- Prologue
- [Block-1] Planning commission (PC) why replace?
- [Block-2] Budgeting reforms
- [Block-3] Banking sector
- Misc.Short term reforms
- [Block-4] Farm subsidies, buffer-stock, PDS
Prologue
Revision of selected topics for GS3 syllabus:
- Issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources
- Government Budgeting.
- Issues related to direct and indirect farm subsidies and minimum support prices; Public Distribution System
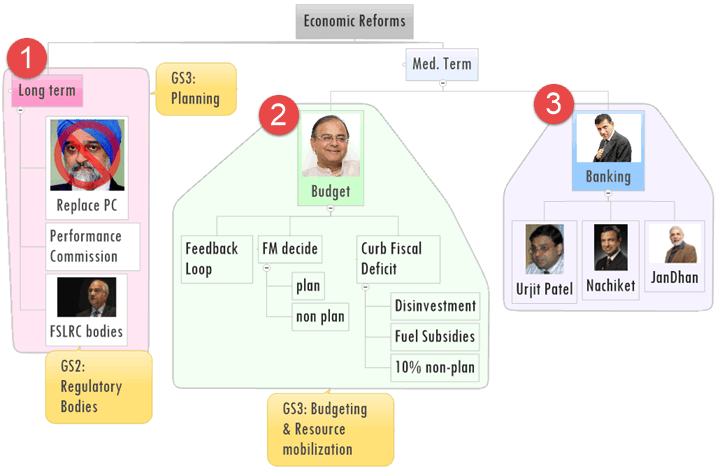
let’s begin from red circle no.1
Planning, budgeting and resource mobilization should be seen from three stage economic reforms. (as suggested by Economic survey)
| Duration | Focus | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Long term |
|
|
| Mid-term | Budgeting |
|
| Banking |
|
|
| Short term | Stroke of a pen @individual ministries | MoEF reforms in 100 days. |
[Block-1] Planning commission (PC) why replace?
Structure functions = read from M.Laxmikanth. Planning commission sucks because:
- Achieved >9% GDP growth-rate during 2005-07, thanks to American boom prior to sub-prime crisis, pretty much all nations of world experienced high growth. So 9% GDP did not come from Montek’s magic wand.
- Post sub-prime crisis, failed to evoke the “animal spirit” in Indian economy. GDP going down, inflation going up for 2008 to 2013.
- Reduced poverty by doctoring the BPL-line. Tendulkar line says 27 crore BPL, if we use Ranga line then 37 crore BPL. Planning commission brags reducing poverty line on Tendu’s parameters.
- Toothless body, can’t hold State/union/ministries/departments accountable for failing to achieve targets.
- Hopes that CAG =>Public accounts Committee will take care accountability part. But PAC too is pretty much toothless.
- Failed to implement land reforms. Faulty policies for MSME, industrialization, Factory-labour law problems we saw in GS2 MFG revision note.
- Office manned by Generalist IAS/IES with short tenure; panel members filled with academicians and jholachhap NGOs. Need subject specialists with international exposure like Rajanbhai.
- Designed CSS with One size fits all approach and a few extra crores to NE/J&K/Hill-states and LWE.
- But for long, it did not use pilot projects / sample testing / interaction with states.
- Hence, IAY, ICDS etc. programs failed to show tangible result despite pumping crores.
- Tried to bypass state Governments via NGO-funding, DRDA. Hence States unenthusiastic about implementing Central-schemes named after you know who.
- Only in 2013- reforms done like reducing # of CSS, 10% flexifund to states, direct transfer of money to state consolidated fun etc. But it’s too late.
- Shortcomings in planning commission => new bodies sprung up like PM’s economic advisory council, PM’s project monitering group and so on=> more brains=> more lack of coordination.
- Modi says planning commission (PC) is beyond fixing- just like Gotham city and Delhi city. Wants to replace it with a body similar to China’s National Development reform commission. (NDRC)
- Moily says NDRC good for China but not suitable for federal nation like India. Better restructure PC again by addressing above 13 bullets.
Modi’s NDRC
Modi wants to replace PC with a body like China’s NDRC. (or atlest experts say so). Let’s
| Chinese NDRC doing following | India present system |
|---|---|
| Makes macro-economic policy | FM+RBI |
| Approves investment & construction projects | CCI, FIPB and many other bodies @union and state level. |
| Energy & oil policy | Oil ministry, DG Hydrocarbon |
| Looks after Poorer Western Provinces | Separate ministry for NE Development |
| Parent: State council headed by President of China | Headed by PM. Disinvestment in ONGC, CIL etc . |
In short, Chinese NDRC controls pretty much everything, just like a communist unitary Government would want. Hence Moily’s criticism- NDRC unsuitable for Federal India.
Productivity commission
- Problem in Environment laws so TSR Subramanium Committee, Problem in railway so Bibek Debroy Committee, problem in IPR so Prabah Sridevan Committee…..such piecemeal approach and firefighting must stop.
- Economic survey says create a separate Statutory body called Productivity commission”.
- To Review laws, regulations, processes continuously.
- Publish report cards of each ministry and department.
- Advanced economies have such bodies.
SriKrishna’s FSLRC
| Sahara-scam | SEBI ordinance |
|---|---|
| NSEL scam | FMC shifted to FM |
| Saradha chitfund scam | Plan to amend Chit fund act |
- Such piecemeal / firefighting approach => scamsters shift base from one sector to another, use technicalities and loopholes to get stay orders & escape.
- Hence we need comprehensive reform in financial rector regulators.
- 2011: Government setups Financial legislative reform commission under Justice BN Srikrishna.
- Gave two type of reforms (1) non-legislative (2) legislative
Legislative reforms:
- Present: dozens of acts for banking, insurance, provided fund, forward market, NBFC etc.
- Srikrishna says repeal them all, and enact a new law “Indian financial code”. (IFC)
- IFC will be a single, unified financial law with precise objectives; clear-cut jurisdictions for fin.sector regulators with adequate checks and balances.
New Financial sector regulators
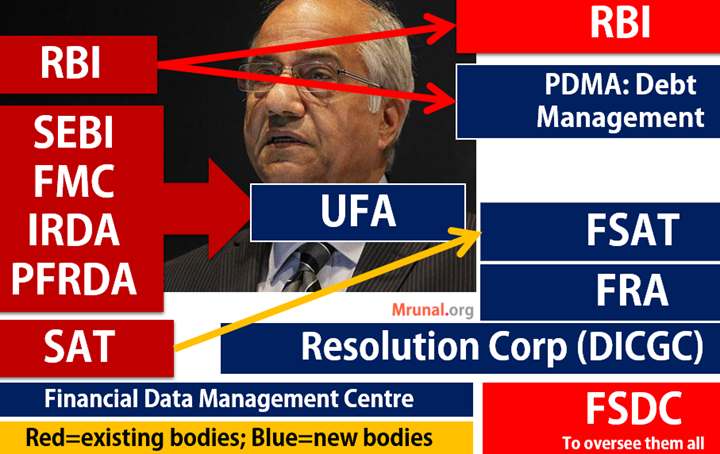
Financial sector legislative reform commission (FSLRC) recommended this
| Present body | Replacement in Srikrishna’s IFC |
|---|---|
| RBI |
|
| SEBI, FMC, IRDA, PFRDA | All to be merged into a single UFA: Unified financial agency |
| SAT (SEBI kaa Baap) | FSAT: Financial sector appellate authority = UFA kaa baap. |
| Ombudsmans, consumer courts | FRA- Financial redressal agency to hear all complaints. |
| FSDC |
|
Misc. bodies: data centre, resolution corp.
PDMA Debt Management
- Present, RBI is the debt manager of the Government. = Conflict of interest.
- Government releases Government securities (G-Sec) to borrow money from market. RBI uses the same G-sec to control money supply = conflict of interest.
- Srikrisha (FSLRC) proposed setting up separate public debt Management office. (PDMA)
| Yes because | No because |
|---|---|
| 13th FC (Kelkar) and FSLRC (Srikrishna) recommend this path.Advanced economies like Sweden, NZ, German, Denmark etc. use this path. Central bank and debt Management office are separate. | Only RBI got necessary staff, infra and expertise to manage debt of both union and state. No time for trial-error with new body |
| No conflict of interest=Better Management of public debt and better monetary policy |
|
PJ Nayak Committee
- Repeal bank nationalization and SBI act
- Sell the shares of Public sector banks to newly setup “Bank investment company”. (BIC)
- BIC to look after appointments, business strategies.
- Until BIC done, setup Bank board bureau (BBB) to look after board-CMD appointments.
- Age tenure reforms for upper Management.
- Result: less Government control = more efficiency in banks.

now, let’s focus on red-circle No.2
[Block-2] Budgeting reforms
- Both rail and general budget 2014 covered under Mrunal.org/economy
- But syllabus says “budgeting”. So, let’s check three reforms in “budgeting” process.
Bud1: FM 4 kharchaa-Paani
Until now, Department got funding decided by two brains
- Non-plan Expenditure = FM
- Plan Expenditure = PC Planning commission.
Result: Sub optimal allocation, Diffused accountability, poor return on the money invested.
Solution: Budget making unified @FM, he’ll decide both plan and non-plan Expenditure.
Bud2: Feedback Loop
Economic Survey observed:
- Government doubled the money spent on each child, in last 7 years.
- Yet as per NGO Pratham’s ASEAR report, >50% of class5 kids can’t read class2 book; >50% of class8 kids can’t do division.
- Every year, ministries given higher funds than last year, irrespective of achievement.
Survey solution: “Feedback loop” mechanism in budgeting.

Budgeting reform: Feedback loop
- After financial year is over, get an independent body to analyze ministry/Department’s performance.
- Next year’s budget depending on performance card: increase fund/ decrease fund/ change scheme features/ give bonus to babus / cut salaries of babus
Bud3: Curbing fiscal deficit
| Angle1 |
|
|---|---|
| Angle2 |
|
| Angle3 |
|
| Reduce this | To this | By this | But present level is this |
|---|---|---|---|
| Effective revenue deficit | 0% | 2015, 31st March | 1.6% of GDP |
| Fiscal deficit | 3% of GDP | 2017, 31st March | 4.1% of GDP (>5 lakh cr) |
So, what has Modi done to reduce fiscal deficit?
- FD1: Disinvestment
- FD2: Fuel subsidies cut down
- FD3: 10% non-plan Expenditure cutdown
FD1: Disinvestment Keypoints
- Pro: less Government control over board= more efficiency. Overstaffing, lossmaking gone.
- Anti: private sector can’t cater poor, Government earning declines, selling assets to fillup fiscal deficit is unhealthy.
Disinvestment in India
- Permitted with 91’s Industrial policy.
- Then Rangarajan, GV Ramkrishan panels and various chillar Prime ministers
| Government | Disinvestment Policy |
|---|---|
| Vajpayee |
|
| UPA-1 |
|
| UPA-2 |
|
| Modi |
|
FD2: Fuel subsidies curbed
- When petrol, diesel, kerosene sold at below international price=> OMC losses (under-recovery)=>Government gives them oil bonds as “subsidy payment”.
- 2010 Kirit Parekh Committee says stop.
- But LPG, Kerosene…administered prices continued.
- Petrol deregulate: OMC+Petro Ministry to decide price
- Diesel deregulation: Jan’13. 50 paisa increased per month. Finally at deregulated @Oct 2014.
FD2A: Diesel deregulation: benefits of
- Jan 2013: diesel price increased by 50 paisa each month.
- Oct 2014: market linked. If international price go down, diesel to be cheaper.
- Became Rs.3 cheaper than Sep.2014 => inflation goes down=> RBI may cut repo rates=>cheaper loans=>more demand of goods and services=>GDP, jobs improve
- Less subsidy burden=>less fiscal deficit=> Soverign credit rating improves=>more FDI, FII to India.
- Under recovery gone=>OMCs can do Biz.expansion, give better service.
- Reliance-Essar can sell diesel. (till now relied on state-OMC bcoz they did not get subsidy)
- Junta to buy Fuel efficient car, no more blind purchase of diesel vehicles because it was cheap.
- More Usage of Public transport
FD2B: Modified DBT

DBT will help reducing LPG subsidy burden
- 2013: Aadhar Linked DBT (12 cylinders)
- 2014: Selected districts: Modified DBT. Don’t need Aadhar. Even bank account no. / LPG customer id sufficient. Rs.568 will be transferred.
- 1/1/15: all India implementation.
- Will reduce subsidy burden by 15%. (LPG subsidy costs ~48k crore)
- Additional reform underway: Government to give LPG subsidy on per kg basis rather than per cylinder basis. Will help even migrants and slum-folks who buy small sized cylinders. At present small cylinders don’t get subsidy.
FD3: 10% cutdown in Non-plan Expenditure
- At present Total Non plan: ~12 lakh crore | Plan: ~6 lakh crore
- FM ordered following, for 2014-15
- No 5-star hotels for conferences
- Only cheapest fare air-travel
- Freeze on new vehicles & appointments
- Result: 10% reduction in non-plan => ~1.2 lakh crores saved.
[Block-3] Banking sector
B1: Why Monetary policy ineffective?
In India, RBI’s monetary policy fails to curb inflation because
- People don’t have many investment alternatives. Commercial banks have high deposits. Repo rate change doesn’t affect their money supply immediatly.
- Monsoon uncertainty, cyclone, flood, draughts => Supply side constrains
- Crude oil, gold prices outside RBI control
- fiscal deficit, public borrowing, subsidy leakage=RBI’s money supply calculations disrupted
- Unorganized money market; Shroff; lack of financial inclusion. RBI can’t control their interest rates.
- Then how reform monetary policy? Ans. implement Urjit Patel Committee report.
B2: Urjit Patel’s reforms 4Monetary Policy

sorry, too much workload, no time to change Chindu’s photo.
Point#1: inflation targeting
- Target=4% CPI, +/-2% Band [=control inflation in 2-6% range.]
- Tool=Repo as policy rate, +/-1% spread in RR-Repo-MSF,
- Time limit: 0/12/24 (months)=10/8/6% (CPI)
- Strategy=keep repo higher than CPI.
Point#2: fixing accountability
- Setup monetary policy Committee (MPC) headed by RBI governor, 3 insider (RBI official) and 2 outsider members.
- Decide policy by majority voting.
- Issue public statement in case of failure.
Point#3: Government to help RBI
- Stop administered prices (MSP), wages (MNREGA), interest rate (farm loans
- Implement Vijay Kelkar fiscal consolidation report.
- Religiously follow FRBM.
B3: RajanBhai’s monetary policy
- Bi-monthly policy from April 2014 onwards(earlier every 45days)
- Kept Repo unchanged to 8%. Although reduce SLR from 23% to 22% => banks left with spare money to lend to private sector=>GDP growth.
- Agreed to target CPI: 8% by Jan’15; 6% by Jan 2016.
- Oct 2014: CPI down to 6.45; meaning its working.
- External challenges: 60% chances of El-Nino, Geopolitical problems in Ukraine, Syria, Iraq & their possible impact on crude oil prices.
B4:Jan-Dhan
- why fin.inclusion important for poverty removal=> check GS1 revision note.
- Fin.inclusion attempts in past: Nationalization, RRB, Coop banks, BCA, Swabhiman, Swavlamban, MFI (24%), No-frills account, 25% rural branch rule, BMB, Bandhan, IDFC.
- Still 49% families- no account; 55% rural dalits borrow from money lenders @34% rate.
What is Jan dhan?

six pillars of Jan Dhan Yojana
Dept of Fin services. 15/08/14; 7.5 cr families in 1 year; 6 pillars strategy
- 1.Sub-service area to cover 1000-1500 families within 5 kms distance
- 2.Each family 1 account, rupay debit card, 1 lakh accident cover, 5k overdraft if good credit history.
- 3.fin.literacy campaign; 4.credit guarantee fund to cover losses 5.sell micro insurance product 6. DBT.
Criticism of Jandhan
- Insurance cover only if rupay card used every 45 days. (NPCL pays your premium, NPCL runs Rupay)
- Banking Correspondence Agent model: 2% commission, misconducts by RBI report. 47% BCA untraceable.
- Hawala via smurfing (sending money overseas in small units) and money mules, fears Rajanbhai.
Nachiket Mor: financial inclusion
- Universal banking account for all residents by 2016
- White label BCA (to tie up with multiple banks).
- Affordable Investment and insurance products for poors.
- Consumer protection in financial services. (Fin. Redressal agency)
- Bank access within 15 minutes; Payment banks, Small banks, wholesale banks.
Small Banks and Payment banks
Rajanbhai wishes to launch these banks for greater financial inclusion under Nachiket’s report.
| Small banks | Payment banks |
|---|---|
| Take deposit, give loan but small area of operation. |
|
| Customer money circulated as loan to MSME, unorganized workers, small/margi. farmers. | Only invest in G-sec. can’t give loans |
|
|
so far, we saw long term reform, med. term reform, now one last point:
Short term reforms
Slow environment clearance, cited as one of the main reason GDP decline. Environment ministry did these reforms:
- No environment clearance needed for following:
- Border: LAC 100kms, BRO permitted
- Naxal: forest land 5ht. Convert for public buildings
- Ganga basin-5 states: industries to install emission monitoring systems.
- Web portal for file clearance
- GIS system forest clearance
- TSR Subramium panel to review green laws=> long term reforms when report comes.
More points can be added by throwing statistics and schemes from 100 day reports by various ministries. but revision cost-benefit not that good.
Misc. topics
| GDP | New GDP calculation with base year with as 2011-12. Will include unorganized sector=> higher GDP, because earlier they were not included |
| PPI |
|
[Block-4] Farm subsidies, buffer-stock, PDS
MSP, FCI, procurement
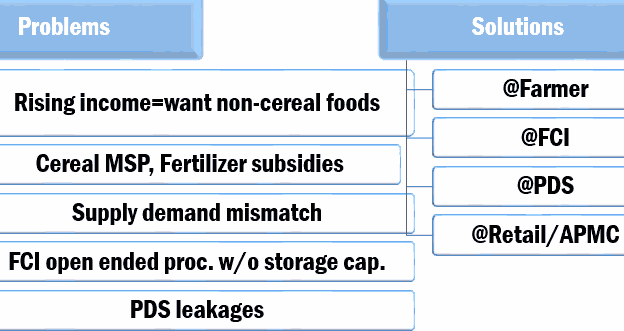
Problems?
- MNREGA+Rising income= more demand fruits, veggies, edible oil, milk, egg, protein food.
- But Government keeps cereal MSP high for farmer vote bank, cheaper electricity and fertilizers=> more farmers grow cereals.
- This Supply demand mismatch=food inflation from non-cereals.
- FCI open ended procurement but lack of shortage capacity=Rotten grain.
- Leakages in PDS=blackmoney + inflation.
Solutions?
- @Farmer: Remove MSP, give direct cash transfer to farmers, include urea in NBS; more R&D to raise productivity, farm mechanization (=more employment in rent+repairs),
- @FCI:
- Decentralized procurement: instead of FCI, states themselves procure and distribute PDS. Started in 90s but only few states adopted.
- Existing: Private.entrp. guarantee scheme+ Grameen Bhandaran + 100% FDI in warehouse, warehousing receipts to get bank loans; offload excess wheat/rice in open market to curb prices.
- @PDS: Food stamps/DBT to poor= no more leakage or hidden hunger; allows PDS shows to sell other items to keep profit & reduce hoarding, online monitoring of stocks etc.
- @Retail: Reform APMC act. Allow- private years, farmer-SHG to direct sell, create national market for agriculture (law), online info on pricing, no more market fees; stable export policies.
lot More bolbachchan can be done but everything boils down to points given above.
Fertilizer Subsidy reforms
- Nutrient based subsidy- on weight of macro/micro nutrients. Farmer gets tailormade fertilizer as per soil requirements (using his soil-health card from budget 2014).
- EPICFail because: Urea not covered, NBS subsidy not given quickly to companies.=> excessive urea use=> soil NPK ratio disturbed; subsidy bill increased to 70k+cr.; higher import=CAD; smuggling.
Sugar pricing (Government intervention)
- State Government administered price (SAP) higher than union’s MSP/FRP (fair remunerative price)
- Mill owners need to pay SAP to farmers=>losses because retail sugar price declining.
- Mill owners in arrears: union giving interest free loans to them. (SEFESU scheme).
- Ranga. Committee says stop SAP & adopt FRP.
National Food security Act (NFSA)
Easy and clichéd topic but its bullets can be used as ‘fallback line’ when “out of content” for a generic question on poverty-hunger-issues.

NFSA: responsibilities of union and state Governments
- 97: TPDS, 2000: Antyodaya Anna; 2013: NFSA (under consumer affairs ministry)
- Union: supply foodgrains; else give allowance to states
- States: identify beneficiaries; give food else allowance
- 67% population covered.
- Quota: AAY: 35kg for whole family, Priority 5kg per person
Entitlements

खाध सुरक्षा कानून से किसको क्या मिलेगा?
- Rice 3; Wheat 2; coarse 1 Rs./kg
- Preg: Free meals, 6k installment; Kids: free meals, take home rations.
- Grievances redressal @distrct & state level; TPDS: ICT, doorstep delivery
- Deadline: Oct14=>extended to April 2015, because very few states implemented, because beneficiary identification problem. SECC survey yet to complete.
- Full implementation: Haryana, Raj, Punjab total 5 states.
Criticism against NFSA
- Hidden Hunger: only carbohydrates given but no vitamins and micronutrients. Global hunger report says >50% Indian women and children have anemia. Solution?
- iodized salt, fortified flour, bio-fortification of crops (nutrifarms)
- National nutrition mission 2014 to reduce anemia
- EcoSurvey says give food stamps, let’em buy whatever nutritious food they want. Jene dreze counters- they’ll buy Desi liquor.
- Fiscal deficit: 1.15lakh crore burden=> 88k given to food security Act.
- FCI storage capacity insufficient=>rotten grain=>inflation
- GPS truck-tracking, CCTV…no. Parliament Committee recommended this but not implemented in NFSA.
- Identifying beneficiaries biggest problem. SECC incomplete.
Donot confuse food act with Food security Mission: Under Agro ministry. Increase production of 5: rice, wheat, pulses, millets and commercial crops.
Next revision article: GS3 Economy- Infrastructure and Black money.

![[Revision] GS3: Environment, Conservation, Disaster-Management: Cyclone Hudhud, Kashmir Floods, Clean India & Ganga](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/Cover-Revision-Environment-500x383.jpg)
![[Revision] GS3 Science-Tech: Biotechnology, Robotics, Nanotech, Computer/IT awareness, Space-tech, Agro, Defense](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/Cover-Revision-Sci-Tech-500x383.jpg)
![[Revision] GS2/GS3: Public Health Special: Indigenization of Medical Technology, Medical-Gadgets applications](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/Cover-Revision-GS3-Medical-500x383.jpg)
![[Mains-2014] Vehicle-pooling, Lodging, Centre Address doubts](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/11/c-cab-pooling1-500x383.jpg)
nicee
can you please post some more clears stuffs regarding loopholes in planning commission and vivid description comparing china and india planning …..and contradicting with niti aayog…
Wow….. One of the best articles to date… Mrunal sir i think this time you have outdone even yourself … Thanks a lot
Hey Neel, Mrunal is indeed habituated to it (outdoing himself time and again). What say?
Government convenes all Party meet on CSAT exam issue: Parties to submit their views on five issues in two weeks :Parties appreciate government’s approach on the sensitive issue —
The Government today discussed the issues concerning the Civil Services Aptitude Test (CSAT) with leaders of various parties in both the Houses of Parliament. The meeting was convened by the Parliamentary Affairs Minister Shri M.Venkaiah Naidu in pursuance of the assurance given by the Government during the last Budget session of Parliament. Home Minister Shri Rajnath Singh and Finance Minister Shri Arun Jaitely, Minister of State in PMO Dr.Jitendra Singh, Ministers of State for Parliamentary Affairs –Shri Rajiv Pratap Rudy and Shri Mukhtar Abbas Naqvi besides leaders of 26 parties represented in both the Houses of Parliament.
Shri Rajnath Singh and Shri Venkaiah Naidu said that the CSAT issue is a sensitive one and the Government would like to have the benefit of considered views of all parties.
A detailed presentation was made by Secretary (DoPT) on the origin and evolution of the civil services examination over the years being conducted every year by the Union Public Services Commission. Dr.Jitendra Singh sought the views of different parties on five proposals. This followed expression of views by leaders of various parties, who said they need to consult their party colleagues in the sensitive matter.
Shri M.Venkaiah Naidu informed the leaders that they will be circulated a detailed note in the matter in three days and suggested that may furnish their views in two weeks on the following five issues:
1.On continuation of English Language Comprehension Skills in Paper – II
2. Reduced weightage of analytical component
3. To make Paper-II qualifying
4.Revert back to Optional Paper
5. Any other alternative.
Several leader complimented the Government for its approach in the sensitive matter.
This is just for providing info on the latest developments. Please carry on with your preparations as usual-Do not waste time on speculation on which one of the 05 proposals will be implemented. Only time will tell how the things actually shape up. It may take up to two-three months for the Govt to decide and for dopt to issue the clarification/notification on the changes in prelims.. i.e. if any changes are there at all !!.
See the link below for the source:
http://pib.nic.in/newsite/erelease.aspx
Do u hv any idea how many bills are brought to the parliament and how many of them bcm an act?
a simple meeting and u people start creating panic. If u dnt want 2 stdy atleast let others 2 do so.
jab notification upsc website pe dekhna tab yahan copy paste karna.
mrunal bhai…. u simply rock…why dont u give this exam again if u r eligible…country need IAS like u
thats true!!!
thanks sir….
Thank you sir for such a lucid explanation.
Chaa Gaye sir aap…..thanks a lot!!!!
Please someone explain……
How modified DBT will reduce LPG subsidy?
modified DBT = old DBT minus Mandatory Adahar. Nothing new.
DBT is beneficial in terms of direct transfer to an individual account.In that sense bringing transparency and tractability of the subsidy.
Better targeting of the subsidy would be possible after implementing Direct benefit transfers. At present, even Amitabh bachchan and mukesh ambani are getting LPG at the same subsidised cost at which a rural poor gets.
So, DBT will allow tranfering the subsidy amount directly into the bank accounts of targeted junata and further LPG prices will be decontrolled and linked to the market prices.
i wait anxiously for new pdfs,download them and read them whole day over my tablet and feel l like a genius…
once again great article thanx sir
Thank you again for your crisp and clear articles.
You can also add links to the main discipline articles along with revision notes.
Superb work although
Modified DBT is per kilo subsidy ..Inne paiso me inna hi milega.. selling of 5kg cylinder – subsidy for 5kg…not cylinder v based which is 14.2kg…
Baki Mrunal bhai batayenge kabhi fursat me…
Ya indeed I also want to know why Mrunal not sitting in this exam if otherwise eligible..You are really doing excellent job..serving the mankind…A big thnks and ha if I could make it this year to IAS…A big gift for you..pakka..
Mrunal Ji.. For geography optional which of the following is advisable…
1. Geography of India – Hussian
2. Indian geography – Khullar
3. Geography of India – RC Tiwari
Please suggest any of the one…
Thanks, great stuff, you are really helpful in off days and especially this revision series is of great help
N if you can provide free technology in aid of farmers, achievement of Indians in science and technology , and if possible some mind map of events and personalities in post modern history , n personalities in Indian freedom struggle segregated according to regions of country (only name will suffice)
What is the logic? When the GDP is up, the credit should not go to planning commission but when the GDP is down the blame should go to planing commission.
2. Everybody agrees that poverty has declines though the percentage is debatable so planing commission should get the credit for that.
Stopped reading after this.
You should read on the hindu rate of growth to know why PC has been a farce!
U r doing amazing work….this revision sseriousis like boon for my mains reviosion…..Plz continue with more areas…..I’m in love with it…..writing vajiram test series with this n focussing on optionals has become so easy…..thanx a lot for everything.
http://www.thehindu.com/business/Economy/rangarajan-defends-poverty-estimates/article6186614.ece
Mrunal sir there is some news from ‘the hindu’ which highlights, that actually poverty has reduced in the country, whether you apply ‘tendulkar’ formula or ‘rangrajan’ method.
They both compared year 2009-10 to 2011-12.
As per Tendulkar line- 2009-10 fig. is 35.4 crore and in 2011-12, 26.9 crore.
As per Rangrajan panel- 2009-10 fig. is 45.4 crore and in 2011-12, 36.3 crore.
A very article.
Plz provide a separate article on fuel price declining
“NO TIME TO CHANGE CHINDU’S PHOTO”….awesome comment , thanks for the laughs :)