- Vegetables Industry
- California: veggies and fruits
- Curious case of oranges
- Von Thunen Agro land use model
- Viticulture, Grapes, Liquor
- Government policy Impact
- Viticulture India
- Mock Questions
In the previous article, we discussed the geographical factors affecting location of Meat, Poultry and Pig rearing industry. Moving to the next topic:
Vegetables Industry: Geographical factors
Fresh vegetables are widely grown near major markets because
- Product=perishable.
- Urban Consumer want it fresh and has the purchasing power.
- high value product= veggie/fruit farmer can risk to buy/rent the more expensive land near city areas (compared to a wheat/corn farmer)
Exception: Apples, Oranges, Mangoes etc. they need particular climate, they can’t be grown everywhere.
California: veggies and fruits
California=leading producer fruits, veggies and nuts, viz
- Asparagus, cauliflower, broccoli, spinach etc.
- orange, lemon, melon, grapes, peaches
- fig, dates, wallnuts, almond, pistachios
| Factor | impact |
|---|---|
| Climate | Mediterranean type = suitable for the fruits/nuts |
| Water |
|
| Labour |
|
| Transport |
|
| Market |
|
Curious case of oranges
Orange are grown in both California and Florida, But
| state | What is done to oranges? |
|---|---|
| California | most of them sold fresh as ‘fruits’ |
| Florida | Most of them turned into concentrated juice. |
Recall the dairy sector: area faraway from market=high transport cost=product has to be ‘concentrated’ to increase its value and shelf-life. In case of oranges
| Cali | itself has a big domestic market due to Silicon Valley and urbanized, service sector oriented economy=higher std. of living=junta consumes more fruits. |
| Florida | Florida is far away from the urban posh people of NY, LA or Europe.Florida is surrounded by ‘backward’ states like Georgia and Alabama. Hence local/regional demand=not that high=> product must be concentrated (fruit to concentrated-preserved juice) before sending to faraway market. |
Fruit for thought: Analyze the situation for Himachal Apples, Nagpur Oranges and Andhra Mangoes.
Von Thunen Agro land use model
- farmers near cities grow vegetables, fruits, milk
- while famers faraway from cities grow foodgrains
- farmers extremely faraway from cities rear sheep/goat etc.
Why ^this type of pattern/distribution? Von Thunen explained it with a theory:
- Farmer like any other businessman wants to maximize profit. But his profit depends on three variables:
- P=V-(E+T)
- Profit P=Value of his produce (V) MINUS [production expenses (E) + transport cost(T)]
- without going into all details, when you plot a graph of distance vs profit for various crops/agro-activities…the ultimate wisdom is:
As the farmer moves away from the city, number of profitable options decreases. Since Transport cost gets higher, he has to pick an activity with lower production cost (e.g. sheep grazing.) to make any profit.
if you apply Van Thunen on Delhi:
| place | Relative distance from Delhi | What will they do? |
|---|---|---|
| Haryana, Agra | nearest | dairy |
| Punjab | medium | wheat |
| Jammu | farthest | sheep/goat grazing |
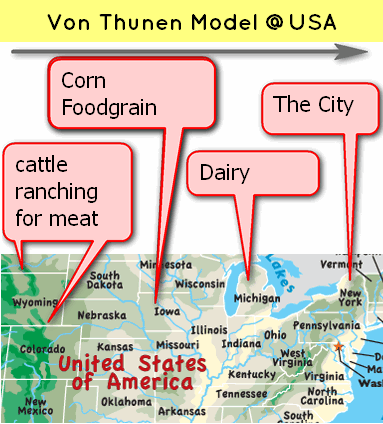
For USA, if you consider New York as only “city” of the whole USA, then observe following map:
If you consider London as the only city of the world, then
| place | Relative distance from London | What will they do? |
|---|---|---|
| Denmark | nearest | dairy |
| Canada | medium | wheat |
| Australia | farthest | sheep rearing |
- Although it doesn’t mean nobody grows vegetables or milk in Australia. At local scale they too have their vegetable, dairy production near their big cities.
- Van Thunen doesn’t apply to specialty crops such as oranges, apples- they’ll only be grown where climate/soil permits them, irrespective of proximity from market.
Viticulture, Grapes, Liquor
Q. Why do Mediterranean countries lead in this grape/wine business?
| factor | impact |
|---|---|
| Climate | Grapes hate cold=> not grown beyond 50 Degree North and 40 Degree south latitude. |
| topography | Grapevines like plenty of sunshine
^This is done to provide maximum sunlight |
| Water |
|
| soil | Grapes like calcium. France-Italy hill have chalk/limestone=good for growth. |
| labor |
|
| raw material |
|
| Market |
|
Factor: Government policy
- When French occupied Algeria they started grape cultivation.
- Why? Because French wanted to export their own premium wines to other countries, so for local consumption in France itself, cheaper variety had to be imported from Algeria.
- Thus, Algeria became a leading grape producing country in the region.
- But When Algeria won independence, the new government did not allow wine industry anymore (because Algeria=Muslim population, alcohol forbidden) =grape cultivation declined.
Some more ‘factors’ on liquor industry
Just passing reference given in the books:
| Liquor Type | factor |
|---|---|
| Beer |
|
| rice wine |
|
| rye |
|
Viticulture India
| Factor | impact |
|---|---|
| Climate | vineyards in Himachal, Nashik, Banglore due to favorable climate,soil |
| Government Policy | State governments giving tax benefits to encourage wine industry. e.g. Maharashtra give stamp and Excise duty exemption, sale tax holiday etc. to new wine units. |
Other than that, books don’t give much wisdom about “location-factors” of wine industry in India.
But on a non-serious note, why are desi-liquor dens located close to slum areas?
| Factor | impact |
|---|---|
| Climate | irrelevant |
| Soil | irrelevant |
| Water | freely available from nearest sewer |
| Raw Material |
|
| Energy |
|
| Labour |
|
| Market |
|
| Government policy | although with corrupt police, government provides indirect support to the industry but to increase the per capita availability of desi liquor, following reforms are necessary :
|
anyways, In the next article we’ll see location factors for plantation crops such as tea, coffee, rubber, sugarcane and later iron-steel industry etc.
Mock Questions
For UPSC General Studies Mains Paper I
5 marks, 100 words
- Why do European producers have supremacy in the wine industry?
- World production of wine is concentrated in the Mediterranean shorelands. Comment
- for any area of your choice, examine the relationship between development of wheat farming with respect to following factors
- climate
- relief and drainage
- labor Supply
- government policy
- What factors give rise to truck farming industry near urban areas? Illustrate with examples.
- Farmers away from urban areas usually grow cereal crops. Comment.
- Analyze the factor responsible for underdevelopment of Dairy industry in tropical regions.
10 marks, 200 words
- In USA, certain groups of states are known as dairy belt, cotton belt and Corn Belt. Explain the factors responsible for such regional specialization of agriculture.
- Discuss the major geographical and economic factors influencing the location of livestock farming in different parts of the world.
- Examine the factors responsible for large production of corn and Wheat in the North America and compare it with suitable states of India.

sir how to convert it as pdf and print out location factor sir
Desi liquor wala part is really good. Govt should seriously implement this. ;D
Lol @ Desi Liquor.. How do you come up with such gems!!?
Entrepreneurs and you know who parts are really amazing………..LOL
Mrunal at his best…………………..
lol…desi liquor part… or shall i call it desi liquor art… too good n too funny
desi liquor should be in ” make in india” campaingn by shri Modi ji :D ..on a serious note good article..
Sir i am a little confused with regards to the approach of this question,
That of the production of corn and wheat in America and comparison.
Should i be generalistic in these types of question or should i make a proper table comparing every aspect i detail??
Amd then again factors of corn and wheat are poles apart!!
Plzzzzz guide sir!!