- Cotton and textile industry
- Climate factors
- Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Osaka, Japan Industry
- Ahmedabad, Gujarat
- Coimbatore, Tamilnadu
- Manchester & Lancashire industry
- American cotton industry
- Chinese textile industry: Shanghai
In the previous article, we saw the factors responsible for location of Lumber, Paper Pulp and Fishing industry (click me). Now let’s check some industries based on natural fibers.
Cotton and textile industry
- Cotton as a raw material=lightweight, non-perishable.
- Cotton to yarn/textile =hardly any weightloss.
- Therefore, proximity to raw material site=not essential, doesn’t offer great cost-saving in transportation. (unlike sugar, cement or steel industry)
- Result=other factors become more important in industrial location viz.
- nearness to market
- nearness to waterbody (for dyeing, bleaching)
- Energy to run powerlooms and textile machines
- cheap labour supply
- availability of capital/finance
Climate as factor
- In dry climate, the cotton-threads will break quickly during spinning. Machine halts, you’ve to join the threads again to restart operation=not good for mass production.
- on the other hand, humid climate= thread will rarely break. So, cotton textiles were setup near costal areas. (e.g. Mumbai, Osaka, Lancashire).
- Today we’ve humidifiers that can artificially increase the air-moisture in factory/workshed= you can setup factory anywhere, run it efficiently, irrespective of climate outside.
Anyways, let’s examine from desi-videsi cotton industries
let’s look @some more cotton mills
Although in the 80s, most of the Ahmedabad mills fell sick and closed down. Industry shifted towards Surat-Khambhat region of Gujarat.
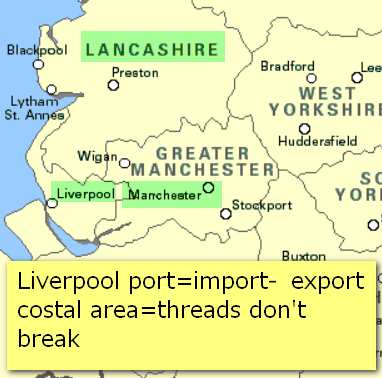
Manchester & Lancashire industry
| Climate | moist Westerlies =humidity=threads don’t break |
| Raw Material | Cheap Cotton from its colonies (India, Egypt). |
| Transport |
|
| Water | Streams from Pennine hills=soft water for dying bleaching. |
| Energy |
|
| Labor | By 1600 production of a fabric called “fustian” started in England. Fustian makers settled in this region because humidity helps in cotton spinning. |
| Market | Demand in Europe + Lancashire faces American ports. |
The decline of British Textile Biz.
- After WW2, Britain lost its colonies one by one, dirt cheap cotton=no longer available.
- during 20th century cheaper imports from Hong Kong, Japan and other parts of Asia. Even the former colonies of Britain also started using those cheaper clothes, so Lancashire=no longer receiving large orders.
- Business moving towards coastal areas for better opportunities in shipbuilding, marine engineering, soap, heavy chemicals industries.
- Hence, Textile industry fading away, old factories are refitted for production of light-engineering items. (Reason? = industrial inertia, we will see that in Iron-steel industry article later on.).
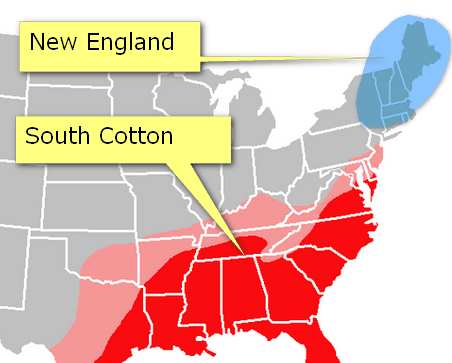
American cotton industries
| New England region | Cotton belt in south |
|---|---|
| 6 States located in the North East corner of US | North Carolina, South Carolina ,Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi. Include parts of Texas and California. |
| Proximity to Boston and New York= ports and domestic market. | large cotton growing areas: US cotton belt is 1200+kms broad and 4000+kms wide. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chinese textile industry: Shanghai
Observe the map and think about the factors that are helping Shanghai
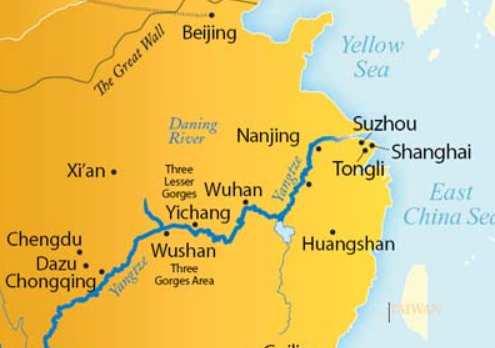
| Factor | How does it help? |
|---|---|
| Climate | port city=humid=threads don’t break |
| Raw Material | Yangtze-kiang delta=good for cotton cultivation |
| Transport |
|
| Water+ Energy | Yangtze river |
| Labor | of course available |
| Market |
|
Apart from Shanghai, Cotton also produced in the areas around Hwang-Ho valley, Sichuan, Nanjing, Beijing and thanks to labor availability (and domestic demand), textile industry is found in those places as well.
In the Next article, we’ll see the factors affecting location of Silk Industry.

Cn u plz tel us abt synthetic textile industry
Why does Ahmedabad need to import cotton from neighbouring states? Gujarat has black soil.