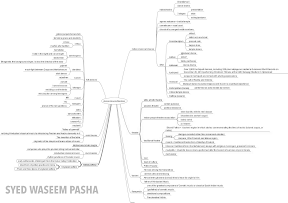
This is a note cum mindmap on Indian Art Architecture is shared by a regular reader who wishes to remain anonymous. If you want to contribute any more data in this topic, please share it in comments!
- Gandhara Art
- Rajput painting
- Saranatha pillar
- Gopurum
- Vijayanagara art
- Bundi School Of Painting
- Sunga art
- Kangra school of painting
- Manjusha Art
- Madhubani Art
- Kishangarh school of painting
- Rock-cut temple
- Mathura school of art
- Chola architecture
- Kulu School
- Chaitya
- nagara style of architecture
- Chandella School Of Arch
- Dravadian Architecture
- Mughal painting
- Mughal Architecture
- Effect Of Islamic Rulers on India Architecture
- HINDUSTAN MUSIC
- Carnatic music
- Ahmadiya movement
- Mindmap
Gandhara Art
Greco-Buddhist art
- the hand of a Greek but the head and heart of an Indian.
- the basic urge, imagery and iconography remained Indian
- north-west
- west-asia settled here
- lotus throne
- central Asian fashion
Rajput painting
- depict a number of themes, events of epics like the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, Krishna’s life
- but many paintings were done on the walls of palaces, inner chambers of the forts,
- colours were extracted from certain minerals, plant sources, conch shells, and were even derived by processing precious stones
- emerged from Persian miniature painting
Saranatha pillar
- lion capital = national emblem
- four lions are seated back to back
- UP:
- column = same place
- lion capital = sarnatha museum
- @ ashoka column
- ashoka chakra = indian flag
Gopurum
- monumental tower, entrance, southern india
- pallavas
- shrine has more than one
- tamil meaning = king and exterior
- urban nodes and focal points
Vijayanagara art
- religious, courtly and civic
- comb = hoysala, pandya, chola
- granite, sandstone and plaster
Bundi School Of Painting

- major cultural hub in the city of Bundi, Rajasthan
- Mewar School, the School of Painting
- uman figures have a unique expression
- red-brown color
Sunga art

- stupas at sanchi
- expansion of mathura school
- sculpture not in bold relief
- male/female large ornaments
- no emotions
- eyeballas conspicuous
Kangra school of painting

- Kangra, Himachal Pradesh
- @ Pahari painting school
- greenery
- naturalistic
- plants and creepers, leafless trees
- colors made of vegetable and mineral extract
Manjusha Art
- Manjushas are temple-shaped boxes
- ade of bamboo,jute and paper
- Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and Tarai area of the Nepal
- Manjusha Art is one of the very old and historically very important Art
Madhubani Art
- Mithila painting
- region of Bihar state
- using natural dyes and pigment
- paintings for each occasion and festival such as birth, marriage, holi
- aditionally by the women of villages
- paste of powdered rice
- mostly depict nature and Hindu religious motifs
Kishangarh school of painting

- elongation of human faces
- Portrayal of Radha and Krishna
- Bani Thani.
- labeled as India’s “Mona Lisa”
Rock-cut temple
- mostly religious in nature
- When Buddhist missionaries arrived they naturally gravitated to caves
- suited to their natural inclinations
- A rock cut temple is carved from a large rock and excavated and cut
- ellora, kailash
Mathura school of art
- ancient
- kushanas
- city of mathura
- hinduism, jainism and buddhism
- first Buddha images
- Sarnath, Sravasti Rajgir
- school excelled in Yaksha (Male)
- lion throne Indian dresses
Chola architecture

- tamil dynasty
- famous for tamil lit + art and archi
- Pallava style
- sanctum = square + circular
- stone and metal scrip
- gopurams
Kulu School

- style of painting
- is one of the prominent examples of centres of pahari school of painting in india.
Chaitya
- buddhist or jain shrine including a stupa
- holding devotees
- providing shelter
- roman = column + arch
- ajanta, ellora
Nagara style of architecture

- hindu temple archi
- elevation convex curve
- plan square shape
- projections of plan are carried to top
Chandella School Of Arch
- diff from other dynasties
- contemporary : khajuraho temple and lakes
Dravadian Architecture
- southern part
- developed for about 10 centuries
- Chola domination was the golden age for Dravidian Architecture
- Northeastern Sri Lanka, Maldives, and various parts of Southeast Asia
- Vimanam, Mandapams,Gopurams
Mughal painting
- emerged from Persian miniature painting
- blending of Persian and Indian ideas
- greater interest in realistic portraiture
- Animals and plants were also more realistically shown
Mughal Architecture
- at fatehpur sikri synthesis of various regional schools of architectural
- islamic, hindu and jain
- Sikri sandstone
- Buland Darwaza, jama masjid, Tomb of Salim Chishti, panch mahal
Effect Of Islamic Rulers on India Architecture
- use of shapes (instead of natural forms)
- decorative lettering or calligraphy
- inlay decoration and use of coloured marble
- all spaces were spanned by means of horizontal beams
- concept of arch or dome was not invented by the Muslims
- borrowed architectural styles of the post-Roman period
- put to use certain scientific and mechanical formulae
- were typical mortar-masonry works formed of dressed stones
- religious=Mosques and Tombs
- secular=palaces and forts
- masjid
- open courtyard surrounded by a pillared verandah
- crowned off with a dome
- mihrab indicates the direction of the qibla for prayer
- tomb
- maqbara = maqbara refers to the graves of all Muslims, it refers especially to the graves (Raula or Rauza) of religious figures or Waliyullahs who dedicated their life to Islam
- qabr = normal muslim person
- dargah = In Asian countries, maqbara also refers to the Dargah of Waliyullahs, Sufis, Sheikhs, Imams
- three sections
- delhi or imperial
- provincial
- jaunpur
- deccan
- mughal
Ahmadiya movement
- Islamic reformist
- Mirza Ghulam Ahmad
- view themselves as leading the revival and peaceful propagation of Islam
- earliest Muslim communities to arrive in Britain and other Western countries
- Most mainstream Muslims consider both Ahmadi movements to be non-Muslim and heretical
Mindmap
This mindmap is contributed by Syed Waseem Pasha. click on following image
another mindmap
Click ME To see the mindmap of this article (created by software Freemind)

![[Laws] DESI liquor special edition Kerala, Mizoram & IPS Training, Tribal insurgency](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/Cover_Polity_kerala-liquor-500x383.gif)
![[Economic Survey] Corrections in the previous articles + Parting words before Qatl ki Subha](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Cover-Economic-Survey-correction-500x383.jpg)
a well compiled collection!thanks a lot to the anonymous contributor!
i am not able to download these material . some pls help me
Thanks a lot Mrunal Sir. You are doing a very great job for young aspirants. Thanks a lot.
tons of thanx to the 1 who contributed it….i have not done culture a word more than what mrunal has taught……so thanx mrunal for not letting me skip over the culture part
thanks to the anonymous friend
thanku sir
Everyone heard about Mahabharata,where Arjuna wishes Lord Krishna to be with him before going to war…Hope Every aspirant is Indeed Indebted to Mrunal..
Indeed!
It is quite a good one.
thnx sir it’s a good collection of indian art nd culture ….
Sir,
Please provide the details about various working committees and their focus areas m
Thanks
thanks,sir!! ur material is really a gemstone…
nice one
Ur blog is very informative and useful for preparing general Studies
Thank you very much
Great job..Mr.Mrunal
Keep going
thanks a lot to mrunal sir,anonymous contributor and everyone contributing.creating true value of internet.
You are doing a wonderful job sir……..@@
Very very helpful…..!!
A heartiest thanks……..@@
@ngii__
The most incomplete topic covered on Mrunal’s site
Very good work , thank u .
sir will you be posting some more of the environment related current affairs before prelims?
Your articles make revising the concepts damn easy and efficient. Or else i ll have to do it myself, pls do tell as i ll plan accordingly.
Hi Mrunal, Can you also provide a space in ur blog where v cn hv kinds of questions asked from Indian culture in past and various kinds of question from each of the topics (on the lines we need to prepare sort of)
Thank you so much in providing such information under one roof. It is very beneficial for me. Hope every body would like it.
In Dravidian architecture, there are 2 terms called gopuram and vimanam. gopuram means entrance tower. vimanam means its tower over sanctum. in pandya architecture always gopuram height is > than vimanam eg, meenakshi temple – madurai. In chola always vimanam hieght is greater than gopuram. eg brihadiswar temple tanjore. a small note that i know
ThNks Karthikeyan for the info.. it was helpful..
thank u so much it is very helpful and in simplified manner.