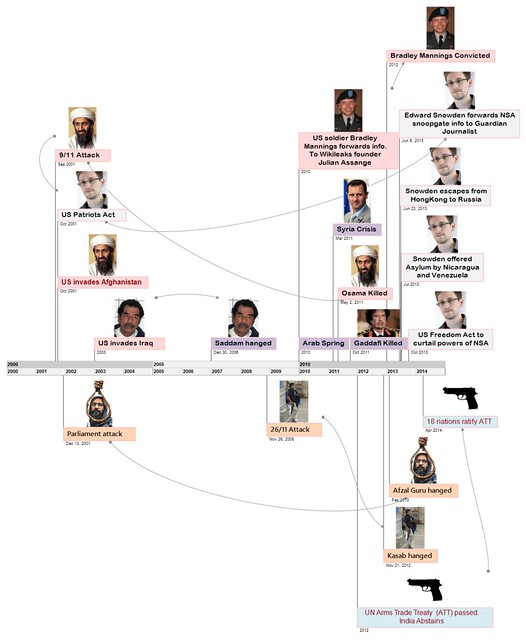
D1: Obama’s NSA reforms
Interview Questions:
- What do you know about NSA snoop gate?
- How is President Obama planning to fix it?
- What do you know about Patriot Act and Freedom Act?
- Do you think we too need these type of acts- to fight against anti-national elements and misuse of social networking media by them?
Background
| Agency | falls under |
| NSA: National security agency | defense department |
| FBI: Federal bureau of Investigation | Justice department |
| CIA: Central Intelligence agency | Independent. |
What is NSA controversy?
| 215 program | Project PRISM |
|---|---|
|
|
- Under the Patriot Act, NSA/FBI doesn’t need to “prove” any terrorist connection, to being the recording.
- They only need to show that information is “relevant” and further investigation is necessary.
- Hence the provisions of Patriot Act were misused by NSA for bulk collection of all call records- both within USA and outside USA.
Obama’s reforms:
- After much furore against NSA, both at domestic and international level, President Obama decided to clean up the mess.
- He decided to stop this practice of systematically storing Americans’ telephone data. (under Section 215 of the Patriot Act)
- NSA will not record all telephones BUT it’ll require telephone companies to keep such metadata.
- And Intelligence agencies would then have to get court approval to access specific records (meaning, Americans are still being monitored!)
Limitations of Obama reform
- Obama is firing from the shoulder of Congress.
- He wants Congress to amend Patriot Act in such way that
- NSA cannot bulk collect data
- but phone companies will still have to record such data
- and later NSA can access it with Court permission.
- That’s all.
- But Patriot Act gives draconian powers to Intel agencies, section 215 is mere a tip of an iceberg.
- For example, Section 315 empowers CIA to bulk collect records of international money transfers from any private company like Western Union. Other provisions to intercept (postal) mails and so on.
- Thus, as long as the fundamental premise of Patriot Act remains the same (that Government doesn’t need to “prove” any connection to a terrorist)….. Until then, powers will be misused, and mass collection of private data will continue.
By the way,
| PATRIOT ACT | FREEDOM ACT |
|---|---|
| After 9/11 attack on World Trade Centre. | after NSA snoopgate, 215 program, project prism, Snowden leaks (=all thanks to misuse of Patriot act) |
| passed in 2001 | This bill was introduced in 2013. Yet to be passed. |
| Aims to give superpowers to US agencies to fight against terrorism. | Aims to curtail those superpowers given under Patriot Act. |
| — | This is a new bill by Republican party. Although democrats also support it because of angry junta. |
| President Bush signed it | President Obama will sign (If the bill is passed in both houses of US Congress.) |
D2: Obama hands over ICANN to world
What is ICANN?
- Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers. HQ: near Los Angeles.
- ICANN is a non-profit corporation, manages internet protocol (IP) numbers and Domain name system (DNS).
- Example: Yahoo.com (domain name) and 67.195.160.76 (IP address).
- Domain name service (DNS) provides translation between that domain name vs IP addresses. so aam-juntaa doesn’t need to mugup the list of IP address for any website.
US control over ICANN:
- ICANN works under contract of US dept. of commerce.
- Mar 2014: Commerce department decide it’d not renew the contract. (Expires in Sep15). But instead, they asked ICANN to design new plan to run this system, with global-participation of stakeholders across the world.
Why is US giving up control over ICANN:
- Now USA thinks that Internet should run under global internet governance (!!) and defend the right to free speech.
- However, its decision came after wide opposition by countries against US snooping/NSA-Snowden controversy. Great opposition by Brazil. Germany went on to declare separate European internet.
Impact on World
- The impact of this decision depends upon the how and what alternative mechanism would be conceived by the international leaders.
- China and Russia want to have internet under auspice of international organisation like UN or ITU, through which it can be regulated as well as constrained.
India’s stand?
- India welcomed US decision.
- India wants democratisation of internet with freedom of expression. (and measures to stop its misuse e.g. hate speech.)
- India fears that US, Russia and China together may form an alternative mechanism that fulfils their own interest- something akin to UNSC/veto power.
- India favours internet governance under a multi-lateral UN body, whose stake-holders are not from government but from civil society, academia and businesses.
Visit Mrunal.org/Diplomacy for entire list articles on Diplomacy & International relations (IR) for Mains GS2 paper of UPSC Civil service Exam.

![[IR By Pavneet 4/5] Art of Answer-writing: Directive Word#2 “DISCUSS” – Impediments to India’s permanent membership at UN Security Council (UNSC)](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/webinar-pvnt-c-500x383.png)
thnx.
I have completed M.A. in Eco n want to appear for IES exam, how to start preparation for it . Plz guide me Sir.