- Prologue
- List of Questions asked
- [Physical 1] Continental Drift Theory 5m
- [Physical 2] Why Hot Deserts in N. Hemisphere?
- [Physical 3] Why no Delta in Western Ghats
Prologue
- December 2013, UPSC conducted Civil Services Mains exam.
- Jan 2013: I published answerkey for Indian History Answerkey and Culture Answerkey for General studies Paper I (GS1). Then I drifted away to economy related articles given the IBPS and IIM interviews.
April 2014: back in the business, starting with Geography. Total three parts article-series
- Physical geography (3Qs) You’re here
- Climate, environment, disaster (4Q) click me
- Energy and Industrial location (4Qs) done click me.
List of Geography Questions asked in GS1
| type | Question | marks | Theory /Current | India/World |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| physical | What do you understand by the theory of continental drift? Discuss the prominent evidences in its support | 5 | theory | neither |
| physical | Major hot deserts in northern hemisphere are located between 20-30 degree north and on the western side of the continents. Why? | 10 | theory | world |
| physical | There is no formation of deltas by rivers of the Western Ghat. Why? | 5 | theory | India |
| location | Do you agree that there is a growing trend of opening new sugar mills in the Southern states of India ? Discuss with justification. | 5 | theory | India |
| location | Analyse the factors for highly decentralized cotton textile industry in India | 5 | theory | India |
| energy | With growing scarcity of fossil fuels, the atomic energy is gaining more and more significance in India. Discuss the availability of raw material required for the generation of atomic energy in India and in the world. | 10 | theory | India |
| energy | It is said the India has substantial reserves of shale oil and gas, which can feed the needs of country for quarter century. However, tapping of the resources doesn’t appear to be high on the agenda. Discuss critically the availability and issues involved. | 10 | current | India |
| disaster | The recent cyclone on the east coast of India was called “Phailin”. How are the tropical cyclones named across the world? Elaborate. | 5 | current | neither |
| disaster | Bringout the causes for more frequent landslides in the Himalayas than in Western Ghats. | 5 | theory | India |
| climate | Bring out the causes for the formation of heat islands in the urban habitat of the world. | 5 | theory | neither |
| climate | What do you understand by the phenomenon of temperature inversion in meteorology? How does it affect the weather and the habitants of the place? | 5 | theory | neither |
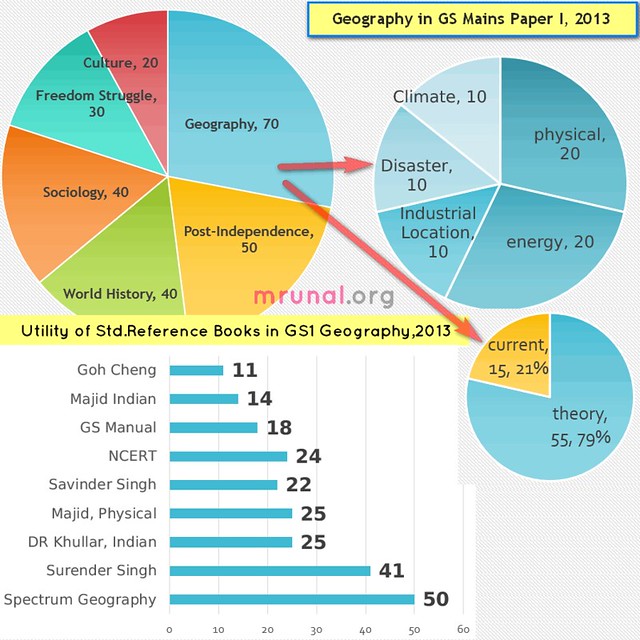
| total 70 out of 250 marks | 28% | only 15 marks current related. | only 15 marks world geography. |
- Contrary to expectations, neither World geography NOR environment-biodiversity dominated the paper. Infact World geography= barely 15 marks.
- Straightforward questions from Industrial location factors (I was afraid they’d ask something about tertiary / service sector / current affairs type question in it.)
- Nothing from flora fauna or climate change (Except heat island).
- OR may be because examiner thought “5 mark =100 words” rule alone was a sufficient shocker so even easy question should become BackbreakingTM, therefore he saved all the tough questions for next mains hahaha.
Continuity of trend from 2011 & 2012
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|
| climate change vs water resource | sustainable development; CDM mechanism | heat islands |
|
|
nothing from wildlife |
| desertification in India | why all hot deserts in N.Hemisphere | |
| Overall 24 marks. | overall 125 marks (mostly environment related) | 70 marks. |
following questions repeated from past general studies (GS) mains papers
| marks in Mains 2013 | asked in GS Mains year | |
| why W.Ghat river= no delta | 5 | 2006 |
| Atomic raw material in India and world | 5/10 | 1989 (only India) |
| total | 10 marks | |
Was it Geography (Optional) friendly?
In other words, was this a Back-BreakingTM section for Non-geography candidates? Answer is both YES and No depending on how you interpret. Following questions were repeatedly asked in previous papers of geography optional subject:
| Question | marks in Mains 2013 | asked in geography optional during |
|---|---|---|
| continental drift theory | 5 | 1980, 1996, 2000, 2007 |
| temperature inversion | 5 | 1995, 2010. |
| atomic raw materials in India and world | 5/10 | 1998 (only India, not world, hence counting five marks) |
| Sugarmill | 5 | 1997 and 2009 |
| cotton textile mill | 5 | 1979, 1982, 1985, 1996, 1999 and 2000. |
| total | 25/70 =36% of Geography. (and 10% of entire GS1). | |
BUT if you look at the nature of question, most of them are not falling from sky- where only Geography optional candidate can solve it and other people cannot.
^the purpose of this discussion: Coaching walla usually try to brainwash new players that “you should only take Geography optional because __ marks worth GS-question came from geography only.” Same sales-pitch goes in Public Administration, sociology, political science, even anthropology. Please don’t pick optional subjects on the sole criteria of “how much does it help in GS?” Every optional has its own headache, called “scaling system”.
How difficult was the Geography section in Mains 2013?
In real life- entire paper can be said tough- because this was the first time UPSC ordered the aspirants to write 100-200 words on everything. 5000 words in three hours is no child’s play. But still for the purpose of theoretical discussion: A question can be said ‘easy’, if
- For five marker, you can recall at least 3 good points, & write it within given time limit.
- For ten maker, you can recall at least 5-6 good points, & write it within given time limit.
| question | Marks | difficulty | comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continental drift | 5 | easy | given in most std. reference books |
| Shale gas | 10 | easy | only IF you followed Hindu diligently. |
| Landslides | 5 | easy | given in most std. reference books |
| Temp. inversion | 5 | easy | Given in most books |
| Delta | 5 | easy | given in most std. reference books |
| Sugarmill | 5 | easy | given in most std. reference books |
| Textile Mill | 5 | easy | given in most std. reference books |
| Atomic raw | 10 | medium | hard to recollect that many sources in “World” |
| Deserts | 10 | tough | At least for non-geography students. hard to recollect that many points. |
| Cyclone Naming | 5 | tough | had to dig official website and still hard to memorize. |
| Heat islands | 5 | tough | Verbatim given in Majid Hussain, Fundamentals of Physical Geography 4th ed. but most non-geography student don’t use it. |
| total | 70 | 40 marks easy; 30 marks medium to tough. | |
Questions “came” from where?
- Exam is long over, even result has been declared. So the only purpose of any answerkey = find out what should be prepared and from where it should be prepared for the next Mains examination in 2014
- Some experts claim 50 marks worth questions came from NCERT. I beg to differ- unless the given book has sufficient content to handle 100-200 marks, only then we can say the question “came” from there. Merely mention of a line or phrase or a sentence doesn’t count. Therfore, NCERT’s real-aukaat is only 24/70 marks in geography. (Proved below)
Now, if we allot yes= full marks, hardly =20% marks and no = 0% marks. then new table will look like this:
| Book | utility in GS1 | Comment |
| Spectrum, Geography | 50 | Highly useful because it covers all three parts: Physical, world and geography. |
| Surender Singh, Geography (TMH) | 41 | Same as above. Although this is one type of “Guide” book for Geography optional (prelims, during pre-CSAT era).So I’m not surprised by its performance. Same for Krishna Reddy’s performance in History/culture. |
| D.R. Khullar, India A Comprehensive Geography | 25 | Despite the fact this book only deals with Indian geography- good performance. (Infact Better than Majid’s Indian geography book) |
| Majid Hussain, Fundamentals of Physical Geography 4th ed. | 25 | Despite the fact this book only deals with physical geography- good performance. (compared to Goh Cheng Leong, Certificate Physical and Human Geographyng’s book) |
| Savinder Singh, Physical Geography | 22 | Since he only deals with physical geography so appreciable performance. Almost parallel with Majid’s Physical. Majid shines over because verbatim answer on heat island theory was given only in Majid book and not in Savinder Singh, Physical Geography. |
| NCERT | 24 | They have their utility in Prelims. Harr stage pe kaam aaye ye bhi toh jaroori nahi. (not necessary that NCERT should come handy at every stage.) |
| GS Manual | 18 | Same as above. |
| Majid Hussain, Geography of India 5th Edition | 14 | For Indian Geography, DR D.R. Khullar, India A Comprehensive Geography is better choice from now onwards. |
| Goh Cheng Leong, Certificate Physical and Human Geographyng | 11 | His Golden Era is finally over. He served well in the late 90s but fast losing relevance under back breaking era. Even CDS and CAPF MCQs have become tougher than Goh Cheng Leong, Certificate Physical and Human Geography |
| MAX. possible | 55(T)+15(C)=70 | (T)=theory, (C)=Current. |
Which Geography Book to use for Mains 2014
As such there is no single book where everything is given slim and trim without bogging down the reader with “Exhautive” coverage from geography optional.
Spectrum or Surender (TMH) seem more beneficial (Atleast statistically) because they were written as guide books for geography optionals.
Same situation was happening with Krishna Reddy’s book in Indian History/Culture answerkey, but there I could find thinner and cheaper jugaad (=TN state books, ). Unfortunatly, same case not happening here.
Therefore, I can think of two approaches:
Approach #1: Selective reading from “all in one guidebook” type book: EITHER Spectrum OR Surender (TMH)
Approach #2: selective reading from three different books: DR Khullar for India; Majid for Physical; Goh Che’s Human & Economy Geography (for world part).
Although Goh Cheng’s Human geo book would be an overkill given the nature of world geo. related questions asked. Majid’s World geograhy=bad cost : benefit.
| all three common (India, Physical, World) |
(DONOT USE BOTH. Both run almost parallel so pick any one) |
| only Indian | D.R. Khullar, India A Comprehensive Geography |
| only physical | Majid Hussain, Fundamentals of Physical Geography 4th ed. |
| only World | Goh Cheng’s Human geography etc but cost : benefit not that great. |
Haven’t included following books/sources in review
| Majid Hussain’s world geography book (TMH) |
|
| Spectrum, Geography’s Indian geography |
|
| coaching /postal material. |
|
Utility of Hindu in GS (Mains) Geography portion?
- Only one question: Shale Gas why not in high policy agenda? 10 marks. Answer verbatim available in Hindu article.
- Other than that, indirectly it also covered heat island and cyclone naming. But verbatim answers = nope. (Otherwise IBN and NDTV will also count in “Cyclone naming”.)
Anyways, enough of book reviewing. Now let’s start answer writing one by one. Total three parts
- Physical geography (3Qs) you are here
- Climate, environment, disaster (4Q) click me
- Energy and Industrial location (4Qs) done click me.
(GS1) Syllabus topic: Salient features of world’s physical geography.
[Physical 1] Continental Drift Theory 5m
Q. what do you understand by the theory of “continental drift”? Discuss the prominent evidence in its support. (5m | 100 words)
Continental Drift theory has been asked in previous Geography optional papers of 1980, 1996, 2000, 2007. Although answer is not “unsolvable” because topic is given entirely in Class11 NCERT.
Sources: Any book on physical geography will contain the topic on continental drift. For example
- Spectrum, Geography, Chapter on Geomorphology, Page17
- Savindra– pg no. 57-60
- Majid Hussain, Fundamentals of Physical Geography 4th ed.: Ch6, first three pages
- TMH, Geography section page 50.
- Chapter4 “class 11 NCERT Physical Geography” Page- 30-31
- Even Orient Longman Atlas- pg. 7 (page no. may change with new edition)
First, Let’s understand the topic, then we prepare answer.
Continental Drift: Explanation
Question demands two answers: 1) what is the theory? 2) What are the evidences?
#1: Theory
- Geographers in the early 18th century were puzzled about the location of lands and water on earth. Why are they in the specific position where they’re right now?
- They came up with many theories, but none plausible.
Finally, Alfred Wegner formulated a theory known as Continental Drift Theory.
- Positions of the continents are not fixed permanently.
- The pieces of landmass have been floating on Earth’s upper-most layer.
- Once they were part of supercontinent “Pangaea”, surrounded by a mega ocean Panthalassa. But in carboniferous period, it was broken into two parts: Laurasia in north and Gondwana land in south, with a shallow sea of Tethys in-between them .
- They got further broken and drifted apart.
- during Wagener’s era, Geographers believed that Earth had only 3 layers in its composition:
| NIFE(Nickle and Ferrous) | inner-most core |
| SIMA(silicon-Manganese) | ocean crust |
| SIAL(Silicon-Aluminium) | Continental crust. |
- Therefore, Wagener believed SIAL layer used to float over SIMA layer.
- With this crude information of Earth’s composition, he was unable to explain what force caused such displacement of the continents.
- So, He claimed tidal forces and centrifugal force were responsible for westward and equator wards movement of the present continents!
- Still, his evidences for the possible drifting of the continents were a landmark discovery.
#2: Evidences of Continental Drift theory
| SIMILARITY IN | HOW? |
| Geography |
|
| Geology |
Same situation for
|
| Paleontological Features | Fossils on the opposite sides of coastline of the continents also share similar characteristics. Examples:
|
| Glacial features |
|
~425words. Let’s compress
First we brain storm to recall points
| THEORY | EVIDENCES |
|
|
+Diagram for additional brownie points.
Sample Answer: Continental Drift Theory
Q. what do you understand by the theory of “continental drift”? Discuss the prominent evidence in its support. (5m | 100 words)
Answer keypoints.
Theory of Continental Drift:
- Alfred Wegner stated that at one time, all continents were part of a super landmass called “Panagea”, surrounded by a mega ocean.
- Over the time, this landmass was broken into smaller continents that drifted away from each other, under the effect of tidal and centrifugal forces.
Evidences:
|
Eastern coastline of South America and Western coastline of Africa fits like jig-saw puzzle. |
|
Mineral composition on the opposite sides of the Atlantic, is identical. e.g. Gold in Ghana vs Brazil, Coal in US vs Norway. |
|
Similar Fossils found in India, South America, South Africa and Antarctica. |
~106 words.
[Physical 2] Why Hot Deserts in N. Hemisphere?
Q. Major hot desert in northern hemisphere are located between 20-30 deg N latitude and on western side of the continents. Why? (10m | 200 words)
Source:
- Goh Cheng Leong, Certificate Physical and Human Geography: Chap 18 The hot desert and Mid-Latitude desert climates
- Majid Hussain, Fundamentals of Physical Geography 4th ed.,ch.28 : subtopic: “rainfall“
- In other books viz. Spectrum, Geography, Surender Singh, Geography (TMH), Savinder Singh, Physical Geography the points are given, albeit scattered in monsoon, ocean current chapters.
Explanation:
- We all know that hot deserts are created due to lack of enough rainfall in the region.
- The rainfall can occur by only 3 ways:
| type | description | where? |
| OROGRAPHIC |
|
Where mountain range located parallel to coastal areas and longitudinal to route of moisture winds. |
| CYCLONIC| FRONTAL |
|
Middle and high latitudes (50-60 Deg. north and south.) |
| CONVECTIONAL |
|
|
Ok now let’s check which rainfall can occur in 20-30N?
| type | Can it occur in 20-30N? |
| CONVECTIONAL |
|
| CYCLONIC |
|
| OROGRAPHIC |
|
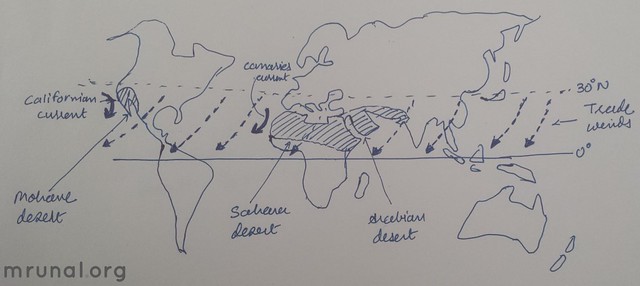
#role of cold currents
- The cold ocean currents pass through western coasts of continents between 20-30N deg
- Result? air becomes cool and dry=> desertification. for example:
| Californian Cold Current | Mohave desert |
| Canaries Cold Current | Shahara desert and Arabian desert |
| Peruvian Cold Current | Atacama desert |
| Benguela Cold Current | Namib desert |
| Western Australian Current | The great Australian desert |
#Relative humidity
- Relative humidity=: ratio of the amount of water in the air at a give temperature to the maximum amount it could hold at that temperature;
- When air becomes saturated with the water vapour at given temperature and pressure, it results into cloud formation.
- But desert = lack of water vapour = very less chances of cloud formation due to lack of water
~360 words. Let’s compress
Q. Major hot desert in northern hemisphere are located between 20-30 deg N latitude and on western side of the continents. Why? (10m | 200 words)
- Lack of Cyclonic Rainfall: The 20-30 N region comes under Sub Tropical High Pressure(STHP) zone, so they experience anti-cyclonic effects on ground. This deters rising of air, cloud formation and cyclonic rains.
- Lack of Orographic rainfall: The eastern region of 20-30N receive rain due to moisture laden trade winds, but by the time they reach western side, they become dry. Hence scanty rain in western region.
- Lack of Convectional rainfall: precondition is moisture laden warm air. But due to Cold currents, the air near coastal areas is cool and dry. This prevents formation of convectional rainfall. And thus lead to desertification effect on western coast of continents. For example: Californian cold current vs. Mohave desert; Canaries cold current vs. Sahara desert and Arabian desert.
- Low level of Relative humidity: When air becomes saturated with the water vapour at given temperature and pressure, it results into cloud formation. But Relative humidity is very low in the desert, every droplets of moisture is evaporated before the air becomes saturated with water. Hence lack of cloud formation.
~ 180 words.
[Physical 3] Why no Delta in Western Ghats
Q. There is no formation of deltas by rivers of Western Ghats. Why? (100 words, 5 marks)
Similar Question was asked in 2006’s GS paper I. “Why do rivers of the West Coast not form a Delta? 125 words.”
Sources (although none gives verbatim answer- points are scattered around):
- Spectrum, Geography, Page 562
- Surender Singh, Geography (TMH) Page 14.14
- DR D.R. Khullar, India A Comprehensive Geography, Ch. on Drainage, Page 87
- Majid Hussain, Geography of India 5th Edition Chap 3: Drainage –The peninsular river systems – table on difference between Peninsular and Extra-peninsular rivers.
- Savinder Singh, Physical Geography– only condition of delta formation are given in page 265 else nothing specific on Western Ghat rivers.
- NCERT Class 9 chapter 3.
- Leong, Chap 15: fluvial process: rivers and related Landforms. (only for theoretical reference)
Explanation
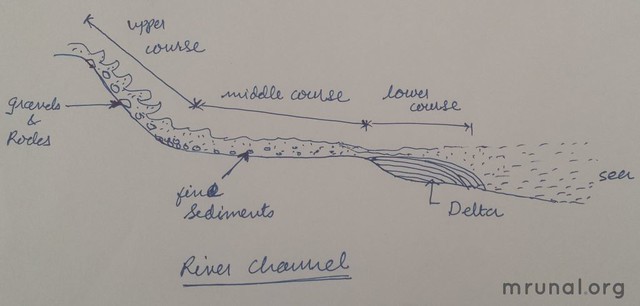
A river has 3 stages of channel development:
| UPPER COURSE |
|
| MIDDLE |
|
| LOWER |
|
The landform created by the sediments deposited by the river at its mouth is called Delta.
What about rivers of Western Ghat?
- Rivers of Western Ghats flow through peninsular plateau. Peninsular plateau has hard rock surface and lacks alluvial material. So rivers do not carry large amount of sediments=> cannot deposit it @mouth of river to form deltas.
- They receive less amount of rainfall compared to Himalayan Rivers.
- West flowing rivers of Western Ghats
- they are small streams. They flow rapidly from steep slopes and merged into Arabian Sea covering very short distance. They can form estuaries and not deltas.
- East flowing rivers
- flow through relatively shallow and eroded valley = less fluvial force.
- Rivers have hardly erosion activity to perform = less amount of sediments
Compressed version:
Q. There is no formation of deltas by rivers of Western Ghats. Why? (100 words, 5 marks)
Delta is a landform created by sediments of large rivers at its mouth.
Unlike, Himalayan rivers, rivers originate from Western Ghats do not form Deltas because:
- Rivers of Western Ghats flow through peninsular plateau, which has hard rock surface and lacks alluvial material. So rivers don’t carry large amount of sediments to be deposited at their mouths.
- They receive less amount of rainfall compared to Himalayan Rivers, some of them non-perennial in nature.
- East flowing rivers flow through relatively shallow and eroded valley, hence unable to produce large amount of sediments.
- West flowing rivers of Western Ghats are small streams, flow rapidly from steep slopes and merged into Arabian Sea covering very short distance. They can form estuaries and not deltas.
~125 words
Remaining answerkeys in next two articles.
Visit Mrunal.org/Geography for more, especially world geography.



sir,is it true that upsc is going to reduce no of attempt and age limit from 2015.
Sir, how no. of words are counted f an answer ??
Sir, as uve suggested a list of reference books for geography,I jus need to confirm that do we even have to deal topics in this much detail that we need to refer these many books only for paper 1 gs mains then what will be the difference between those who hv geography optional
Best compilation……hats off !!
Hi Sir,
Thanks for the answer keys, however I feel your answer to the desert question is not accurate.
The simple reason why deserts are 20-30 degree north is because water evaporated at equator rises and reaches a Max level then it proceeds further in all directions N,S,W,E. The air cools down and and rain falls by the time air reaches 20-30 degree north air contains no moisture so no rain fall. Further this area lies in easterly trade winds where winds flows NE to SW, if we look look at all deserts here no ocean can be found in North east of them so trade winds contain no moisture for them further these easterly trade winds are the reason for deserts to be in west of the continent because by the time tree winds reaches western cost moisture of trade wind is already gone.
This holds true not only to 20-30degree north but south also.
If we go by logics of cold ocean current then western coast of Europe, north america and eastern cost of norther n Asia should also be a desert.
Sir, Spectrum is a good book but is very huge so, do I need to read full book or selective reading will work
Two of my friends gave interview last year just by reading NCERTs i dont know y ur suggesting so many books
Hi mrunal sir & team
thank u very much for ur great work to help students.
U r truely a simplest sir I hv ever seen
sir, mains exam of CSE is comming, so plz explain some Geography questions-answers which r more difficult asked in previous GS paper.
this is a amazing for the optional geography student but gs paper also for our future as well as how to improved ourselve for mains exam of civil service.
Well done work