- Prologue
- Indian food processing industry: Significance
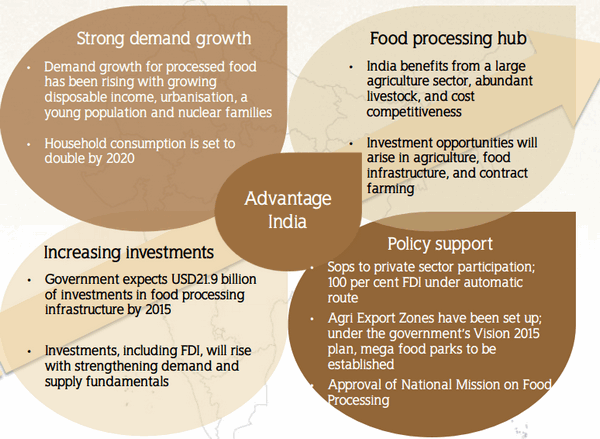
- Scope/Potential
- Obstacles to food processing?
Prologue
In the new Mains syllabus, UPSC has included: Food processing and related industries in India-
- their Scope, significance, Location
- Supply chain management (SCM)
- Upstream and downstream requirements
But ^that’s not “the end”. Food processing topic also overlaps with
| GS-2 |
|
| GS-3 |
|
+ same food processing points can be selectively used for discussing rural-unemployment, food inflation, general inflation, FDI in multi-brand retail; even current account deficit and rupee depreciation: whether its essay / interview or group discussion (in case of SBI/CAT) hell even RBI Officer phase II descriptive papers.
Structure of the [Food processing] Article series:
- We get basic overview of significance-scope-potential-obstacles
- Truckload of Government schemes related to post-harvest management, Mega Food parks etc.
- Model APMC acts, the direct cooperative marketing etc.
- Finance, taxation, FDI, export related issues
- Then we start basic theory of supply chain management (SCM), and upstream downstream issues of individual food processing sub-sectors viz. Dairy, Fruit and Veggies, Egg-Meat-Fishes, Confectionary, Wine, Edible oil etc.
References used for this article series
| Source | Title | comment |
| Books |
|
Initial chapters provide the challenges/problems with food processing industry. Rest goes into actual management, accounting, sales, marketing strategy for a food entrepreneur=useless from UPSC point of view. |
|
Some chapters deal with food industries in China, Australia etc but hardly any good fodder pointsSome chapters provide details of individual food processing sector but mere copy paste job from Vision 2015 PDF document. | |
|
for theory on supply chain management, upstream-downstream requirements | |
| PDFs | State of Indian agriculture 2012-13 (By Agricultural Ministry) | for agro-livestock-fish-production information and schemes |
| Vision 2015 for food industries: part 1 and 2 | for opportunities and obstacles in individual sector: dairy, meat, wine etc. | |
| Flavors of Incredible India: A report by Ernst & Young and FICCI | for supply chain diagrams of individual food processing sector+ Additional points for opportunities, obstacles. | |
| Planning commission’s report on Encouraging Investments In Supply Chains and cold storages | plenty of fodder on
|
|
| 12th FYP documents | doesn’t have much specific fodder points for food processing though. | |
| IBEF report on Food processing industry | some fancy charts, numbers. | |
| Web | pib.nic.in, Indian express | for government schemes, salient features, export/dumping issues. |
Note: All those Food processing related PDFs have been uploaded on https://files.secureserver.net/0sL2N0Ej5XwsWc
12th Five year plan uploaded on https://files.secureserver.net/0sLrYY0FFJRric
Indian food processing industry: Significance
| size |
|
| location | Location wise: Maximum factories in (ie. more than 1000 in given state)Coastal states: Andhra, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala, Gujarat, Punjab, WBNon-coastal States: UP, Punjab
Observe majorities of the food processing factories are concentrated in the coastal states. |
Increasing Employment
- Food processing industry provides plenty of direct and indirect employment opportunities, because it acts as bridge between Agriculture and Manufacturing
- As per ASI survey in 2010, Food processing industry generated highest employment among all industry. Giving employment to almost 17 lakh people.
- 12th Five year plan (FYP) wants to create more than 50 million jobs. Out of that, Food processing sector is to create one million jobs.
Curbing Migration
When food processing plants are setup near agro/rural regions, they reduce:
- Poverty among villagers,
- disguised unemployment
- exploitation of farmers
- rural-urban migration
- unplanned urbanization,
- slums/hygiene/social problems in cities
Curbing Food Inflation
- In the last few years Food inflation has been a major problem. Food inflation is eventually passed through into manufactured goods through higher money wages.
- Therefore persistent high food inflation= bad for general macroeconomic stability.
- well-developed food industry + compact supply chain=reduces food inflation via:
- Disintermediation (meaning no middlemen/commission agents)
- less wastage/spoilage of perishable products
- Thus food industry is significant for reducing food inflation.
Crop-diversification
- Indian villagers are away from market= have to grow cereals. (as we learned in Von Thunen model)
- In recent years, Government increased Minimum support prices for rice and wheat.
- That leads to surplus grain production=>Pvt. Players give less price to farmer=>government has to buy wheat @Minimum support price (MSP) but FCI didn’t have enough storage capacity
- Result: Wheat gets rotten @godowns and railway stations.
- On the other hand, we’ve to rely on imported oilseeds because of higher MSP, farmers prefer to grow rice/wheat than oilseeds=> higher oilseed import adds to Current account deficit and leads to 1$=62 rupees=>crude oil expensive=petrol expensive=everything transported through petrol/diesel gets expensive=thus the cycle of middle class exploitation is complete.
- Coming to the original point: we need crop diversification, all farmers shouldn’t be growing just rice and wheat. But if want to seduce the farmers into growing other crops, then following must be done
- Promote food industry with backward linkages to farmers growing fruits, vegetables, milk, fish, meat, poultry, grain, etc.
- Aggressively market the processed food in India + Abroad
once we’ve done #1 + #2=> then even the farmers away from market area will see good income opportunity in growing non-cereal crops => crop diversification => the excessive “rotting-wheat” surplus problem is solved.
Some filler significance points: food processing
1. Increases shelf life: milk vs butter
2. Increase value: milk vs butter
moveing to….
Scope/Potential
Abundant Raw Material
| India’s world Rank | in production of |
| 1 | milk, ginger, chickpea, banana, guava, papaya, mango, buffalo meat |
| 2 | rice, wheat, potato, garlic, cashew nut, groundnut, dry onion, green peas, pumpkin, gourds, cauliflowers, sugarcane, tea |
| among top five | coffee, tobacco, spices, oilseeds |
With such a huge raw material base, we can easily become leading food supplier in the world. (But we haven’t, because of the obstacles discussed later).
Geographical advantages
- 46 out of 60 soil types are present in India.
- More than 26 types of climatic conditions= can cultivate large variety of fruits, crops, vegetables.
- Large coastline, villagers in 13 states engaged in fishing as their secondary activity.
- Variety domestic animals such as cows, buffaloes, goats, chicken, lamb, sheep.
- Large irrigated area under cultivation. Ample supply of fresh water for human, plant and animals.
New Demand
In the upcoming years, there will be good demand for healthy, modern food products due to following reasons:
- Youth population (age group 15 – 25): doesn’t shy away from trying new food products.
- More Nuclear families: usually working couple => less cooking time + expensive maids=need ready to eat / ready to cook food.
- Rising incomes, middle class and rich families=can afford processed food.
- Emergence of Tier 1 and Tier 2 cities, shopping mall culture.
- Growing migration from rural to urban India + rising income = demand for bread, butter etc.
- Media penetration, advertisements=> “demand” is created for health-drinks, noodles, cream-biscuits, cornflakes etc.
- Celebrity chefs, cookery channels= new dishes, international cuisines introduced=>demand for their ingredients, vegetables in India.
- Diabetes, obesity, Blood pressure, lifestyle diseases =>demand for healthy food.
As a result, food processing industry is expected to reach
| year | turnover USD |
| 2015 | >250 billion |
| 2020 | >300 billion |
Government Initiatives
- Many food processing sectors that were earlier reserved for small scale industries (SSI) have been de-reserved
- FDI limits have been relaxed, Excise duties have been reduced, export subsidies given
- National mission on food processing, Vision2015 for food processing,
- New schemes for mega food parks, cold chain etc.
- Many states have reformed their outdated APMC laws.
and so on… (^all these elaborated in later articles.) Together they facilitate the expansion of food processing industry in India. More ‘scope’ points, specific to individual sector (i.e. Dairy, meat, fish etc) later articles.
so far everything sounds hunky dory but if our food processing industry was so awesome, then UPSC wouldn’t have included it in the syllabus. Then, what are the….
Obstacles to food processing?
| country | __ % of total fruits/vegetables processed |
| India | barely 6-7 |
| China | >20 |
| USA | >60 |
So, why low level of food processing in India?
Economies of scale
When you produce something on large scale, the unit production cost decreases. How / Why?
- When you purchase raw material in large bulk, you negotiate/bargain with supplier.
- Fixed cost remains same (building rent, cost of lights, initial cost of buying machinery etc.) e.g. you bought a ice cream machine for 10 lakh- whether you make 100 liters ice cream or 1000 liters ice-cream per day- its upto you but the more ice cream you produce, the average unit cost decreases. (think of 100/5 vs. 100/50)= hence bigger the plant, cheaper to produce.
Most of Indian food processing units/companies/enterprises/factories are small sized meaning = poor economies of scale. It leads to following problems:
| Aspect | problems of small company / poor economies of scale |
| Pricing | Since unit production cost is high, he can’t sell his products cheap unlike a big MNC, and Indian consumers are price sensitive. |
| Brand-Building | Small players=small profit, seasonal business. In global market they can’t establish themselves as a long-term player – they only do opportunistic businesses, undercut each other. |
| Low Technology |
|
| Marketing |
|
| Un-Export Quality |
|
| retailing |
|
But why do we have this poor economies of scale?
- For long, many food processing items were reserved for Small scale industries only.
- High input costs due to multiple taxes, middle men. Profit level is low=can’t expand.
- Government schemes, subsidies, grants have ‘low-ceilings’ =Individual person can’t setup big plants
- Hard to get bank loans. (more elaboration in later article)
- Bigger the plant, bigger the headache in terms of tax-liabilities. Creative Indian entrepreneurs rather setup multiple small plants to get subsidies/tax benefits of MSME-industries, and sell unbranded food products.
Anyways, some more obstacles for Indian food processing industry:
| Price Sensitivity | Indian public=Low per capita income = higher price sensitivity and higher income elasticity in relation to food expenditure. |
| Preference For Fresh Food | Indians prefer freshly cooked products as compared to packaged products. Traditional mindset: fresh = nutritious. |
| Agri Problems | truckload of agri-problem. We’ll see the individual problems in later articles. for the overview:
|
| Supply Chain Problems |
|
| Logistics |
|
| Infrastructure |
|
| Finance |
|
| Taxation |
|
| Schemes |
|
| Laws |
|
| Market Information |
|
| Manpower |
|
| Packaging |
|
*High packaging cost
| Packaging cost is ___ % of total production cost | |
| Potato Chips | 20% |
| Fruit Juice | 19% |
| Jam | 12% |
| Chicken Nuggets | 8% |
| Branded Atta | 6% |
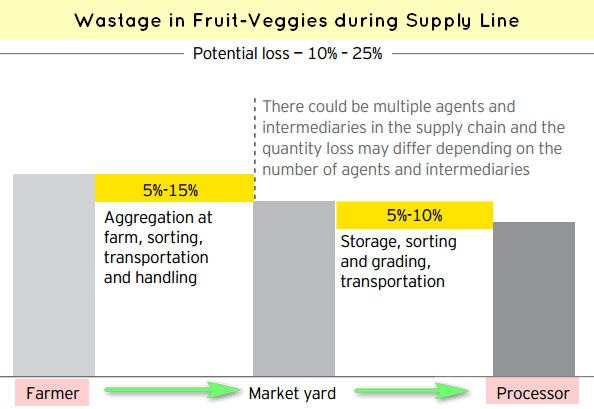
A recent ICAR study on Status of Post-Harvest losses
| type | post-harvest % loss | |
| cereal | wheat | 6 |
| pulses | blackgram | 6 |
| oilseed | groundnut | 10 |
| fruits | guava | 18 |
| veggies | tomato | 12 |
| spices | turmeric | 7 |
| marine | inland-fish | 7 |
moving to more problems faced by Food processing industry:
Lack of organized retail
In USA there are two types of retailers
- Big malls: Walmart etc.
- small kirana walla known as mom and pop shops
But both of them have cold-storage facilities, hence they sell l both dry and wet/fresh food products
| dry | fresh |
| bakery items, noodles, pasta, flour, cheeze etc. | fruits, milk, veggies, meat, chicken, fish |
- But in India, kirana stores don’t have cold storage facilities=> they only sell dry food products.
- and fresh produce is sold through vendors with push-carts=>wastage because they don’t have cold storage.
- Meat, poultry and marine products are primarily sold in separate markets but they too don’t have cold storage=>wastage.
Thus, lack of organized retail, leads to
|
|
Lack of Food testing facilities
- The number of laboratories in the country is insufficient. Most of these laboratories lack world-class facilities and infrastructure. Equipment, Testing manuals outdated
- Many laboratories are not equipped with basic facilities such as for testing antibiotic residues, heavy metal contamination and other toxic contaminants in the food items.
- Very slow response time of Government controlled food laboratories is long, extending to upto 5 years.
- Most laboratories at sea ports are not fully equipped to handle testing of imported products, organic foods, residual radioactive matter, new toxins and allergens, textural analysis, residues of veterinary drugs, enzymes and hormones etc. these tests are necessary for complying with Codex, HACCP , GMP , GHP etc before exporting to in US/EU markets.
Lack of Skilled Manpower
A food processing unit requires skilled manpower, including
|
|
Problems
| Lack Of Men |
|
| Lack Of Courses |
|
| Outdated Syllabus And Professors |
|
| Inspectors |
|
| Engineering |
|
Lack of R&D
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- There is a huge opportunity for developing and commercializing desi foods for export e.g. ethnic beverages such as kokum, coconut water and ethnic food such as khakra, amla preserve etc. But, to make them appealing to foreign consumers, R&D required for product development, food-texture, rheology, mouth-feel, smell, color, packaging etc.
- Internationally, following research-developments are ongoing, while we are generations behind in research:
| area | What foreign players are doing in R&D? |
| processing |
|
| packaging |
|
Transport problems
| Transport capacity | India | developed countries |
| Normal distance covered by trucks/trailers | 250 -300km / day | 600- 800 km/day |
| roads’ capacity to handle maximum weight | 16 tonnes | 36 tonnes (USA) |
- Indian national highways account for only 2% of the total road network but carry 40% of all cargo.
- This puts a high pressure on the highways due to the high traffic volumes => delays in transit + damage to perishable products
- Though highways are well-spread, they’re yet to connect all 550,000+ villages in India
| Railway problems |
|
| Ports |
|
Export Problems
Although India is the second largest producer of food in the world but its share in world’s exports is very low despite its inherent strength in tea, spices and rice. Why?
| expensive Raw Material |
|
| low processing |
|
| low quality |
|
| Branding |
|
| transport |
|
| Packaging |
|
| Dumping |
|
| Devaluating |
|
^these are just few of the many problems/obstacles faced by Indian food industry. In the next article, we see various government schemes related to post-harvest management, food processing industries and agro-export.

![[Win23] Economy Pill4ABC: Sectors: Agri, Mfg, Services, EoD, IPR related annual current updates for UPSC by Mrunal Patel](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/win234b-500x383.jpeg)
we salute you sir for your sincere dedication towards us..
thanks alot mrunal..
well explained sir.thanks a lot.
thank you sir:)
Thanks sir, article is well explained.Need ur guidance for my further preparation.
thanks for such a wonderful work..:)
you’re the real man of steel…
MIND BLOWING JOB
I think MaunMohan should take your service …..Thanks Shri Mrunal Saheb…
Thank you sir…keep heLping everyone…
You are doing a great job…:)
so much potential yet again even more obstacles in food processing..would require ages to develop full potential…Lucidily listed out Mr Mrunal
Sir,
I have one question regarding answering the mains Questions. Can I also write in points as you because I think it will be interesting for a reader in-spite of reading a paragraph.
Please give your feedback on the same then I will prepare in the same way.
Regards,
Nitish Singh
Ghaziabad
mrunal-G your all images gets outdated please update this.
Thank You very much sir for this wholesome answer.
what i can read for storage,transport and marketing of agriculture produce and issues and related constraints?
thanks man … thank a lot
thanks
shukriya jinaab, u r truly serving the humanity……
Sir.. unable to download files .. its showing some error… please help
Hello Mrunal sir… i m first time visiting your site… i m a scholar doing ph.d on the topic of ” linkages and structure of food processing industry of india”… i m lil bit confused about the variables which can be used as a linkages of this industry… i m really confused… i found ur knowledge about food industries is too gud… plzzz plzzz help me out to prepare my chapter for my thesis.. i would be veryyyy thanklful to u….
mrunal sir, i have low vision problem (-4.5 &-4.6 myopia ) so can i eligible for reservation (under low vision category )??
Thank u sir .. this material is very useful for us & my project is completed by this . Thanx once again
thank you sir…. this information is helpful for the mp psc aspirants as well…..
The wikipedia of civil services preparation is Mrunal.org !
thank you so much sir…. though this i got many informations
Great material..very useful nd knowlegable
Food processing is the art to preserve food and maintaining its authenticity it can be done through many ways and different methods are used to preserve the food like canning, pasteurisation but due to lack of resources there are so many hurdles comes on its way like lack of advanced testing facilties , transport issues, manpower Quantum Univeresity is an educational hub providing Bsc hons in food science
ultimate …..the best..
thankyou sir for given useful knowlage.
aapke is support se hum kafi labhanvit ho rahe hai.. ????
Thank you sir…Pls help us…..Please post articles on daily basis
amazing! greatly helful work. . thank you sir