- Roads
- Shipping
- Major ports: East vs West
- National Automatic Identification System (AIS)
- Transchart
- Vallarpadam
- Sethusamudram project
- Adam’s Bridge / Ram Sethu
- Maritime agenda 2020
- Shipping: Challenges
- Inland Water transport authority of India
- Kaladan Multimodal Transport Project
- Indian waterways: challenges
- 12th FYP: Inland Water Transport
- Aviation
- Mock Questions
Roads
Name |
Responsibility of |
Connect |
| National Highways | Central Government | State capitals |
| State highways | State Government | State Capital to District HQ |
| district roads | Zila Parishad | District HQ to tehsil and Blocks |
| village roads | Gram Panchayat | Villages to neighboring towns |
- in terms of total road length (bigger to smaller): Other roads >> State highways >> National highways / expressways
- within national highways, in terms of total road length: (bigger to smaller)= Double lane >>(4/6/8 lane) >>Single lane
- National highways comprises only 2.0 per cent of the road network but carry 40 per cent of the road-based traffic.
Width of National highways
- in case of single lane highway: 3.75 meter
- in case of multilane highway: 3.5 meter per lane.
Org 4 highway construction
done by three organizations
- National highways authority of India (NHAI)
- State Public Works Department (PWD)
- Border roads Organization (BRO)
Where does NHDP get money?
- Budgetary Support
- A part of cess (under Central Road Fund) is allocated to National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) to fund the NHDP
- External Assistance through World Bank, ADB, JBIC, and so on.
- Public Private Partnership(PPP)
- Market Borrowings by NHAI
BRO
started operation in the 60s, we just two projects
- East: Project Tusker (renamed into project Vartak)
- West: Project Beacon
- BRO also developed roads abroad, eg Delaram Zaranj road in Afghanistan, and highways in Bhutan, Myanmar.
Central Road Fund
- Under the Act of 2000
- Money comes from Rs.2 per liter as cess on petrol and High speed Diesel. (additional excise duty)
- Money thus collected, first goes to the Consolidated Fund of India
- from there, Central Government allocates money to Central Road Fund (CRF) from time to time, after deducting the expenses of collection.
- Money is used to develop and maintain national, state and village roads + railway overbridges, underbridges and other safety measures
Bharat Nirman
Has 6 components for basic rural infrastructure and one of them is roads.
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY)
- Launched in 2000
- National rural roads Development agency under Rural Development ministry looks after this. (and not NHAI under highways ministry)
- programme seeks to connect all habitations
| With population of ___ (as per 2001 census) | In |
| 500 and above | Plain areas |
| 250 and above |
|
12th FYP: Road Transport
Highways
- Golden Quadrilateral and North–South and East–West corridors will be finished.
- Development of road corridors in Delhi– Mumbai industrial corridor project
- National and State Highways would be upgraded to minimum two lane standard by the end of the Plan.
- development of 15600 km of express-ways would be developed
- The National Highways had added 10000 km in the Eleventh Plan. Another 10000 kms will be added during the Twelfth Plan so that the total length of the highways becomes 91200 km.
Port connectivity
- special links for feeder roads to important railway routes and ports. This is essential for development of domestic and international trade.
- road connectivity for about 50 minor ports
- road connectivity for 24 Airports
Rural areas
- All villages will be connected with all-weather roads by the end of the Plan.
Naxal areas
- Roads in Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) affected districts will be continued and works taken up earlier in the Eleventh Plan be completed during the Plan.
- Special Package for development of roads in the Schedule Areas (under Fifth Schedule) under Tribal Sub-Plan—1000 km.
JK and North East
- Road Development in the North-East: Trans-Arunachal Pradesh Highway.
- The capacities of NHAI and BRO would be further developed for this purpose.
- State roads in the State of J&K from strategic considerations
Misc
- Reforms in Motor Vehicles Act to simplify inter-State movement with simplified procedures.
- Creation of truck terminals to ease traffic congestion
Electronic Toll Collection (ETC)
- Committee was set up under the Chairmanship of Shri Nandan Nilekani
- Recommendations of the Committee have been accepted and notified by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways for the use of National Highways.
- pilot project on ETC was inaugurated in 2012 on a section of NH-5 between Delhi and Parwanoo.
- second pilot project on the Mumbai and Ahmedabad
NATRIP
- The National Automotive Testing and R&D Infrastructure Project (NATRiP)
- under Department of Heavy Industry (with representatives from automobile sector)
- to set up testing, validation and R&D infrastructure across seven locations in India.
SARDP-NE
- Special accelerated road Development program for North Eastern Region
- For improving road connectivity between State Capitals and District HQs in North Eastern Region.
Shipping
- 100% FDI is allowed in shipping sector
- India’s coastline: 7517 km
- 9 Maritime states (5 in Western coast and 4 in Eastern Coast)
- 13 major ports (guided by Central Government) and 200 non-major (minor) ports (guided by respective State governments)
Major ports: East vs West
| West | East | ||
| name | state | Name | state |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Anadaman Nicobar | ||
- Older books would say 12 major ports but in 2010, Port Blair was added as the 13th major port.
Important org. under Shipping ministry
| Director General of Shipping |
|
| Director General of light houses and light ships | To Help vessels to safely navigate in in Indian coastal waters. |
| Shipping Corporation of India | Navaratna PSU |
International Maritime Organization (IMO)= specialized agencies of UN, HQ: London.
National Automatic Identification System (AIS)
- To provide information about the ship to other ships and to navy, coast guard etc. automatically.
- This information includes the ship’s identity, type, position, course, speed, navigational status.
- Prevents collision, helps in search and rescue operations and coastal surveillance.
- Contract given to Swedish defense company “Saab”- they fitted systems on Indian lighthouses for AIS tracking.
- Data will be used by directorate general of lighthouses and lightships (DGLL), the Navy, Coast Guard and DG Shipping.
Transchart
- It is the centralized ship chartering wing of the shipping ministry.
- to make shipping arrangements for Government Controlled cargoes
Vallarpadam
- India’s first dedicated international container transshipment terminal setup here.
- This project reduces our dependence on foreign ports for transshipment of India’s export-import containers.
Sethusamudram project
- Sethu Samudram is the sea that separates Tamil Nadu, India from Sri Lanka.
- It encompasses the Gulf of Mannar, the Palk Strait, and Adam’s Bridge(Ram Sethu).
- Sethusamudran Project will create a shipping canal linking the Palk Bay and the Gulf of Mannar between India and Sri Lanka. This will reduce the time (and fuel) for ships navigating through the region.
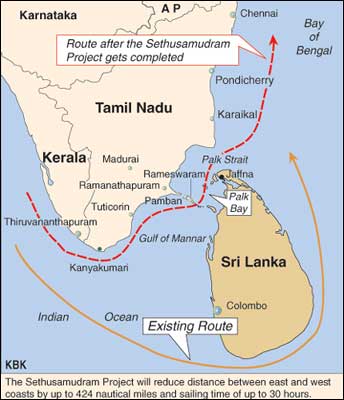
Adam’s Bridge / Ram Sethu
- It is a discontinuous chain of sandbars and corelreefs between
- Rameswaram island (India) and
- Talaimannar (Sri lanka)
- Sethusamudram project aims to dredge the shallow ocean region here and create an artificial passage for ships.
Anti Agruments
- R.K. Pachauri Committee (appointed by PM) said entire Sethusamudram project is unviable: from both economic and ecological point of view. Yet central Government adamant to launch it
In Supreme Court, TN Government said it was against this project because
- The project is a serious threat to the biodiversity of the region and will affect the livelihood of the fishermen.
- + sensitive religious sentiments of the people of the country, given that Ram Sethu said to have been built by Lord Rama’s army to reach Lanka.
TN Government also wants central Government to declare Ram Sethu as national monument.
Pro-arguments
- The project will reduce the shipping time and fuel costs
- It’ll improve ship traffic (and income) for the minor ports of TN, Andhra, Odisha and WB
Maritime agenda 2020
- for the decade 2010 to 2020
- by Ministry of shipping
- to increase the growth in shipping sector
- To create a port capacity of around 3200 MT
- promote coastal shipping as it will help in decongesting our roads and is environment friendly.
- increase India’s share in global ship building to 5% from the present 1%.
- Increase Indian seafarers (personnel) in the global shipping industry.
From Economic Survey
- 95 per cent of India’s trade by volume and 68 per cent in terms of value is transported by sea
- 31 January 2013, India had a fleet strength of more than 1100 ships public-sector Shipping Corporation of India having the largest share.
- India is one of the major ship-breaking destinations.
- India is also one of the major countries supplying seafarers.
Shipping: Challenges
Baltic Dry Index
- It is the the barometer of merchandise trade as well as shipping services,
- It has been in the red since the global crisis of 2008 (more discussed in ch.7 click me)
Ageing ships
- Indian ship fleet is ageing.
- There is urgent need to increase the shipping fleet so that it is adequate atleast to meet India’s trade volumes.
- A large and modernized shipping fleet will lead to higher growth, employment and higher earning/ saving of foreign exchange,
- It will also increase our bargaining power with foreign liners who carry Indian cargo as per their schedule and also discriminate in the transport rates.
Port Services
- Performance of shipping services and merchandise trade depends on the efficiency of ports.
- There was a decline in traffic at major ports, which accounted for more than 60 per cent of total traffic
- As per the World Shipping Council, Shanghai port ranked at the top in terms of total cargo volume handled
- The Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (JNPT) is ranked 30th in terms of total cargo volume handled in 2011
- Thus efficiency of our ports needs to be improved further.
- Government has been following the strategy of increasing investment in infrastructure through a combination of public investment and PPP.
- The Twelfth Five Year Plan with an outlay of more than 3000 crores for the port sector
Taxation
- Against its counterparts, Indian shipping as against its counterparts is currently subjected to 12 types of taxes.
Manpower
- Seafarer= A man who serves as a sailor.
- Main Seafarer supplying countries = China, Philippines, Turkey and Ukraine
- India should take advantage of its demographic dividend to supply more officers in the international maritime sector.
- Government has established an Indian Maritime University (IMU) in Chennai, with campuses in Kolkata, Mumbai, Visakhapatnam, Kochi, Chennai and Kandla. But more needs to done.
- There is need for welfare measures for seafares, including a free/subsidized health and insurance policy.
- Indian ships have to mandatorily employ Indian seafarers, and cannot employ foreign sea-farers as per the Merchant Shipping Act. This needs reform.
Inland Water transport authority of India
- For development and regulation of inland waterway
- India’s Inland Waterways which totals about 14500 kilometers in length
National Inland waterway |
Length (km) |
|
1620 (longest) |
|
891 (third longest) |
|
205 |
|
1078 (second longest) |
|
588 |
|
121 |
btw, longest national (road) highway= #7 connecting Varanasi with Kanyakumari.
Kaladan Multimodal Transport Project
- This project was conceptualised by the Ministry of External Affairs
- to provide alternative connectivity from Mizoram to Haldia/Kolkata ports through River Kaladan in Myanmar.
Some other projects/ports for inland water transport:
- Pandu port in Guwahati
- Palatana Power Project in Tripura
Indian waterways: challenges
- Large parts of Indian Waterways have inadequate Least Assured Depth (LAD) for commercial movement of cargo. at least 2.5 m, preferably 3.0 m. LAD is necessary for round the year navigation
- Several rivers meander (move in spiral / curved / snake like shape) =resulting in increase in distance to be travelled on water-ways as compared to road and rail. Then it becomes uneconomical to transport cargo via river.
- On many rivers, there are bridges with low vertical clearance which impede passage of bigger vessels on the waterways such as NW-3. These bridges need to be raised to atleast 5m.
- ‘water tourism’ theme has potential to generate considerable income for the local economies and additional income from tourism. For example, in Kerala, over 2000 people are employed in houseboats and other motorboats that cruise the inland waterways filled with tourists.
12th FYP: Inland Water Transport
- policies to promote manufacture of Inland Waterways Vessels for cargo movement by private sector
- Development of National Waterway 4 and 5
- Development of night infrastructure facilities to help 24 hours navigation.
- Promoting connectivity with Bangladesh
Aviation
| Sector | FDI permitted |
| Scheduled air transport/domestic scheduled passenger airlines | 49% FDI (100% for NRI) |
| Helicopter services | 100% |
| Airports: Greenfield projects | 100% |
| Airports: existing projects | 100% |
Chicago convention
- Held in 1944, for aircraft registration and safety.
- Led to birth of ICAO, the specialized agency of UN international air travel.
ICAO
- International civil aviation organization (ICAO)
- HQ: Montreal, Canada
- India is member since inception of ICAO.
Airlines in India
- Public sector:
- Air India and its subsidiaries
- Private sector
- Jet Airways = Naresh Goyal
- Jetlite Airlines (originally owned by Sahara, now by Jet Airways)
- Kingfisher =you know who.
- Spicejet = Sun group (of Kalanidhi Maran)
- Interglobe Aviation (IndiGO)
- Go Airlines
- Three cargo airlines
- Deccan cargo (Deccan 360) =under Kingfisher.
- blue aviation
- express Logistics
DGCA
- directorate general of civil aviation
- it is the regulatory body in the field of civil aviation
- registration of civil aircrafts
- gives license to pilots, airlines maintenance engineer
- supervision of flying/gliding clubs
- investigation of minor accidents
- implementing Chicago Convention
Bureau of civil aviation security
- initially it was a cell in DGCA, now an independent department under the Ministry of civil aviation, after Kanishka Tragedy in 85
- for matters related to hijacking, training of civil aviation security personnel
Pilot Training
- Indira Gandhi Rashtriya Udan Akademi (IGRUA)
- in Raebareli UP
- WOMBAT: pilot aptitude test Trainer
- TALON: the pilot training at IGRUA is managed by this web based training Management system.
- Rajeev Gandhi National flying training Institute
- in Gondia
- Joint venture of AAI + a Canadian company
AAI
- it is a public sector undertaking (PSU) under Ministry of civil aviation
- for development and Management of airport infrastructure
FANS
- Future air navigation system
- AAI implementing it.
- Includes
| Shifting from | To |
| voice communication | digital data communication |
| ground based navigation | satellite-based navigation (GAGAN) |
GAGAN
- GPS aided Geo augmented navigation system
- it is a satellite-based navigation system development by AAI + ISRO
- GAGAN GPS devices help pilot to fly in difficult weather, fog, tough terrains.
- GAGAN will also help in
- high-quality Air Traffic Management (ATM)
- to all modes of transportation, including maritime, highways, railways
- public services such as defense services, security agencies
- disaster recovery management by aiding in search and rescue to locate the disaster zone accurately,
- telecom industry and personal users of position location applications.
Air India
Chief: Rohit Nandan
Subsidiaries of Air India
- Hotel Corporation of India
- Vayudoot ltd
- Alliance Air
(it has other subsidiaries too but they contain “air India” in their name, hence unworthy of tricky MCQs hahaha)
Pawan Hans Helicopter ltd
- it is a government-owned company
- provides helicopter service to
- ONGC’s offshore drilling platforms
- hilly and inaccessible areas
- Amarnath Yatra
- emergency evacuation
Airport economic regulatory authority (AERA)
- to foster healthy competition among major airports
- regulate airport tariffs
Aviation: recent Developments
- Dharmadhikari Committee was setup by Civil Aviation ministry to address the contentious HR issues caused due to merger of AirIndia and Indian airlines.
- State Government of Kerala wants to launch “Air Kerala”. (more details on Pravasi Bharatiya article click me)
- Tata and Malaysia’s Air Asia formed Joint venture to enter in Domestic airline business In India.
- Jet Airways (Naresh Goyal) sold (FIPB) to sell 24% stakes in the company to Etihad Airways (Abu Dhabi, UAE based)
- Air India has warned the government that foreign investment (e.g. Jet Etihad) will hurt the interests of domestic airlines and prevent Indian airports from developing into international hubs. (lolz in other words, Air India is saying that since we don’t have the aukaat to grow, don’t let others grow either!).
Aviation Challenges:
#ATF
- high taxation on aviation turbine fuel (ATF)
- ATF alone accounts for 40% of the operating cost of Indian airlines
- ATF is priced 60% higher in India compared to other countries in the region
- ATF should be accorded the status of “Declared Good” that carries lower and uniform tax rate.
#predatory pricing
- Predatory pricing is the practice of selling a product or service at a very low price, to drive competitors out of the market, or to prevent potential new competitors from coming in the market.
- Indian airlines often use the predatory pricing to destroy their competitors (and in the process bleed and make losses for themselves as well).
#Other
- High aircraft to man ratio
- Loss making Airindia and its frequent strikes.
Greenfield and Brownfield
Greenfield |
Brownfield |
| Setting up new project in a virgin / vacant site. | Redevelopment in site where buildings, infrastructure already exists. |
| International airport @Devanahalli near Bengaluru.It is a PPP involving Larsen n Toubro, Siemens | Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport, Mumbai |
| International airport @Shamshabad near Hyderabad.PPP involving GMR group and Malaysian company.Both PPP projects have BOOT model: Build-own-Operate and Transfer. | Delhi International Airport, DIAL |
Another greenfield airport that has been in news= Panvel, Navi Mumbai because of environmental issues.
12th FYP: Aviation
- Encouraging emergence of regional airlines to cater to air transport needs of Tier II and Tier III tours and promoting low cost carriers for this purpose
- Double of passenger handling capacity of Airports primarily through private investments (PPP).
- Upgradation of Air Navigation Services (ANS) using the latest technology
- New Policy for ATF to improve Airline competitiveness
- Set up of National Aviation University
Mock Questions
- What is the width of single lane highway in meters?
- 3
- 3.5
- 3.75
- 4
- Which of the following is/are sources of funding for NHDP?
- Cess
- External assistance from World bank, ADB
- Market borrowing
- All of above
- Project Vartak, Beacon are associated with
- Ministry of Environment and Forest
- DG Shipping
- BRO
- None of above
- Central Road fund is utilized for Development of
- national highways
- village roads
- railway overbridges
- all of above
- Which of the following is not a component of Bharat Nirman?
- Rural housing
- rural roads
- irrigation
- rural employment
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana falls under Ministry of
- Highways and roads
- Panchayati Raj
- Social welfare
- Rural Development
- PMGSY seeks to provide all weather roads to habitations in plain areas with population ____ or above as per 2001 census
- 500
- 1000
- 1500
- none of above
- National Automotive Testing and R&D Infrastructure Project (NATRiP) is associted with ministry of
- HRD
- Communication and IT
- Heavy Industries and Public enterprises
- Science and Technology
- Lenght of India’s coastline in Kms
- 7513
- 7515
- 7517
- none of above
- Correct Statement
- India has 9 maritime states
- 5 on Eastern Coast
- 4 on Western Coast
- None of above
- On Eastern coast, which state has maximum number of Major ports?
- WB
- AP
- TN
- None of above
- On Western coast, which state has maximum number of Major ports?
- Guj
- MH
- Karnataka
- None of above
- In India, which state has maximum number of Major ports?
- MH
- TN
- Goa
- None of above
- National Automatic identification system (AIS) is meant for
- habitual criminals
- heavy vehicles
- endegered wild species
- Ships
- Sethusamudran Project wants to connect ____ and ____.
- Adam’s bridge, Ram Sethu
- Gulf of Myanmar, Bay of Bengal
- Gulf of Mannar, Palk Bay
- None of above
- PM had formed a Committee for Sethusamudram Project, who was its chairman?
- Justice JS Verma
- DD Gadgil
- RK Pachauri
- None of above
- Maritime Agenda 2010-2020 is related to
- International Maritime Organization
- BIMSTEC
- Ministry of Shipping
- None of Above
- Which National inland waterway is lengthiest?
- 3
- 5
- 7
- None of above
- Which national highway is lengthiest?
- 3
- 5
- 7
- None of above
- 6th National inland waterway is associated with ___ river
- Barak
- Luni
- Krishna
- None of above
- Kaladan multimodal transport project aims to connect ___ with ____.
- Dhaka, Kolkata
- Aizwal, Kohima
- Mizoram, Kolkata
- Myanmar, Assam
- GAGAN is jointly Developed by ___ and ____
- ISRO, CSIR
- ISRO, Airforce
- AAI, Airforce
- AAI, ISRO
- Which of the following is not a subsidiary of Air India
- Hotel Corporation of India
- Vayudoot Ltd
- Alliance Air
- Express Logistics
- Which of the following is a site for greenfield airport
- Devanahalli
- Shamshabad
- Panvel
- all of above
- Which of the following is not a function of DGCA?
- registration of civil aircrafts
- supervision of flying/gliding clubs
- Management of airport infrastructure
- all of above
- In India, Future air navigation system (FANS) is being implemented by
- Airforce
- DRDO
- AAI
- None of above

![[Laws] DESI liquor special edition Kerala, Mizoram & IPS Training, Tribal insurgency](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/Cover_Polity_kerala-liquor-500x383.gif)
![[Economic Survey] Corrections in the previous articles + Parting words before Qatl ki Subha](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Cover-Economic-Survey-correction-500x383.jpg)
oh..mrunal..thank u so much 4 making huge info available free 4 all…u gave me a ray f hope 2 prepare myself 4 xamz siitin 8 1 corner f d country…lot f thnx n best f wordz n praise 2 u…
Friends, an easy way to remember the programmes under Bharat Nirman:
WITHER
Water
Irrigation
Telecom
Housing
Energy
Road
(will not take credit for this, it is by one Mr.Nikhil Kumar)
bhaiya mrunal apke lekh ministry ko bheje ja sakte hai itna khul ke kulla mat karo
@mrunal sir,
Under “Electronic Toll Collection (ETC)”sub heading…you said that ETC was taken as a pilot project on NH-5 B/w delhi and parwanoo
But those places are not touching the NH-5.Wats the meaninf of that one ..pz clarify it sir..
Dear Mrunal Sir, You have mentioned this in the above article in the shipping section ”Manpower”…..
”Indian ships have to mandatorily employ Indian seafarers, and cannot employ foreign sea-farers as per the Merchant Shipping Act.” This needs reform.
Sir by ”reforms ”if you/India year book/Economic survey means that foreign nationals should be allowed to work on Indian ships then I would like to tell that many of our ”competent” seafarers[ crew as well as officers especially junior officers] are not getting jobs as there are less ships and more men…. and for this situation our government, its policies for seafarers and the concerned authorities [DG shipping & various Crew n officers unions are responsible]. Even I am a seafarer have done my written exams [Jr. officer for coastal area] but since there is no good career scope in near future… I am preparing for state PSC at this age [30 yrs]. Even many of my friends coastal as well as foreign ticket holder India officers are struggling from the last year or so…Here govt. is posing many ”restrictions” on Indian seafarers [ due to domination of SCI. Ltd] and hence we can’t compete with the chinese or philipines crew n officers… at the international level and some seniors have more dull predictions for near future for seafarers career.. which is true in my opinion too… Where my friends were getting around 1 lac/month in 2009-10 working for 6 to 7 months a year… now due to excess availability of man power in coastal shipping companies are offering around 30 K to 40 K per month only…. so if doors are opened for foreigners to work on India ships we can imagine what the situation is going to be…. Dear Sir this is not written with the intention of hurting you or nor I have any doubts about your knowledge/efforts….in fact you[ via answering my mails] n your blog has helped me a lot regarding how to prepare n which books to refer etc etc. but still after reading that line in the Manpower paragraph of this article I couldn’t stop myself from writing my feelings. Regards…
shipping is useful for many people for transportation.In many ways people use this option.
Isn’t a cess deposited in the public account of India? How come money collected under central road fund goes to consolidated fund of India.. Shouldnt that be public account of India