- Prologue
- What is corporate governance
- Type of companies
- Holding, Subsidiary and Associate companies
- Board of Directors
- Annual General Meeting (AGM)
- Audit related provisions
- 4 new statutory bodies
- 2% Corporate Social responsibility (CSR)
- SEBI’s corporate governance norms
- Appendix: Related party transactions (RPT)
Prologue
As such I’m writing summaries of Economic survey 2013. But Companies Act, 2013 is a recurring term in many chapters. Therefore, needs to be covered parallel.

What is corporate governance
Many definitions, you need to memorize at least one- for the GS4.
Corporate governance is a way of directing the company
- To protect stakeholders’ interest. Observe the word “stakeholder” not “Shareholders”. Meaning, company should look after its customers, raw material suppliers, wholesales, dealers, employees, shareholders…all for them
- To comply with legal-regulatory requirements. Not just from technical / audit point of view but from ethical point of view as well- for example misleading ads, harmful products, environmentally unsustainable production methods etc.
- Absence of corporate governance – leads to fraud, mismanagement, embezzlement and harm to society and environment.
| Companies Act | SEBI norms |
|---|---|
| original act made in 1956 |
|
| new act passed in August 2013 |
|
|
|
Type of companies

| Companies Act 1956 | Companies act 2013 |
|---|---|
| no such thing |
|
| private limited: 2 to 50 members | 2 to 200 members.minimum capital Rs.one lakh |
| public limited: same in both acts | 7 to unlimited membersminimum capital Rs.FIVE lakhswithin that, two subgroups |
- Listed company- if shares listed on any Indian stock exchange e.g. Infosys, TCS etc.
- Unlisted company: self-explanatory. e.g. Nokia India, Sahara’s those two Housing finance companies*.
* which were selling OFCDs & got Subrato in Jail, for he did not get SEBI permission before selling OFCDs and did not repay investors’ money when SEBI ordered him to.
- overall, 9 lakh companies in India
- >90% of Indian companies are private limited.
Holding, Subsidiary and Associate companies
- Holding company = itself owns 20% or more shares of another company.
- that “Another company” is further classified into:
| subsidiary company | associate company |
|---|---|
| If 50% shares owned by holding company. | If 20% or more shares owned by holding company. |
Board of Directors
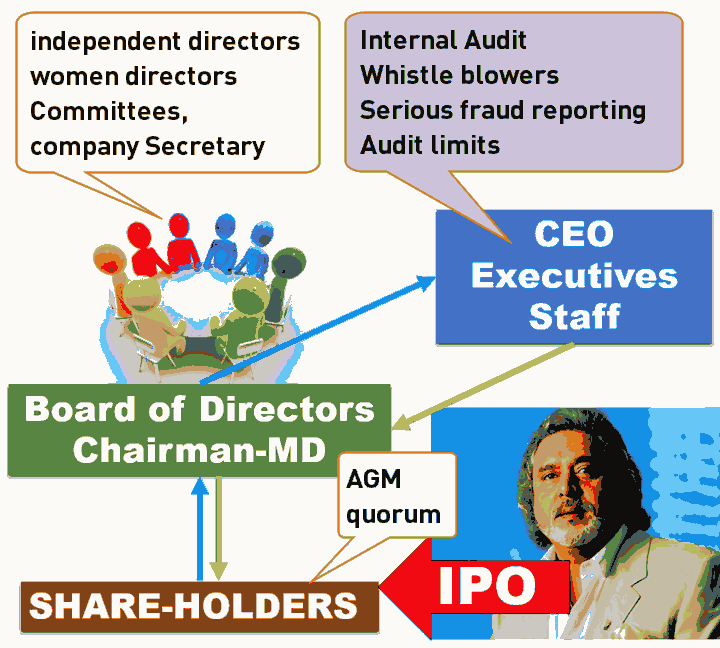
Companies Act 2013: Salient features for corporate governance
| democratic country | voters => parliament =>executive |
| companies | Shareholders (AGM) =>board of directors => CEO, executives. |
Board of directors consists of
- Chairman
- executive directors / full time directors
- nominated directors (By banks or central Government- e.g. during mega scam like Satyam)
- Independent directors: to protect the interests of minority shareholders.
Now let’s check provisions of Companies act 2013 for directors
Minimum directors in each company
| One person company | 1 |
| private ltd. | 2 |
| public ltd. | 3 |
- Maximum 15 directors
- Can add even more directors by resolution in AGM (Annual general meeting of shareholders).
- One person can serve as director in maximum 20 companies
- One director must be Indian resident (i.e. staying in India for 182 days or more)
- One director Woman in the board. (SEBI norms says the same)
- If director remains absent for 12 months- consider his position vacant, and get new guy. Means Sachin and Rekha will have to think twice before becoming directors in any company.
Anyways, these are provisions for directors, in general. Now let’s check specific provisions for Independent directors
Independent directors (ID)
Job of Independent director = protect the interests of shareholders, particularly the minority shareholders. He has to fulfill following criteria:
- He is not a Promoter of the company, NOT nominated by the Chairman
- He has no pecuniary interest in the company, except salary as director. (meaning company’s wholesaler, retailer etc. cannot become independent directors)
- He is not an employee of the company
Companies Act 2013- ID requirements
- 1/3rd directors in public ltd. company must be Independent directors. (so, if company takes 15 directors, 5 must be ID)
- They’ll have 2 terms of five years each = total 10 years
- But their performance will be reviewed in shareholders’ Annual General Meeting (AGM). Means again Sachin and Rekha will have to think twice before becoming Independent directors of any company.
- After 10 years’ service, if they want to join same company as ID again, they’ll have to wait for 3 years cooling period.
SEBI norms: Independent directors
Let’s pause from companies act for a while. We know that
| Companies Act | SEBI norms |
|---|---|
| new act passed in August 2013 |
|
so, what does SEBI norms say about these independent directors?
- 10 years term yes BUT from retrospective effect. Meaning, if I were an Independent Director in a company since 2010, then my “retirement” is 2020. (and not 2014+10=2024).
- One person can become Independent director of seven companies at most.
- If he is a ‘full time’ director in a single company, then he can become ID in 3 companies at most.
Enough of directors, moving to next topic:
Board meetings- duration and quorum
- Doesn’t apply to one person companies.
- Company must hold minimum 4 meetings per year
- must not have more than 120 days gap between two meetings
- Quorum: 1/3rd strength or two directors, whichever is max.
- If directors cannot give physical presence, video conferencing is permitted.
- Directors must be given 7 days prior notice. (So they can make prior travel arrangements.)
BoD: Committee
just like parliament has PAC, estimate Committee, departmental standing Committee etc. same way, Companies will be required to make following Committees out of their board members
- Audit committee
- Stakeholder relationship committee (SRC)
- CSR committee (CSRC)
- Nomination and Remuneration committee (NRC)- they’ll observe following
- MD/Directors’ salary doesn’t exceed 11% of company’s profit
- Pay rise of CEO, directors etc. vs company performance
- They’ll present this data in AGM.
So far, we checked provisions related to directors and board meetings. Mock questions can be formed by twisting the facts, for example
Which of the following statements are correct as per the new companies Act?
- 1/3rd directors must be Indian residents
- atleast one woman director must be Indian
- atleast one independent director must be a woman
- none of above (Correct answer)
Moving to next topic
Annual General Meeting (AGM)
- One person company: no need
- Public & pvt LTD. companies…yes they’ve to hold AGM.
- General notice can be sent by letter / email to shareholders.
- Proxy voting permitted.
- Electronic Voting also permitted (as per SEBI’s corporate governance norms).
- Quorum depends on number of shareholders.
| members | quorum |
|---|---|
| private ltd company | 2 members |
| public ltd company upto 1000 shareholders | 5 members |
| public ltd >1000 upto 5000 | 15 members |
| public ltd. >5000 shareholders | 30 members |
Audit related provisions
Audit Committee
- Have to make an audit Committee from board of directors.
- Its chairman must be an independent director.
- Provision for internal audit by CA, Accountants, even other (non-CA) persons. ICAI is opposing this.
- Companies will have to setup whistleblower mechanism.
External Auditors terms and responsibility
- One auditor can audit maximum of 20 companies.
- If he finds any fraud- he must report to both Union Government (ministry of corporate affairs) and during the AGM.
| individual auditor | 5 years |
| audit firm | 2 terms x 5 years = 10 years |
After that cooling off period of 5 years.
Why? Well, same reason why Government officials should be transferred after 3-5 years so they don’t develop nexus with local thugs.
Company Secretary
- Company Secretary acts as a link between board of directors and shareholders.
- He arranges BoD meetings, AGM, ensure quorum, minutes of the meeting etc.
- Companies above certain share capital, have to compulsorily hire company Secretary.
| Companies Act 1956 | Companies act 2013 |
|---|---|
| Companies above capital of Rs. 5 crore => have to compulsorily hire company Secretary. | 10 crore |
- There are hardly ~7000 companies in India having share capital of 10 crore or above. (While there are >20,000 people doing this course).
- For remaining companies- not necessary to hire company Secretary = less jobs available for company Secretaries.
- Therefore company Secretaries and their national body, are opposing this new provision.
Company’s Loans
- Company cannot give loan to director / related persons
- If company gives loan to anyone- then its minimum interest rate must be higher than that of Government securities (G-sec). (Otherwise CEO might pass loan to his own “puppet” driver at 2% interest and then use It for betting in cricket or share market!)
- Company must get Credit rating (“A”, BB, C etc.) before accepting public deposit (in collective investment schemes)
- Companies have to appoint a chief finance office to look after audit and account.
4 new statutory bodies
Not 1, not 2, not 3 – total 4 new statutory bodies will be created under Companies Act 2013.
In other words, if any ministry wants to learn how to harass UPSC aspirants- they should take COACHING from babus @ministry of corporate affairs.
| Matter | Statutory body |
|---|---|
| tribunal / litigations |
|
| accounting norms |
|
| awareness generation |
|
| fraud detection |
|
Let’s check their features one by one
#1: National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)
| Composition | Judicial + technical members |
| Deadline | have to finish case in 3 months |
| Hearing | You can present case by your own, via lawyer, CA or company Secretary. |
| Appeal | If either party is unsatisfied with NCLT verdict, they can approach NCLAT (national company law APPEALATE tribunal). |
Disputes where NCLT will adjudicate:
- Company fails to comply with any provisions of the act (e.g. quorum not maintained, auditors not changed after deadline etc.)
- Merger and acquisition disputes
- Converting Public ltd. To private ltd.
- Filing Class action suits (e.g. Satyam’s US shareholders filled such suit in USA and recovered money. But Indian shareholders couldn’t because 56’s act had no such provision)
#2: National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA)
- 1 Chairman + 15 members
- Will set Accounting standards for companies
- Will have Powers of civil court.
- Aggrieved party can appeal at NFRAA (National Financial Reporting APPELATE Authority)
- Can debar CA and accountants for professional misconduct.
- ICAI unhappy with this provision- because under Chartered Accountants Act, 1949, they’ve the powers to take action against CAs.
#3: Investor and Education Protection AUTHORITY
- As the name suggests, this fund money is used for awareness generation, financial literacy so investors don’t fall into traps like Saradha chit fund, Sahara OFCD etc.
- Where do they get money? Ans. Companies have to pay dividend, interest and principal to their investors.
- But if any money remains unclaimed (death, disappearance of investor etc.)=> Money goes to corporate affairs ministry => into this fund.
This is not a new thing. Already exists, But 2013’s act gives it statutory status, with following provisions
- HQ at Delhi. Regional offices across India.
- Chairman: Secretary of Corporate affairs ministry
- Membership: executive directors from RBI, SEBI; experts from legal and financial sector.
#4: Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO)
- Not a new body, already setup in 2003 under corporate affairs ministry (based on Naresh Chandra report)
- It has solved- Saradha chitfund, Satyam scam etc.
Then what’s new in Companies Act 2013?
- SFIO is made a statutory body.
- It’ll have power to Search seize arrest (until now, it could only examine documents)
- SFIO investigators will have same powers under CrPC, like a police officer.
- Once SFIO gets case, other agencies can’t proceed.
- State police, ED, CBI etc. will have to handover documents, witness and cooperate in further investigation.
2% Corporate Social responsibility (CSR)
Under the new act, Companies will have to spend 2% of their last three years’ average profit on CSR activities. (e.g. schools, slum redevelopment, “chowkidari” to prevent junta from urinating/defecating around railway station etc.)
| Net profit | 5 crore (before tax) |
| Net worth | 500 crore |
| turnover | 1000 core |
- 2% rule doesn’t apply to income earned from foreign branches of the above companies.
- Above companies have to setup CSR Committee made up of 3 board of directors.
- Committee will formulate & monitor CSR policy.
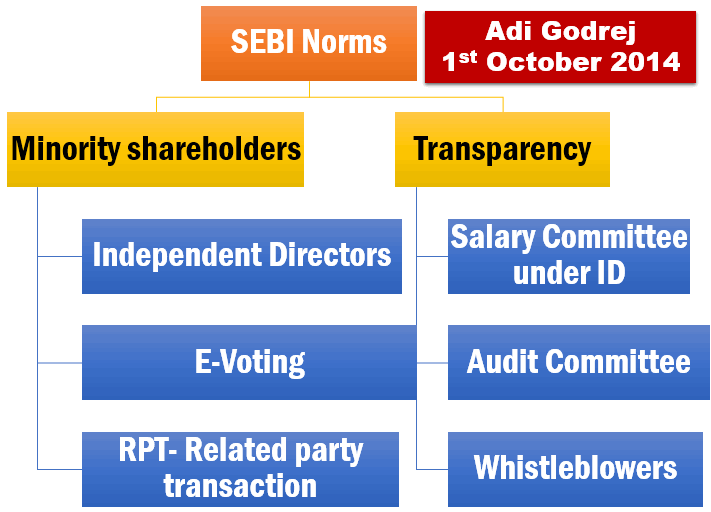
SEBI’s corporate governance norms
- 2012: Adi Godrej Committee
- 2014, Feb: SEBI notified the norms
- 2014, 1st October: these rules will become effective.
- They run parallel to what is already given under companies act.
- Following diagram summarizes it- just write two lines on each of them and you’re done with 100-200 words question in mains.
Appendix: Related party transactions (RPT)
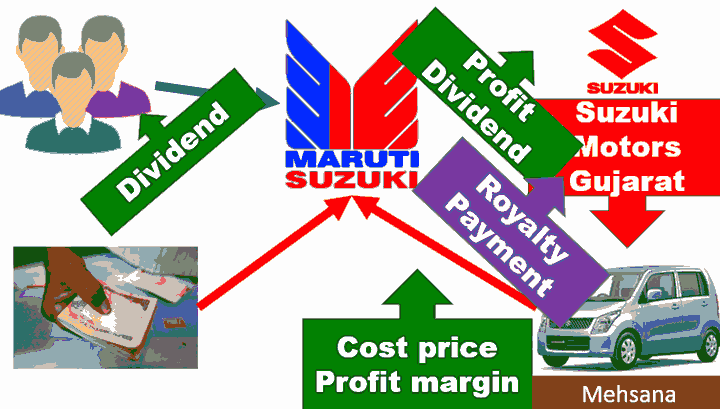
Lengthy topic, not important for prelims. But will be important for (MBA) interviews because this Maruti-Suzuki controversy will drag on for long.
| majority shareholder | Suzuki Japan |
| minority shareholder | HDFC, Reliance Capital, ICICI, SBI etc. |
- 2012: Strike in Manesar plant, Haryana. Manager died, more than 3000 crore lost due to halt in production.
- After this, Suzuki (Japan) registered a separate company “Suzuki Motors, Gujarat” to setup separate factory in Mehsana, Gujarat.
- Suzuki itself will manufacture the cars in this Gujarat plant, will hand It over to Maruti Suzuki for selling through its showrooms.
| before | after |
|---|---|
|
|
So in this case, we’ve two parties
Holding Company Suzuki (Japan) that owns ~56% in Maruti Suzuki India ltd.(Subsidiary company).
Now one party (Japan) is taking an action (of setting plant in Gujarat), which will have negative ramification for the investors in other party (Indian Maruti).
This is one type of “related party transaction”.
As per companies Act 2013, Related party transactions require voting-approval from majority OF the minority shareholders.Therefore, Suzuki has decided following:
- First they’ll do roadshows and seminars for awareness generation among shareholders (about the benefits of Gujarat plant)
- (Rumors) They have even hired investment bankers to influence the FIIs who own shares in Maruti Suzuki India.
- Voting will be done probably in September 2014’s AGM
- At that time, Suzuki can’t vote (because majority shareholder) but IF from the remaining shareholders, if 3/4th vote in favor, then Suzuki can proceed in setting up Gujarat plant.

![[Win23] Economy Pill4ABC: Sectors: Agri, Mfg, Services, EoD, IPR related annual current updates for UPSC by Mrunal Patel](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/win234b-500x383.jpeg)
u r doing a great job sir, thank u…
Sir, im confident about prelims result and taking commerce optional for mains. For CA exams after november new company act 2013will be followed. But what about UPSC mains?? 2013 act Or 1956??? Pls assist.
Pls try to answer after enquiring from ur sources. It will be a great help.
thank you for sharing knowledge sir
Sir u r all life saviour for me…..u make these concepts so easy DAT I can’t express.wt a great social work u r doing for us……thanks a lot ….in a few days m gonna face my bank interview n m very much clear through ur blog….one more thing how can I search particular topics in ur site….m unable to find DAT……
CAN I USED THIS INFO. FOR B.COM HON 2ND YEAR EXAM IN 2015 FOR SOL..
PLS.. ANYONE TELL ME..
thank you sir…
Hi murnal, could you pls help me understand how are the shares of a public ltd company traded if it is not listed
You are simply the best Mrunal….
THANKU SIR
Thanks sir ….. It is better for us …… we receive a lot of knowledge for your notes. It is a step by step Notes
Thank you Sir….I prepared well for interview with your stuff.
Excellent job Sir. .
Sir, Companies Bill indirectly made CSR. So what may be the challenges expected in its implementation?
Thank You soo much sir
THANKING YOU
THANKU GREAUTY FUL TOU
thanks sir
Sir I want to know about preparation of Indian economic service.suggest me.plz
Sir, what is dabba trading ?
sir,i want to registered company …under act 2013 how the process to registered…plzzz give me some hint ..like what type of documents reqires …plzzz sir help me
I’m impressed
I m fully satisfied with u’r information.simply it is aa short nd sweet…it is very useful for my CMA exams thnx alot
Thnx allot for ur lectures and Note’s Sir i am big fan of ur lectures. ..sir i am preparing for civils exam 2018 may i know these notes are usefull for preparation for 2018 Orel’s i shud make some changes.. ..it’s better for me if u suggest some lectures of you in which i can modify notes..plz sir
Awesome great information