- Steel Based Industrial Regions
- Integrated vs Mini steel plants
- Desi (Indian) Steel Plants
- Secondary industries
In the previous article, we saw the geographical factors affecting the location of iron and coal industry. Now moving to the next topic:
Steel Based Industrial Regions
- Since most of the coalfields are located in the middle-latitudes=> iron-steel industry developed here.
- Since steel is the raw material for many secondary industries (heavy/light engineering, machine tools, automobiles etc.). => Important industrial regions of the World usually found @middle latitudes.
- On the other hand, tropical belt doesn’t have any significant coalmines => hardly any industries belts.
- Africa doesn’t have coal or iron ore (Except some parts of S.Africa)=> hardly any industrial development.
- anyways, let’s check out a few Videsi steel based industrial regions (list not exhaustive)
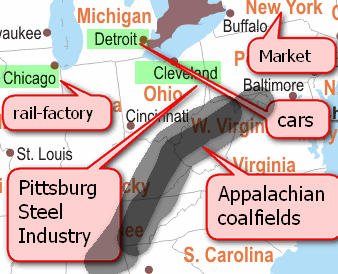
USA, Great Lakes-Pittsburg region
| Factor | impact |
|---|---|
| Raw Material |
|
| Energy | Coal locally available and hydroelectric power from Niagara falls (Cleveland) |
| water4cooling | lake Erie etc. |
| Transport | St Lawrence seaway facilitates transporting raw material and finished products |
| Labour | Large population with diversified skills, due to years of “brain gain” |
| market4steel | The region has diversified industrial activities, one feeding raw material to other.for example
|
Canada: St Lawrence Valley
| Raw Material |
|
| Energy | Hydro electricity from Québec |
| Transport |
|
| market4steel | Machine building for paper-pulp and lumber industry + shipbuilding |
Germany, Ruhr Valley
| Raw Material |
|
| water4cooling |
|
| Transport |
|
| market4steel | Dusseldorf=automobile hub, Volkswagen, Mercedes etc.Ship building industry in Hamburg |
Britain: Birmingham, Midlands
| Raw material | Staffordshire, Warwickshire coal field.Although, nowadays iron smelting industry moving towards coastal locations for imported iron ore. |
| Transport | Central location=>Dense network of railroads. |
| market4steel |
|
Sweden, Central region
| Raw Material | Sweden has one of the richest iron ore resources of Europe. Although they mostly rely on German pig iron as we saw earlier, due to lack of coking coal. |
| Energy | Mountainous terrain + fast flowing river= abundant hydroelectric power (HP).Cheap HP=electric furnaces @steel plants, and electro-chemical industries. |
| Transport |
|
| Market4steel | Volvo cars, bofors guns, Electrolux refrigerators etc. |
CIS: Ural region
| Raw material |
|
| Energy | Volga River= Kuybyshev dam= hydroelectric power |
| Transport | trans-Siberian Railway |
| Market4steel | Agricultural machinery, because Agriculture developed in Central Volga region. |
China: Steel industry
In the late 19th century, in Britain, the coal production and urban industrial growth occurred parallel. Same story repeating in China.
During Mao’s era,
- The railways was in nascent stage and lacked the capacity to move massive quantities of coal to industrial areas.
- Various regions of China did not have interconnected electricity grid.
- Therefore, many industrial regions were setup in North, near the coal mines.
|
|
|
|
|
|
China: Backyard Furnaces
- At the end of 1950s, Chairman Mao had started a campaign called “Great Leap forward” with the aim to transform agrarian Chinese economy to industrialized economy (similar to Russia).
- One of the tool under “great leap forward”=backyard furnaces.
- Mao had ordered each commune, to setup small furnace and produce steel using local wood-charcoal and metal scrap. But this communist-experiment was an epic fail. Because:
- Peasants did not have the skills for metallurgy, work was done in haste, sometimes villagers would just melt their kitchen utensils and product an unusable metal lump meet ridiculously high steel production ‘targets’ given to each commune.
- Although Mao wanted to “double” the National steel production, But result was:
- Steel produced by such backyard furnaces was very weak and non-uniform in quality. If you made any machinery or building with this substandard steel, it would breakdown in a few years.
- Farm laborers were shifted to collect scrap-metal and cut jungles for charcoal=>agro productivity declined and led to famines in later years.
- Forests were cut down to make charcoal => environment problems, soil erosion etc.
before going into Desi steel industry, let’s understand the difference between
Integrated vs Mini steel plants
| Integrated steel plant | Mini steel plant |
|---|---|
handles everything in one complex –
|
|
| takes years to construct an integrated steel plant | Low gestation period. |
| in India, they’re concentrated in Damodar Valley region (Eastern India) | They’re usually away from areas having integrated steel plants (Western India), to meet local demands + to avoid competition from integrated steel plants of the East. |
Indian Steel Plants
Note: maps for most of the following steel plants are given on page 88 and 89 of NCERT Class 11 (India People and Economy), do refer to it.
Moving to the next two Indian steel plants:
Moving to the next two Indian steel plants:
Steel Plant: South India
Vishakhapatnam, AP
| Iron ore | Bailadila, Chhattisgarh |
| Coal | Damodar Valley, Jharkhandalso imports metallurgical coal from Australia |
| Limestone | From MP, Odisha, Chhattisgarh |
| Energy | Natural gas from Krishna-Godavari Basin |
| Transport | Vishakhapatnam itself a Port= rail connectivity with other states.+ helps in import of raw material and export of final products. |
| trivia | First shore based plant of India. |
Secondary industries
- these industries rely on the raw materials produced by other industries
- therefore seconded industries are often located near the companies which make their raw material industry, for example
| industry | located near |
|---|---|
|
steel factories |
|
crude oil refineries |
Engineering industries
| engineering | Light | Heavy |
|---|---|---|
| examples | kitchen utensils, refrigerators, vacuum cleaners and variety of home and office appliances. | shipbuilding, railway wagons, hydro turbines, thermal generators, transformers etc. |
| location | Can afford to transport steel over longer distances and therefore scattered in distribution. | Need large quantities of steel => located fairly close to iron-steel industry to reduce transport cost. |
Heavy engineering industry
They require:
- huge amount of power
- large capital investment
- skilled labor
But main factor is: transport cost for heavy and bulky raw material (steel)=> Heavy engineering industry is usually located near steel plants.
Earlier we saw that steel plants themselves are located in the Damodar Valley and surrounding region (WB, Odisha, Jharkhand) for easy availability of iron ore, limestone, coking coal, energy and cooling water. Now let’s see examples of how heavy engineering industry is also located in the same region, because of those steel plants.
| Place | Heavy Industry |
|---|---|
| Jharkhand | Heavy engineering Corporation Ltd in Rachi. They make blast furnaces for steel plants, heavy crushing and grinding equipment, rolling mills, rigs for oil wells |
| WB |
|
|
|
| Odisha |
|
| Chennai |
|
For the list of heavy industries in Foreign countries, we already saw the examples in those industrial region tables above.
Machine tools
Unlike heavy engineering industry, the machine tool industry doesn’t need to be right besides steel plants. Proximity to market and skilled labor = deciding factors. For example:
| HMT | Hindustan Machine tools.has units in Bangalore, Pinjore (Haryana), Ajmer (Rajasthan), Srinagar etc. |
| Rajasthan |
|
| Kerala |
|
Observe that none of above places are famous for iron-steel production.
Light engineering industry
- These articles are fairly light and require small amount of raw materials. (e.g. various household and office equipment)
- Such industries rely on electricity rather than coal or oil for power.
- For them skilled labour, transport, market, favorable government policies (SEZ/Taxation) are more important factors than proximity to raw material.
- They can be found near major cities rather than in traditional industrial areas near coalmines.
- We’ll see about them in detail later in the articles for market/labour factors in industrial location.
In the next article, we’ll see geographical factors affecting the location of automobile industry and shipbuilding industry.
visit Mrunal.org/geography for the Archive of all geography articles published so far.


Thank u so much sir……after reading ur articles I like generstudies….
plese sir write a articles about relevent of weberian industrial location theory in india.
thanks you sir for the article . . sir you mentioned that tropical regions doesnt have any significant coal fields , but India and Australia have coal fields in good number . can you please clarify it sir . thank you .
India is sub-tropical.
what a lovely superb Post.
It is very beautiful done and I have studied well through this thank u so much
Really very Beautifully done once again thank you