Prologue

H1,H2=heading, subheading. For more, read their detailed interviews at Mrunal.org/Toppers
- For GS1 to GS3, the Maximum Aukaat of any topic is 200 words, and the minimum time, I take to research and write any GS-article is 2 days.
- So, if I were to run full length articles on Cyclone Hudhud, relevance of planning commission, Make in India, Clean India, Ganga cleaning etc. then mains would be over. (Less than 3 weeks left while I’m typing this).
- In GS1 to 3: you’ll have to face minimum 75 different topics. (10 marks each x 25 questions per paper x 3 papers)
- 4-5 key points x 30 words on each = 120-150 words easily.
- Therefore, I’m preparing a final round of [Revision] notes for “selected-topics” I consider important/useful for Mains-2014 GS paper 1 to 3. (Selected topics only because I can’t build Taj-Mahal in 23 days).
- There won’t be prelim-cum-mains-cum-interview coverage in those notes….Just street-smart 3-5-7 keypoints on selected topics so it can be revised quickly and a “jugaadu” 100-200 words answer can be assembled in the exam hall.
Q. You used to upload those weekly topiclist and essay list. What happened to that?
Ans. I’ll continue doing that. But Hardly 23 days left before Mains-2014. So, priorities shifted temporarily.
Q. If question paper is already set, then should I stop reading newspaper?
Ans. No, you must read newspaper every day. Lot of direct/indirect fodder keeps coming. It’ll help you a lot in Essay and GS.
[Block-1] Urbanization, Globalization
Official GS1- syllabus says:
- Urbanization, problems and their remedies
- Globalization and its impact on Indian society.
As such these are easy topics with truckload of points in Geography books and web pages.
- But if you take it casually -“isme kya prepare karnaa”=>you will waste lot of time in recollecting and organizing points during exam. Then 5m and 10m questions can’t be finished in 4 minute & 7 minute timer respectively.
- Therefore must memorize 4-5 points on every topic for Heropanti JudaadpantiTM in GS
Urbanization problems and remedies

Bollywood already released sufficient “Study-material” for Urbanization problem topic
| Factor | Consequence | remedies |
|---|---|---|
| 1.Migrant inflow | Under-employment, Informal employment, exploitation | factory-labour reforms, RURBAN mission (GS2*) |
| 2.UnderEmployment | crime, drug abuse, alcoholism Desi liquor, childlabour |
|
| 3.High land prices | Black money, slums, illegal societies | Tax-adm-reforms, BEPS, GAAR, PMLA (GS3*) |
| 4.Muni. Insufficient funds due2 black money |
|
PPP, Smart cities, REITS, INVITs (GS3*) |
| Factor | Consequence | remedies |
|---|---|---|
| 1.High rent & land prices |
|
|
| 2.Electricity crisis |
|
|
| 3.Slums |
|
|
| 4.Gardens & buildings |
|
Eco friendly buildings & gardening |
(*) means more details about those remedies in upcoming revision notes on environment and economy.
Globalization: impact on Indian Society
As such infinite topic. But few keypoints must be memorized to finish answers under 4/7 minutes timer.
- Culture-religion-lifestyle angles: good and bad impact.
- Economy and environment angles: good and bad impact.
Culture-Lifestyle: Good
- English +IT + Internet=> youth from small town / villages=>social empowerment.
- Job, Prosperity, Free flow of Ideas => social taboos & caste structure less rigid. e.g. Girl can cremate father’s body.
- Social networking, media, candle marches =>Nirbhaya campaign, More voices against domestic violence, crime against women.
- Indian literature, music, movies got international recognition and vice versa. Free flow of ideas and influence both ways.
- Fusion in fashion, food, lifestyle.
Culture-Lifestyle: Bad
- Religious conversations via lure of money, Missionary-Naxal-NE-secessionist angles.
- Middle-East Jihadi funding to Madressa.
- Internet, Facebook, whatsapp: Brainwashed nsura youth to join ISIS; Riots in UP, Delhi; piracy.
- Decline of classical art, language, literature. (more money in English novel than vernacular).
- Valentine’s day, live-in relations, kiss-of-love, commodification of women, Pornography, MMS-Voyeurism, vulgar reality shows, etc. angles
- Divorce, Nuclear families, erosion of Alok Nath “sanskaars” in child upbringing in the imported
- Flaunting money in social gatherings (DJ, 50 types of soups)=> Materialized society=>must get rich quickly, take bribes, exploitation, no empathy for poors, elderly etc.
- Fast-food, 24×7 social networking: obesity, lifestyle diseases; Bird-flu, HIV, Ebola
Eco-Env: GOOD
- Trade liberalization employment.
- Agrarian economy=>mfg | service economy=>better GDP and revenue collection => more social services=malnutrition decline (said Global hunger report)
- MNC=cheaper and wide variety of goods=>power to customer.
- FDI, FII, Crowdfunding= Indian startup companies.
Eco-Env: BAD
- All points from urbanization table.
- MNC Mining=> tribal land alienation, tribal culture society diminish
- Resource exploitation Climate change=>flood nsuran, disasters=hurting Indians living
- MNC=> desi artisans, small MSME hurt. Jobless growth, income inequality
- Income inequality=>crime, child labor, desi liquor, drug abuse, domestic violence.
[Block-2] Population, Poverty, Development issues
GS1: Official syllabus says:
- Population and associated issues.
- Poverty and developmental issues.
Above subjects have many subtopics in theory and current. But I’m focusing only on a few topics that can be used in variety of scenarios-as last fallback line when you can’t think of anything and need 4-5 keypoints.
Human Development report (UNDP)
This report provides sufficient keypoints to assemble answers for many generic questions about poverty and Development.
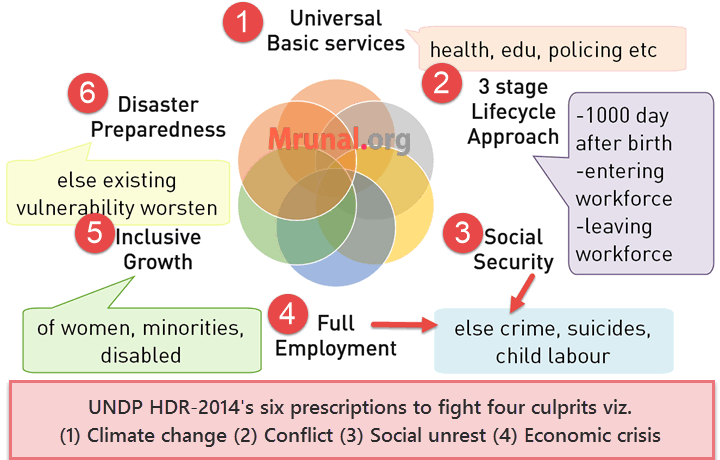
Poverty/Development: How to reduce vulnerability & build resilience?
- Theme: reducing vulnerability and building resilience of human Development
- India rank 135: lowest among BRICS except in Life expectancy.
4 culprits that increase vulnerability
- Climate change (Food production down)
- Conflict (ISIS, Syria, Pak-border shelling, Maoists, NE-secessionist raping and murdering women in front of families)
- Social unrest (Riots at UP,Delhi)
- Economic crisis (inflation, unemployment: blue collar by policy paralysis and whitecollar by subprime)
6 prescription to build resilience
- Universal basic service: health (NHRM, NRUM, Health assurance), education (SSA, MDM, RMSA), water supply, sanitation (Clean India) and public safety (Nirbhaya Fund, policing).
- Protect person @3 vulnerable stages of life:
- First 1000 days after birth (vaccination programs, ICDS, newborn child action plan)
- When Entering workforce (skill India, din Dayal Antyodaya, Udaan, STAR, NSDC)
- When leaving workforce. (Jivan Praman certificate, NPS, Swavlamban, )
- Social protection (80% of world lacks). Lack of social security = people sell their assets, child labor.
- Full employment (50% world informal jobs). Unemployment = crime, suicides; child labour, malnutrition.
- Include women, disabled and minorities in development.
- Disaster preparedness. Else they worsen poverty, inequality, social unrest, climate damage etc.
India specific prescription in HDI:
- Spend 4% of GDP on social security including NREGA, universal primary health coverage, old age and disabled pensions and child benefits
- 1999 Odisha cyclone >10,000 dead but 2013 cyclone <50 dead. Political and bureaucratic-will necessary.
Financial inclusion for poverty removal
Topic hot due to Jan Dhan and Nachiket.
- Meaning: easy access to banking, loaning (credit), investment (beyond 4-9% return in bank) and insurance (life and non-life)
- Benefits: Savings turn to into investment. Loans to businessmen and customers=>demand boost, GDP.
- Investment and insurance =Protected against Unforseen circumstances.
- Japan, S.Korea, USA all were @India’s current level but marched past in 60s thanks to financial inclusion.
- Lack of Fin.inclusion =>money lender, Ponzi scheme, MLM, Saradha Chit fund.
- women Empowerment, Social harmony, less recruits for naxals
- E-Payment: Cashless subsidies, payments, salaries= Government’s Rs.1 lakh cr can be saved (Mckinley study)
Population policy 2000
Control Population: get TFR: 2.1 (now 2.4) HOW?
- Safe abortion, Sterilization
- child, family planning. => ASHA and ASHOK workers.
- Stable population @2045= stable growth rate, stable age composition
Get MMR: <100 / lakh birth (+nt 200 says UNDP). HOW?
- Girl Marriage @20.
- 80% institutionalized deliveries=>Indira Matritva sahyog, mother child tracking, RCH, Janani/Shishu suraksha, +need compulsory rural service for MBBS.
- Compulsory registration of birth and death
- HIV control, Universal immunization.=> National urban and rural health mission. + upcoming national health assurance mission.
Demographic dividend
- Majority of population in working age group
- Age pyramid shows “bulge” in the working age-group
- India: 65% below 35 age (says Modi.)
- To reap dividend=> National Youth Policy, skill training necessary.
National youth policy 2014 (NYP)
- Youth definition=15-29 years.
- Ministry of Sports and Youth affairs to implement it
- Will form a Youth Council to oversee implementation.
- Policy to focus on 11 pillars. I’ve consolidated those under five heads.
- Education, employment, skill, entrepreneurship=> RMSA-RUSA, Sakshar Bharat, Skill India program, Din Dayal Antyodaya, Apprentice bill, Venture fund for SC etc.
- Participation in politics and governance=> PMRDF fellowship making young men nsura of DM in naxal areas.
- Inclusion, Social justice=> Various schemes for skilling SC/ST/Women/Minorities/J&K/NE
- social values, Community engagement, youth engagement
- Healthy lifestyle, Sports.
Rangarajan Poverty line
- Earlier: Tendulkar per capita Expenditure method: ~22% junta / 27 crore junta.
- Ranga family of 5 monthly Expenditure: 7035 (U); 4860 I. now 37 crore junta poor.
- Per person Per day Expenditure:47(U); Rs.32 I
- Food Expenditure=Calorie +Protein + fat.
- Includes food + nonfood items such as education, healthcare, clothing, transport, rent.
- Bottom 35% rural junta always be considered poor. Same way for 25% for urban
- Poverty ratios should be disengaged from entitlements under Government schemes. NFSA (food security) act not on BPL-ness, but social-caste census etc.
Census 2011: facts when everything else fails
When everything else fails, one can always fall back to stupid statistics to create fish market in GD and fillup 100-200 words in mains. Although its upto examiner to give marks on that.
| Urban junta | 30% (exact 31.15%) |
| Rural junta |
|
| Villages, total | 6 lakh villages. (NOFN etc talk about broadband for 2.5 lakh gram panchayats.) |
| Minorities | (1) Muslims > (2) Christians > (3) Sikhs > (4) Buddhists > (5) Jains > (6) Parsi |
| Literacy % | Total 74, men 82, women 65 |
| TFR | 2.4. higher in rural than urban because they don’t have TV said Khursheed. |
| Birth rate | 21/1000 |
| Deaths |
|
| Sex ratio | 943/1000 all age; 914/1000 for children |
| Population growth rate | 17.7% |
Next [Revision]: GS2 Economy- Policies, schemes intervention for manufacturing sector.

![[Revision] GS3: Environment, Conservation, Disaster-Management: Cyclone Hudhud, Kashmir Floods, Clean India & Ganga](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/Cover-Revision-Environment-500x383.jpg)
![[Revision] GS3 Science-Tech: Biotechnology, Robotics, Nanotech, Computer/IT awareness, Space-tech, Agro, Defense](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/Cover-Revision-Sci-Tech-500x383.jpg)
![[Revision] GS2/GS3: Public Health Special: Indigenization of Medical Technology, Medical-Gadgets applications](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/Cover-Revision-GS3-Medical-500x383.jpg)
![[Mains-2014] Vehicle-pooling, Lodging, Centre Address doubts](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/11/c-cab-pooling1-500x383.jpg)
How can I prepare of Pre and mains .My subject is Public administration.Which topic is most popular for paper.My medium language is hindi.
Sir please tell me how to prepare for mains with which material especially in ncert book what chapters have to covered as per syllabus
Sir i want this artical in pdf formate plz give me ittttt
Sir i want this artical in pdf formate plz give me it
Sir i want this artical in pdf format plz give me it
SIR PLEASE GIVE THESE KIND OF SHORTNOTE DATA FOR OTHERS TOPIC OF GS-1 LIKE DISTRIBUTION OF KEY RESOURCES ACROSS WORLD AND GS2-ISSUE RELATED TO POVERTY HUNGER, ISSUE RELATED TO SOCIAL SECTOR SERVICE,DEVELOPMENT PROCESS,WELFARE SCHEME