Third and last part in the series. Indo-US cooperation in Education, Environment and Energy (EEE), with special focus on Kerry’s visit (4th strategic dialogue).
- Education
- Data-sharing
- Fulbright-Nehru Program
- India’s “Connect India” program
- In-step initiative
- Museum
- Obama-Singh Knowledge Initiative
- Raman Fellowships
- UGC
- USA’s “Passport to India” initiative.
- Environment related
- Arsenic
- Durban platform
- REDD+
- Short lived Climate pollutants
- Summits
- Energy
- IREED
- PACE
- Gas hydrates
- Coal bed Methane
- Gas market
- Tech-upgrades
- New Silk road strategy
- Solar thermal
- Summary
- Mock Questions (General Studies Mains Paper II)
Education
The United States is the most favored destination for Indian students, with more than 100,000 Indian students pursuing higher studies in the United States. But the flow of American students coming to India=very low. Both sides agreed to increase it.

India US Education cooperation
| Data-sharing |
- direct India-U.S. advanced science and education network has been setup to supporting enormous data flows between institutions/universities. (terabytes of data in a single download)
- This is a PPP project involving Tata Communication.
|
| Fulbright-Nehru Program |
- for students and scholar exchange.
- Since 1950, it has benefited thousands of American and Indian students and scholars.
|
| India’s “Connect India” program |
- Encourages the US students to come to India for a semester of study.
- They’ll be given exposure to Indian culture and economy, corporate companies and interaction with political representatives, including the totally awesome legends such as A.Raja.
- was announced during the India-U.S. Higher Education Dialogue held in 2012
|
| In-step initiative |
- India-Support for Teacher Education Program (In-STEP)
- joint project between USAID and Indian HRD ministry.
- to build the capacity of teacher educators in India.
|
| Museum |
- Indian culture ministry signed MoU with New York’s Museum for cultural exchanges, training and visits undertaken by museum professionals.
- As part of the celebrations of the 150th birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda, a Chair was established in the University of Chicago
|
| Obama-Singh Knowledge Initiative |
- When Mohan 1st visited USA in 2009
- Each side committed $5 million each
- funds given to selected colleges and universities.
|
| Raman Fellowships |
- for placements of young India faculty and researchers in U.S. universities. (sponsored by UGC)
|
| UGC |
- University Grants Commission (UGC) of India has finalized guidelines for twinning arrangements between Indian and foreign educational institutions.
- The guidelines will facilitate greater collaboration between Indian and U.S. universities.
|
| USA’s “Passport to India” initiative. |
- For American students coming to India for internship.
|
| TUV scam |
- Tri-valley university visa scam in USA, 2012
- ~400 Indian students were duped in this.
|
- Collaborations in Massive Open Online Courses, technology-enabled learning.
- Developing India’s vocational training sector through collaboration with U.S. educational institutions.
- Establish community colleges in India.
- enhance people-to-people connectivity
- Higher Education Dialogue. and MoU with AICTE +additional institution-to-institution agreements to be signed on the margins of the Higher Education Dialogue
Environment related
India US Environment cooperation
| Arsenic |
U.S. companies providing the technology and knowhow for Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water in Indian villages. |
| Durban platform |
- In Durban platform under UNFCC, the parties decided work toward a climate change agreement applicable to all countries from 2020, to be adopted by 2015.
- Both India-US resolved to work on Durban Platform: with a protocol and legally binding treaty on all parties.
|
| REDD+ |
- Indian Ministry of Environment and Forests and USAID initiated a five-year, contract to take Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD+) actions in India.
|
| Short lived Climate pollutants |
- Short-lived climate pollutants include black carbon, tropospheric ozone, methane, and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
- They are called “Short-lived” because these pollutants have atmospheric lifetimes of only days to a decade and a half (compared to CO2 which can persist in the atmosphere for millenia.)
- India and the U.S. will work together to exchange information on short-lived climate pollutants, including black carbon.
|
Summits
|
Both sides welcomed the decisions/outcomes of following summits:
- Doha/COP-18 (UNFCC)
- RIO+20
^click on the names to read full articles on those summits. |
Plus, cooperation in
- monsoon studies
- Integrated Ocean Drilling Program.
- climate change adaptation
- disaster preparedness
- water resources
- forest carbon inventory monitoring
- clean energy
- strategies to achieve low carbon inclusive growth
- tropical cyclones,
- Research on key pelagic fish stocks and harmful algal blooms.
Energy
- energy =critical for sustaining economic growth and securing prosperity,
- India-US Energy Dialogue
- Developing smart grid technologies, energy efficient buildings, Air conditioners, solar power, clean energy.
India US energy cooperation
| IREED |
- Indian Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Policy Database (IREEED)
- Launched by India’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy and the U.S. Department of Energy
- This is an online repository of India’s central and state government renewable energy and energy efficiency policies, regulations, and incentive programs.
- It provides one stop information to benefit of policy makers, project developers, businesses, and consumers.
|
| PACE |
- India-US Partnership to Advance Clean Energy (PACE).
- When Mohan had visited America in 2009.
- So far, PACE has mobilized ~ $2 billion to India for clean energy projects.
- PACE initiative has financed nearly 40 percent of India’s first 1,000 MW of installed solar energy capacity,
|
| Gas hydrates |
- MOU for Cooperation in Gas
- To increasing the understanding of the geologic occurrence and the potential of methane production
- from natural gas hydrates in India and the United States.
- for more on gas hydrates, read article on Economic Survey ch.11, part 1 of 2
|
| Coal bed Methane |
- U.S. Trade and Development Agency (USTDA) signed an agreement to help Essar Oil Limited in further assessing its coal bed methane license areas for the presence of commercial grade shale deposits.
- US established a research house with Coal India on coal mine and coal bed methane.
- Coal India is using this facility to explore prospects for commercially viable methane capture systems to both reduce emissions and recycle methane as an energy source.
- This (coal bed methane) will take India to a potential new domestic energy resource offering cleaner alternatives to coal.
- For more on coal bed methane read article on Economic Survey ch.11, part 1 of 2
|
| Gas market |
- discussed the development of an Asian natural gas market to provide more secure and diversified supplies of natural gas throughout the region.
|
| Tech-upgrades |
- directors of Indian PSU refineries to meet with U.S. companies specializing in a range of refinery efficiency up-gradation technologies.
- USA is also collaborating with Indian oil and gas companies to capture and reuse fugitive methane from gas facilities.
|
| New Silk road strategy |
- America’s “New Silk Road Strategy” links the energy rich Central Asian Republics as Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan with Bangladesh and South East Asia.
- Last year when Hilary visited Mamata, she said Kolkata would become an important hub in this new silk road strategy.
|
| Solar thermal |
- In Dec 2012, US-India started initiative for concentrated solar power (CSP).
- It converts solar energy into thermal energy (heat). Then heat is used to run steam turbine= electricity produced.
- name of project=SERIIUS (Solar energy research initiative of India and US).
|
Summary
So, what is the big picture? Where do these individual pieces fit in the Indo-US relationship? click on following chart to find out.
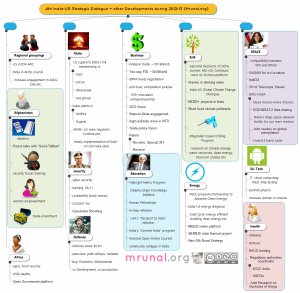
Indo-US relationship 2012-13 (click to enlarge)
Mock Questions (General Studies Mains Paper II)
Write note on following, 2 marks each
- India-US PACE program
- Connect India program
- Obama Singh knowledge initiative
- SCOMET list
- SERIIUS (for GS3)
- IREED (for GS3)
Answer following for 10 marks (200 words)
- Discuss the development of Indo-US defense ties in the recent years.
- Write a note on Indo-US cooperation in space and science research.
- Write a note on Indo-US cooperation in health care and medical research.
- Give an outline of Indo-US cooperation in climate change with respect to UNFCC and Doha platform.
- Write a note on Indo-US cooperation in Environment protection and Energy security.
- What are the various consultative mechanisms between India and US to improve and strengthen the trade and investment relationship?
25 markers (250 words)
- Examine the areas of cooperation and irritants in the Indo-American relations in recent years.
- Write a note on the evolution the strategic partnership between India and US after the collapse of USSR.
- Former US ambassador Robert Blackwill was once reported to have said: “India wants the US to invest, India wants the US to keep its markets more open, India want’s more Visas for its professional, India wants us to be more helpful on Kashmir and in dealing with Pakistan, India wants US support for membership of the UN Security Council, India wants this and India wants that. Tell me what will India give in return?” What will be your reply to ambassador Robert Blackwill?
- From US point of view, what are the main ‘drivers’ of the India – US relationship?
- ‘US – India Strategic dialogues offer sound bites, not solid actions.’ Do you agree/disagree? Give reasons in support of your answer.
- American strategic generosity towards India, remains an investment in its own geopolitical well being. Comment.
- Write a note on Trilateral relationship among India-US-Japan.
- Write a note on Trilateral relationship among India-US-Afghanistan.
For more on diplomacy, international relations: visit Mrunal.org/diplomacy



![[IR By Pavneet 4/5] Art of Answer-writing: Directive Word#2 “DISCUSS” – Impediments to India’s permanent membership at UN Security Council (UNSC)](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/webinar-pvnt-c-500x383.png)
world history ke article kaha gaye mrunal sir
u have nt posted on world history for long time now
I would love to, but unfortunately I’m overstretched in many projects. But yes, World History will be covered in upcoming days.
It would be great if you could give a link to your History and Culture articles in the NOTES menu
Sir,
When time permits, could you shed light on the “post-independence consolidation & reorganization within the country”?
Thanks for this article on diplomacy.
eagerly waiting for the upcoming days
good morning murunal sir,
sir FCI me jo managment trainee ke post nikli h usme tecnical post ke lea eligiblity B.SC.or B.tech in agri/food science/agri engg hai lekin maine M.sc.(ind chemistry) ke bad M.tech Agricultural proceess and food engg me kea hai.to kya me eligible hu iss post ke lea?or iska study plan kese karna h and last year ke enterance papers ke bare me bhe btaea..please reply me soon. i will wait..
an awesome one,and question you put in mock sextion is seriously too good
I really love the mock questions.
It would be great if you could give a link to your History and Culture articles in the NOTES menu
Mrunal sir
Can we mail u our ans?
awesome work sir…..
sir, thanks. This article is very useful on topic of diplomacy.
Thanx a ton SIR
sir,
This material was of great help to us do u mind to give preparation strategy for the latest syllabus
sir which book should i purchase for regional development and planning for geography main? is R C Chandna’s good ?
what is difference between gram nyalaya and gram panchayat….can anybody clarify my doubt??
sorry instead of gram panchayat make it nyaya panchayat
hey guys did u notice this our tutor has come in hindustantimes
http://www.hindustantimes.com/India-news/NewDelhi/6-of-100-IAS-aspirants-flunk-in-language-tests/Article1-1020342.aspx :)hope u didnt notice b4
@me
yes… i have read it … now mrunal is becoming popular for his noble work…….
salute to Mr. Mrunal
congrats sir g! gud work is recognized by national daily.
Great work …Mrunal Sir….
awesome work :)
Can anyone pls provide ans points on this ques (Ques 3 of 25 marks)-
Tell me what will India give in return?” What will be your reply to ambassador Robert Blackwill?
Q 3,4 & 6 are one and the same.
Statement of Q 6 is in a way answer to Q 3.
I would say – “You don’t have to act so smart! Everybody knows, American strategic generosity towards India, remains an investment in its own geopolitical well being. Assisting India to develop its national capabilities is intended not merely to uplift its humanity but rather to advance the vital US interest in preserving a stable geopolitical balance in Asia and globally. Support for India promoted US strategic goals.”
Some pointers:
1. Mention how Indian Software engineers are contributing for US economy.
2. How Indian diaspora in US (Per capita income of Indians there is far higher than Americans) is contributing to their economy.
3. How India can help contain China. (Although, both sides won’t accept this openly).
4. US company need market – Where will Monsanto go otherwise? Wall mart? India provides 300 million middle class people who drink coke!
5. Strategic location of India in Indian Ocean. US considering to focus in Indian ocean in future.
6. Security/Piracy/Environment/ – Both of them can work towards protecting global commons.
7. Role of India in future Afghanistan.
And many more such points that you can think of! But the bottom line is – Support for India promotes US strategic goals!
India can give following to US:
1. Investment destination for US companies
2. Inward investment for US
3. Market for US goods and services eg. defense equipment, nuke plants etc
4. Collaborative research & development in areas such as SPACE, Health, Climate change, etc
5. Support for US actions at global platform
6. Act as rival power in Asia to contain rise of China.
7. India, fast growing economic power is inevitable to ignored in present global setting.
8. Support for promoting Democratic principles
9. India can play constructive role for Afghan peace, security and development
10. many more…..
Sir, please teach us paper 4, relating to ethics, integrity etc.sir, pl donot go by my name i m a sincere student.As there is no study material available.
sir ji u r doing awesome work. thanku sir. sir please send me public administration diagrams sir please.i will be very greatful to u
Yes, Rightly said in the above post.Many big indian companies like Tata, is investing heavily in U.S. and by opening company there, Indians are generating employment for the american nationals, which, in turn will improve the economic condition of the U.S. Citizen.
sir pls inform which are the NCERTS should be read for UPSC mains….sir pls reply me..i dinn get any reply for my many queries….pls….
Hi Mrunal,
I’ve shifted to feedly,however I am unable to add the following sites:
1.http://www.mea.gov.in/Portal/XML/Articles_in_Foreign_Media_1.xml
2.http://www.mea.gov.in/Portal/XML/In_Focus_Article_1.xml
3.http://www.mea.gov.in/Portal/XML/Media_Briefings_1.xml
Could you please help me in this regard?
Regards
which test series is gud??crackias or vision ias??somebody please tell me as i really need to get my answers checked
hey, can anybody plz tell me how 2 get stuff from e-gyankosh? i have registered myself umpteenth no. of times but not getting a password for access.
Very informative.Thank you.
sir plz post material on representation of people act 1951
sir plz post some material on representation of people act 1951
sir,
you are guiding for all non technical exams and its extremly awesome… it will be nice if you are able to guide for technical exams also… if not pls help us by giving certain sites like yours which helps us to get widwr technical knowledge regarding those exams.. ll be thankful to you..
sir is New vishals mains solved paper or ariant mains solved paper is good??? which is better to buy… pls reply me sir…
hi mrunal,
can u plz suggest where to do the topic on comparative constitution in gs paper 2 from? not able to find any resources. thanks a lot!