0 | 12.5 | 12.5 |
| IR | Inst., Group,Agreements | 10 | 50 | 12.5 | 25 |
| Total | 250 | 250 | 250 | 250 |
[Block-1] Polity
Polity: Basics of Constitution
GS2 Syllabus Topic: Historical underpinnings & evolution; Features, amendments, significant provisions, basic structure; Comparison of Indian constitutional scheme with other countries’
| Discuss each adjective attached to the word ‘Republic’ in the preamble. Are they defendable in the present circumstances stances? | 2016 |
| Discuss the possible factors that inhibit India from enacting for its citizens a uniform civil code as provided for in the Directive Principles of State Policy. | 2015 |
| Khap Panchayats have been in the news for functioning as extra-constitutional authorities, often delivering pronouncements amounting to human rights violations. Discuss critically the actions taken by the legislative, executive and the judiciary to set the things right in this regard. | 2015 |
| Does the right to clean environment entail legal regulations on burning crackers during Diwali? Discuss in the light of Article 21 of the Indian Constitution and Judgement(s) of the Apex Court in this regard. | 2015 |
| What do you understand by the concept “freedom of speech and expression”? Does it cover hate speech also? Why do the films in India stand on a slightly different plane from other forms of expression? Discuss. | 2014 |
| Discuss Section 66A of IT Act, with reference to its alleged violation of Article 19 of the Constitution. | 2013 |
Polity: The Executive
GS2 Syllabus Topic:
- Executive (structure, organisation, functioning);
- Ministries and Departments (of Union and State govts.)
| Instances of President’s delay in commuting death sentences has come under public debate as denial of justice. Should there be a time limit specified for the President to accept/reject such petitions? Analyse. | 2014 |
| The size of the cabinet should be as big as governmental work justifies and as big as the Prime Minister can manage as a team. How far the efficacy of a government then is inversely related to the size of the cabinet? Discuss. | 2014 |
Polity: Legislature

GS2 Syllabus Topic:
- Union and State Legislatures (structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges; issues therein);
- Salient features of the Representation of People’s Act.
| The Indian party system is passing through a phase of transition which looks to be full of contradictions and paradoxes.” Discuss. | 2016 |
| The ‘Powers, Privileges and Immunities of Parliament and its Members’ as envisaged in Article 105 of the Constitution leave room for a large number of un-codified and un-enumerated privileges to continue. Assess the reasons for the absence of legal codification of the ‘parliamentary privileges’. How can this problem be addressed? | 2014 |
| The role of individual MPs (Members of Parliament) has diminished over the years and as a result healthy constructive debates on policy issues are not usually witnessed. How far can this be attributed to the anti-defection law, which was legislated but with a different intention? | 2013 |
Polity: Separation of Powers
GS2 Syllabus Topic:
- Separation of Powers (between different organs, dispute redressal mechanisms, institutions);
- Judiciary (structure, organisation functioning)
| What was held in the Coelho case? In this context, can you say that judicial review is of key importance amongst the basic features of the Constitution? | 2016 |
| Resorting to ordinances has always raised concern on violation of the spirit of separation of powers doctrine. While noting the rationales justifying the power to promulgate ordinances, analyze whether the decisions of the Supreme Court on the issue have further facilitated resorting to this power. Should the power to promulgate ordinances be repealed? | 2015 |
| Starting from inventing the ‘basic structure’ doctrine, the judiciary has played a highly proactive role in ensuring that India develops into a thriving democracy. In light of the statement, evaluate the role played by judicial activism in achieving the ideals of democracy. | 2014 |
| The Supreme Court of India keeps a check on arbitrary power of the Parliament in amending the Constitution. Discuss critically. | 2013 |
Polity: Federalism & Local governance
GS2 Syllabus Topic:
- Functions & responsibilities of the Union and the States; issues and challenges of federal structure;
- Devolution of powers and finances to local levels; challenges therein.
| Discuss the essentials of the 69th Constitutional Amendment Act and anomalies, if any that have led to recent reported conflicts between the elected representatives and the institution of the Lieutenant Governor in the administration of Delhi. Do you think that this will give rise to a new trend in the functioning of the Indian federal politics? | 2016 |
| To what extent is Article 370 of the Indian Constitution, bearing marginal note “Temporary provision with respect to the State of Jammu and Kashmir”, temporary? Discuss the future prospects of this provision in the context of Indian polity. | 2016 |
| Did the Government of India Act, 1935 lay down a federal constitution? Discuss. | 2016 |
| The concept of cooperative federalism has been increasingly emphasized in recent years. Highlight the drawbacks in the existing structure and the extent to which cooperative federalism would answer the shortcomings. | 2015 |
| In absence of a well-educated and organized local level government system, `Panchayats’ and ‘Samitis’ have remained mainly political institutions and not effective instruments of governance. Critically discuss. | 2015 |
| Though the federal principle is dominant in our Constitution and that principle is one of its basic features, but it is equally true that federalism under the Indian Constitution leans in favour of a strong Centre, a feature that militates against the concept of strong federalism. Discuss. | 2014 |
| Recent directives from Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas are perceived by the `Nagas’ as a threat to override the exceptional status enjoyed by the State. Discuss in light of Article 371A of the Indian Constitution. | 2013 |
| Many State Governments further bifurcate geographical administrative areas like Districts and Talukas for better governance. In light of the above, can it also be justified that more number of smaller States would bring in effective governance at State level? Discuss. | 2013 |
| Constitutional mechanisms to resolve the inter-state water disputes have failed to address and solve the problems. Is the failure due to structural or process inadequacy or both? Discuss. | 2013 |
Polity: Bodies
GS2 Syllabus Topic: Appointment to various Constitutional posts; Constitutional Bodies (powers, functions and responsibilities); Statutory, Regulatory and Quasi-judicial bodies
| Exercise of CAC’s powers in relation to the accounts of the Union and the States is derived from Article 149 of the Indian Constitution. Discuss whether audit of the Government’s Policy implementation could amount to overstepping its own (CAG) jurisdiction. | 2016 |
| What is a quasi-judicial body? Explain with the help of concrete examples. | 2016 |
| What are the major changes brought in the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 through the recent Ordinance promulgated by the President? How far will it improve India’s dispute resolution mechanism? Discuss. | 2015 |
| “For achieving the desired objectives, it is necessary to ensure that the regulatory institutions remain independent and autonomous.” Discuss in the light of the experiences in recent past. | 2015 |
| National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) in India can be most effective when its tasks are adequately supported by other mechanisms that ensure the accountability of a government. In light of the above observation assess the role of NHRC as an effective complement to the judiciary and other institutions in promoting and protecting human rights standards. | 2014 |
| The setting up of a Rail Tariff Authority to regulate fares will subject the cash strapped Indian Railways to demand subsidy for obligation to operate non-profitable> | 2014 |
| Discuss the recommendations of the 13th Finance Commission which have been a departure from the previous commissions for strengthening the local government finances. | 2013 |
| The product diversification of financial institutions and insurance companies, resulting in overlapping of products and services strengthens the case for the merger of the two regulatory agencies, namely SEBI and IRDA. Justify. | 2013 |
[Block-2] Policies for sectors, services
Welfare: Policies & Schemes
GS2 Syllabus Topic:
- Welfare Schemes (centre, states; performance, mechanisms, laws, institutions and bodies constituted for protection of vulnerable sections);
- Poverty and hunger issues
| Though there have been several different estimates of poverty in India, all indicate reduction in poverty levels over time. Do you agree? Critically examine with reference to urban and rural poverty indicators. | 2015 |
| Do government’s schemes for up-lifting vulnerable and backward communities by protecting required social resources for them, lead to their exclusion in establishing businesses in urban economics? | 2014 |
| Two parallel run schemes of the Government viz. the Adhaar Card and NPR, one as voluntary and the other as compulsory, have led to debates at national levels and also litigations. On merits, discuss whether or not both schemes need run concurrently. Analyse the potential of the schemes to achieve developmental benefits and equitable> | 2014 |
| The Central Government frequently complains on the poor performance of the State Governments in eradicating suffering of the vulnerable sections of the society. Restructuring of Centrally sponsored schemes across the sectors for ameliorating the cause of vulnerable sections of population aims at providing flexibility to the States in better implementation. Critically evaluate. | 2013 |
| Electronic cash transfer system for the welfare schemes is an ambitious project to minimize corruption, eliminate wastage and facilitate reforms. Comment. | 2013 |
| The basis of providing urban amenities in rural areas (PURA) is rooted in establishing connectivity. Comment. | 2013 |
Welfare: Social Services: Health, Edu, HRD
GS2 Syllabus Topic: Social Sector & Social Services (health, education, human resources – issues in development, management);
| Professor Amartya Sen has advocated important reforms in the realms of primary education and primary health care. What are your suggestions to improve their status and performance? | 2016 |
| Examine the main provisions of the National Child Policy and throw light on the status of its implementation. | 2016 |
| “Demographic Dividend in India will remain only theoretical unless our manpower becomes more educated, aware, skilled and creative.” What measures have been taken by the government to enhance the capacity of our population to be more productive and employable? | 2016 |
| The quality of higher education in India requires major improvements to make it internationally competitive. Do you think that the entry of foreign educational institutions would help improve the quality of higher and technical education in the country? Discuss. | 2015 |
| Public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that the private sector could help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives would you suggest? | 2015 |
| An athlete participates in Olympics for personal triumph and nation’s glory; victors are showered with cash incentives by various agencies, on their return. Discuss the merit of state sponsored talent hunt and its cultivation as against the rationale of a reward mechanism as encouragement. | 2014 |
| Should the premier institutes like IITs/IIMs be allowed to retain premier status, allowed more academic independence in designing courses and also decide mode/criteria of selection of students. Discuss in light of the growing challenges. | 2014 |
| The concept of Mid Day Meal (MDM) scheme is almost a century old in India with early beginnings in Madras Presidency in pre-independent India. The scheme has again been given impetus in most states in the last two decades. Critically examine its twin objectives, latest mandates and success. | 2013 |
| Identify the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) that are related to health. Discuss the success of the actions taken by the Government for achieving the same. | 2013 |
Welfare: Sectoral Policies
GS2 Syllabus Topic: Government Policies & Interventions for development of various sectors (issues in their design, implementation)
| Has the Indian governmental system responded adequately to the demands of Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization started in 1991? What can the government do to be responsive to this important change? | 2016 |
| Though 100 percent FDI is already allowed in non-news media like a trade publication and general entertainment channel, the Government is mulling over the proposal for increased FDI in news media for quite some time. What difference would an increase in FDI make? Critically evaluate the pros and cons. | 2014 |
[Block-3] Governance & groups
Governance: Accountability & E-Gov
- GS2 Syllabus Topic: Important aspects of governance; Transaparency and accountability (institutional and other measures); Citizens Charter;
- GS2 Syllabus Topic: E-Governance (applications, models, successes, limitations, potential)
| “Effectiveness of the goverment system at various levels and people’s participation in the governance system are inter-dependent.” Discuss their relationship with each other in context of India. | 2016 |
| In the integrity index of Transparency International, India stands very low. Discuss briefly the legal, political, economic, social and cultural factors that have caused the decline of public morality in India. | 2016 |
| In the light of the Satyam Scandal (2009), discuss the changes brought in corporate governance to ensure transparency, accountability. | 2015 |
| “If amendment bill to the Whistleblowers Act, 2011 table> | 2015 |
| Though Citizen’s charters have been formulated by many public service delivery organizations, there is no corresponding improvement in the level of citizens’ satisfaction and quality of services being provided. Analyze. | 2013 |
| ‘A national Lokpal, however strong it may be, cannot resolve the problems of immorality in public affairs’. Discuss. | 2013 |
Groups: Civil Services, NGO, SHG, Pressure Groups
GS2 Syllabus Topic:
- Development Processes & Development industry (role of NGOs, SHGs, groups & associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders)
- Pressure Groups & Formal, Informal associations (and their role in the polity)
- Role of Civil Services in a democracy.
| NGO-SHG | Examine critically the recent changes in the rules governing foreign funding of NGOs under the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 1976. | 2015 |
| NGO-SHG | The Self-Help Group (SHG) Bank Linkage Programme (SBLP), which is India’s own innovation, has proved to be one of the most effective poverty alleviation and women empowerment programmes. Elucidate. | 2015 |
| NGO-SHG | How can the role of NGOs be strengthened in India for development works relating to protection of the environment? Discuss throwing light on the major constraints. | 2015 |
| NGO-SHG | The penetration of Self Help Groups (SHGs) in rural areas in promoting participation in development programmes is facing socio-cultural hurdles. Examine. | 2014 |
| NGO-SHG | The legitimacy and accountability of Self Help Groups (SHGs) and their patrons, the micro-finance outfits, need systematic assessment and scrutiny for the sustained success of the concept. Discuss. | 2013 |
| Pressure Group | Pressure group politics is sometimes seen as the informal face of politics. With regards to the above, assess the structure and functioning of pressure groups in India. | 2013 |
| Pressure group | “In the Indian governance system, the role of non-state actors has been only marginal.” Critically examine this statement. | 2016 |
| Civil Services | Has the Cadre based Civil Services Organisation been the cause of slow change in India? Critically examine. | 2014 |
| Civil Services | “Traditional bureaucratic structure and culture have hampered the process of socio-economic development in India.” Comment. | 2016 |
[Block-4] IR Diplomacy
IR/Diplomacy: Neighbors
GS2 Syllabus Topic: Effect of Policies & Politics of Developed and Developing countries on India (India’s interests, diaspora)
| “Increasing cross-border terrorist attacks in India and growing interference in the internal affairs of several member-states by Pakistan are not conducive for the future of SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation).” Explain with suitable> | 2016 |
| Project `Mausam’ is considered a unique foreign policy initiative of the Indian Government to improve relationship with its neighbors. Does the project have a strategic dimension? Discuss. | 2015 |
| Terrorist activities and mutual distrust have clouded India-Pakistan relations. To what extent the use of soft power like sports and cultural exchanges could help generate goodwill between the two countries? Discuss with suitable> | 2015 |
| With respect to the South China sea, maritime territorial disputes and rising tension affirm the need for safeguarding maritime security to ensure freedom of navigation and over flight throughout the region. In this context, discuss the bilateral issues between India and China. | 2014 |
| The proposed withdrawal of International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) from Afghanistan in 2014 is fraught with major security implications for the countries of the region. Examine in light of the fact that India is faced with a plethora of challenges and needs to safeguard its own strategic interests. | 2013 |
| What do you understand by ‘The String of Pearls’? How does it impact India? Briefly outline the steps taken by India to counter this. | 2013 |
| The protests in Shahbag Square in Dhaka in Bangladesh reveal a fundamental split in society between the nationalists and Islamic forces. What is its significance for India? | 2013 |
| Discuss the political developments in Maldives in the last two years. Should they be of any cause of concern to India? | 2013 |
| In respect of India — Sri Lanka relations, discuss how domestic factors influence foreign policy. | 2013 |
| What is meant by Gujral doctrine? Does it have any relevance today? Discuss. | 2013 |
IR/Diplomacy: Not-Neighbors but affecting interests
GS2 Syllabus Topic: India and its Neighbourhood (relations)
| Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. | 2016 |
| Increasing interest of India in Africa has its pros and cons. Critically examine. | 2015 |
| Economic ties between India and Japan while growing in the recent years are still far below their potential. Elucidate the policy constraints which are inhibiting this growth. | 2013 |
IR/Diplomacy: Institutions, Groupings, Agreements
GS2 Syllabus Topic: Important International institutions, agencies, for a (structure, mandate); Bilateral, Regional, Global groupings & Agreements (involving and/or affecting India)
| “The broader aims and objectives of WTO are to manage and promote international trade in the era of globalization. But the Doha round of negotiations seem doomed due to differences between the developed and the developing countries.” Discuss in the Indian perspective. | 2016 |
| What are the aims and objectives of the McBride Commission of the UNESCO? What is India’s position on these? | 2016 |
| Discuss the impediments India is facing in its pursuit of a permanent seat in UN Security Council. | 2015 |
| The aim of Information Technology Agreements (ITAs) is to lower all taxes and tariffs on information technology products by signatories to zero. What impact should such agreements have on India’s interests? | 2014 |
| Some of the International funding agencies have special terms for economic participation stipulating a substantial component of the aid to be used for sourcing equipment from the leading countries. Discuss on merits of such terms and if, there exists a strong case not to accept such conditions in the Indian context. | 2014 |
| India has recently signed to become founding a New Development Bank (NDB) and also the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) .How will the role of the two Banks be different? Discuss the significance of these two Banks for India. | 2014 |
| WTO is an important international institution where decisions taken affect countries in profound manner. What is the mandate of WTO and how binding are their decisions? Critically analyse India’s stand on the latest round of talks on Food security. | 2014 |
| The World Bank and the IMF, collectively known as the Bretton Woods Institutions, are the two inter-governmental pillars supporting the structure of the world’s economic and financial order. Superficially, the World Bank and the IMF exhibit many common characteristics, yet their role, functions and mandate are distinctly different. Elucidate. | 2013 |


![[Download] Topicwise UPSC GSM2-2023 Paper- polity, Governance international relations in Hindi and English with topic wise analysis](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/ana-gsm2-2023-mrunal79-500x383.png)
Aur sab to theek hai but Mrunal bhai ka logo dekha ? :P
thanks sir hindi k liye
Indepth analysis and excellent comparison…
thank you Mrunal…
Difficult paper….3-4 questions were completely out of my expectations…..
Thanks
Gs 3…..easy and scorable this year……expecting 100+….same as Gs 1……
“Difficult to shift gear of brain into 4th gear (Ethics) while having spent previous night mugging up GSM1 and 2.” Lol so true!
Thanks mrunal bhai, jaldi GS3 and gs4 ke analysis kardo bhai iam waiting :)
Sir! Logo zabardast hai.
as usual upsc issue …. surprisingly ..something unexpected… old topic … kaha kaha dhyan dena man .. ridiculous . mrunal sir thanks a tonne \,,/
thanks a lot to providing paper very soon
Good evening sir how to start as a last year graduate student and a starter for IAS preparation s??
thanks….
IR Coehlo case asked..why?
Justice SH Kapadia was one of the judge in the nine judge bench..he was CJI, appointed 2010..he died this year..so upsc waalin ne dhunda ik famous case unse related..:p
Transparency international has Corruption Perceptions Index and not Integrity Index. What did they do copy paste from google translate [Hindi-English]
Very helpful information……very short and concised
thanks
Sir coelho case ki jankari dejiye please
Hi Sir,
Thanks a lot for In-depth Analysis for mains Paper..
THANKS ALOT MRUNAL !
Plz sir mains ke 2016 ke sare question paper send kr do Meri id p taki mujhe help mil ske bt all questions paper Hindi midium ke ho plz send me