- [Act 1] Economy
- E1: RBI: Monetary Policy April 2014
- E2: GI Tagging & EC model code
- E3: Predatory pricing by Aviation Companies
- E4: BIS New labelling guidelines for Electronics
[Act 1] Economy
Current Affairs for April week 1 (1st to 7th April). Total three parts
- Part 1/3: Economy= You’re here. (bank license topic discussed separately)
- Part 2/3: Environment, Biodiversity, Polity and Culture click me
- Part 3/3: Diplomacy-international relations (click me)
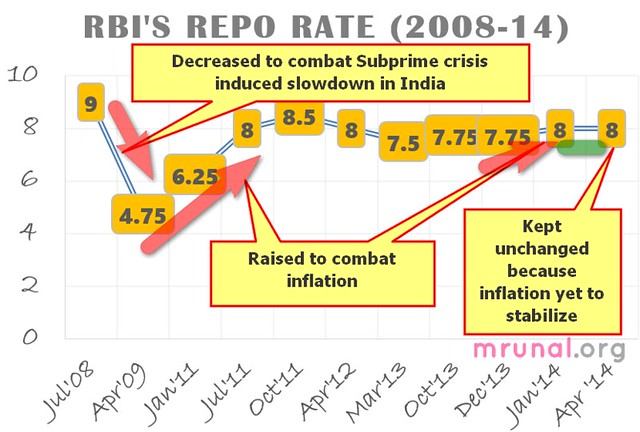
E1: RBI: Monetary Policy April 2014
- Make sure you know the theory of repo, reverse repo, LAF, MSF, CRR, SLR, if not then click me
- 28th Jan 2014: Monetary policy (and Rajan said he’d update it after two months = Feb, March)
- 1st April 2014: monetary policy update
Key rates unchanged:
| Bank Rate | 9% | |
| Marginal standing facility (MSF) | 9% | |
| LAF | Repo rate (policy rate) | 8% |
| Reverse Repo rate | 7% | |
| Reserve ratios | Cash Reserve ratio (CRR) | 4% |
| Statutory liquidity ratio (SLR) | 23% |
These rates are one and same like previous update (Feb 2014).
Rajan did not change the policy rate (repo rate) for the following reasons
- Yes, inflation has declined but not sufficient enough where repo rate should be reduced.
- Rajan fears that even in 2015, (CPI) inflation will not go below 8%, because…
- Geo-political developments (like Ukrain) and their (negative) impact on crude oil, gold & other international commodity prices.
- El Nino effect = less monsoon = less food production
- fuel, fertilizer and electricity subsidies = more money supply (from government’s side)
- MSP (Minimum support prices) on foodgrains. = more money supply (from government’s side)
Other measures
- Accepted some recommendations of Urjit Patel Committee, like targeting CPI (combined) inflation. Detailed coverage of Urjit Patel, pros/cons discussed already in earlier article click me.
- KYC norms are being simplified for Foreign Portfolio Investors. (FIIs)
- To reduce volatility of FII investment in Government securities (G-Sec), Rajan made new rule- those FIIs can only invest in G-sec only with maturity of one year or above.
- will allow more companies /entities to get Banking correspondence (BC) license.
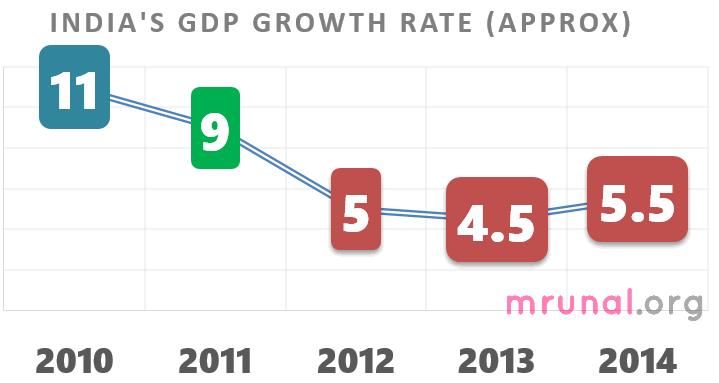
Rajan’s other projections:
| 2013-14 | 2014-15 | |
| GDP growth rate% | 5 | 5-6 |
| CAD as % of GDP | – | 2% |
Minimum Balance
- Rajan asked banks not to levy penal charges on customer, if he doesn’t maintain minimum balance. (but bank may suspend his facilities on until he puts money)
- Counter argument:= since banks have to incur expenses for record maintenance, staff salary even on such non-minimum balance dormant accounts. So banks will raise the charges on ATM, Debit card etc. on all customers, to cover those losses and keep profit margin same.
Table: Penalty rates at the moment:
| Bank | Min. Balance necessary (monthly) | penalty (Urban) | Penalty (rural) |
| SBI | 1000 | 204 | 102 |
| ICICI |
|
250-350 | 250-350 |
| HDFC | |||
| KOTAK MAHINDRA | |||
| HSBC | 1.5 lakh | 350 | |
| Citibank | 2 lakh | 500 | |
E2: GI Tagging & EC model code
- What is Geographical indicator tag, what benefit does it offer? = already covered in my old article Click ME
- Geographical indications (GI) registry is one type of quasi-judicial body.
- But as per Election commission’s model code of conduct, even they had to pause giving new GI-registration.
- Following is the list of product awaiting GI registration:
| Dharmavaram handloom silk sari | Andhra |
| Firozabad glass | UP |
| Kannauj perfume | UP |
| Moradabad metal craft | UP |
| Saharanpur woodcraft | UP |
These places/items become important at two places
- MCQ : theory / static content
- GS Mains Paper 1: (Geography) location factor of various industries.
#1: Dharmavaram Pattu Silk Sarees: Andhra
Location factors:
- Climate: semi-arid tropical = less rainfall = good because silk yarn breaks easily in rainy weather.
- Water quality-soft = best suited for “degumming” and dying the silk.
- Raw silk as such as harsh and unsuitable for dye treatment.
- Hence it is subjected to degumming treatment= soak in boiling water with soap and soda ash.
- But if water is hard, then soap/soda won’t dissolve easily. That’s why soft water essential.
- >1000 ft. above sea level = temperature ~25-40 degree = good atmosphere for labor. Because Dharmavaram silk is essentially handloom woven and not power loom.
- This town is ~50 kms away from Anantapur in the Rayalaseema region of Andhra Pradesh= good transportation facilities
Raw material:
- 100% pure mulberry silk only. (no mixing with cotton etc.)
- Zari brought from Surat. (lightweight, non-perisable) hence silk industry doesn’t need to be setup near Surat’s zari. PS: Surat Zari also enjoys GI status.
Designs:
- Lepakshi temple murals (near Anatapur)
- various flora, fauna and epic scenes.
Acid Dye (theory)
- Acid dyes can easily color protein fibres like silk and wool. (Hence acid dyes used in silk industry and not alkaline dyes).
- Acid dye colors highly durable and can last upto 50 years.
- Applied generally in the presence of an organic or inorganic acid and hence are called acid dyes.
- After dyeing phase is over, workers mix Sodium Hydroxide to remaining dye => acid neutralized=> effluent discarded in the drainage. Hence the process eco-friendly. No chemical diseases reported in the region.
Product:
- Silk Pattu Sarees And Paavadas for grand occasions
- also for Bharath Natyam and Kuchipudi dancers.
#2: Kannauj Attar, UP
History:
(ya this type of stupid MCQs are asked whether abc ancient text mention xyz thing or not?….dig last CDS and CSAT- Kalhan’s Rajtarangini and Huen Tstang respectively.)
- Perfume dates back to over 5,000 years to the Indus valley civilization. Excavation of perfume distillation sites.
- Perfumes even mentioned in ancient Pali and Islamic texts.
- 1St AD: Greek text Periplus mentions sandalwood imported from India.
- ~600AD: Emperor Harshvardhan made Kannauj his capital and encouraged the perfume industry. Some perfumer makers were so influential, they were allowed to mint their own coins!
- ~1550AD: In Aain-e-Akbari, Abul Fazal mentions Emperor Akbar was fond of perfumes. His court chamber was continuously scented.
- ~1600AD: Tojak-e-Jahangiri, claims that queen Noorjahan invented a perfume called “rooah-e-gulab”.
Science/Botany
- Perfumes are essential oils from flowers, mixed with a “base” material.
- Essential oils are volatile, liquid aroma compounds, usually sourced from plants. Essential oils are not oils in a strict sense, but have oil like properties e.g. poor solubility in water.
- Essential oils often have an pleasant odour, hence used in food flavouring and perfumery.
Raw material: base
- Base is the liquid in which flowers are sunk to extract the essential oil.
- Sandalwood oil is the best base for attar making. (source: Karnataka and Kerala)
- but scarcity of sandalwood= sky high prices, hence traditional perfumer makers nowdays use artificial chemical base such as liquid paraffin and Di-Octyl Phthalate (DOP)- for making cheaper attars.
- Attars are made using the centuries old copper vessels called Deg (Kettle) or Still and Bhapka (Receiver).
- The Deg & Bhapka system is based on hydro-distillation technique.
Raw material: flowers:
Local crops of Kannauj= Jasmine, Kadamb, Merigold, Henna etc. remaining flowers brought from other states.
| Rose | Hathras and Aligarh in Uttar Pradesh and Palanpur in Himachal Pradesh |
| Khus | Bharatpur (Rajasthan) |
| Chameli | Chandoli in Jaunpur district, |
| Raat Rani | Viaywara district (Andhra Pradesh), |
| Kewra | Burahanpur, Ganjam in Orissa |
| Saffron | Jammu & Kashmir. |
| Spices and herbs | North-East States of India and Himalaya |
Products: Fragrances (attars), incense sticks, dhoop/hawan material, gulkand (made of rose petals and sugar), Rose water and scent sprays.
#3: Muradabad Metal craft UP
History:
- Mughals brought Kansa (an alloy of copper, zinc and tin) from Iran, Turkey, Egypt. Some migrants also settled here and started crafting kitchen utensils.
- Designs influenced from Iranian style. Usually, king travelling on elephant, Mughal monuments etc.
- Present city established during Akbar’s time.
- boost in demand due to Kanuaj Attar business (perfume bottles).
- today >2000 cr export, >25000 cr artisans employed.
Science
- Brass= 60% copper + 40% Zinc – but proportion can be varied according to product.
- Bass has low melting point (~900C) = easy to melt and moult.
- Electroplating technique used for changing surface properties
#4: Saharanpur woodcraft, UP
Raw material
- wood/timber of mango, rosewood and shesham
- Timber should be less than 15% moisture content = become seasoned.
- Seasoning process- drying of timber to remove the moisture contained in walls of the wood cells.
Design:
| Srinagar Woodcraft | geometrical designs |
| Mysore woodcraft | human and animal motifs |
| Saharanpur woodcraft | Monuments of Sultanate & Mughal age, grapevines, floral patterns. |
- Wax polish used to increase brightness.
- Earlier woodcrafting done manually with handtools, nowadays use of machinery.
Products: Coat Hangers, Cupboards, Dressing Tables, Embroidery Frames, Table Tops, Tea Carts.
#5: Firozabad Glassware, UP
Raw material:
- Soda ash and Silica
Techniques:
- Glass ware manufactured using mouth blown technique
- The artisans use to roll glass layer on wooden rods, which were cut into the shape of bangles
- nowhere else done in the world
- Hence Firozabad = World Glass Bangles Capital.
Products: glass bangles, chandeliers, glass status of gods and goddess
E3: Predatory pricing by Aviation Companies
Interview questions:
- What is predatory pricing: how is it good/bad for business/ economy?
- Why is Spicejet accused of predatory pricing?
- What has DGCA done in this regard?
What is Predatory Pricing?
- Means deliberately selling product below the cost price, to eliminate competition.
- Usually predatory pricing is done by firms with deep pockets (like Walmart), because they can afford to make such temporary losses.
- in short, it may appear good to customers- because products available @cheap rate
- But in long term, the firm establishes monopoly and starts exploiting the same customers.
- Sometimes the strategy misfires, company makes heavy losses (e.g. AirDeccan and Kingfisher).
Why Spicejet accused of Predatory pricing?
- They’ve launched a scheme “Rajiv Gandhi One Rupee Air ticket”
- Sounds good? but there are hidden terms and conditions
- Offer valid only if you book tickets during April 1 to 3.
- Only one or two seats offered in each flight under “One rupee” scheme.
- So this is both “predatory pricing” + misguiding customers.
- Spicejet already making losses, and now they’ve launched this scheme=> other aviation companies will also be forced to launch similar schemes to stay on competition => everyone starts bleeding and making losses=> ultimately some get on verge of collapse like Kingfisher= staff salary not paid, loss EMIs not paid, Bank NPA increases and so on….
What has DGCA done?
- Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) is empowered to take action against such predatory pricing (under Aircraft rule #135)
- He has ordered Spicejet to immediately stop this scheme.
E4: BIS New labelling guidelines for Electronics
Q. (GS2-Regulatory bodies) What is BIS? Why is the electronics industry opposed its new labelling guidelines? (200 marks)
- Bureau of Indian standards is a statutory body under Consumer affairs ministry, to set the quality standardization criteria for consumer goods.
- It has recently updated the labelling guidelines for IT & electronics industry- for products such as printers, scanners, wireless keyboards, set-top boxes and microwave ovens.
- Earlier companies had to merely put stickers on the products.
- But as per new guidelines, BIS requires them to screen print, emboss or engrave the labels onto the product and its packaging material.
- Manufacturers also need increase their font size such that product description is clearly visible.
IT & electronics Industry is opposed to this guideline because:
- Increase in the production cost. In certain cases almost by 100%.
- BIS ordered the companies to implement this from April 2014, a deadline almost impossible to achieve.
- Difficult to engrave certificates on some delicate gadgets such camera, tablets and mobiles.
- No apparent benefit to customers.
- No such labelling rules followed anywhere else in the world.
~170 words.
Visit Mrunal.org/CURRENT for entire Archive weekly current affairs compilations published so far.





![[Current] Economy SepW1: Wilful Defaulters, MNREGA reformed, Global Competitiveness Index, BSNL-MTNL Merger, Gold Account scheme](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/Cover-Wilful-defaulter-500x383.jpg)
great job.. v soon and quickly updated. thanks mrunal.
Rajiv Gandhi One Rupee Ticket lolz :D :D
I have been preparing for civil services ,,since 2011 and almost have looked in to the study material of all famous grand old coaching,,,but you really deserve a salute for bringing such a comprehensive package for developing a clear cut understanding on such complex issues
Hello, Mrunal Sir u always been very help to me through ur posts and explanations. Can you plz suggest essay regarding SBI PO. It will be very grateful.
IT & electronics Industry is opposed to this guideline because:
No apparent benefit to customers
SIR i think there is a benefit for customers by engraving labels, because it avoids label on label by middle men,
isnt it ???
and it doesn’t fades away like stickers of product i.d, windows key,logo etc. on your laptop fades.
Next year onwards
Modi one Rupee Ticket / Atal Awas Yojana etc
thanks mrunal.
Great way of describing..thnks
@Mrunal thanks again. But why there’s a ban by EC on giving GI status, you havhaven’t mentioned. Any clarification given by EC?
And what’s ur plan about Rajiv Gandhi All India Prelims Mock Test Series scheme under mrunal.org? There’s a growing demand by aam admi for it these voting season!!
Giving GI tag increases the price value of the commodity and inturn benefits the weaver/bangle manufacturer community. So, govt can influence voting pattern by claiming credit.
sahi bat mr P_G
me 2 waitng for Rajiv Gandhi All India Prelims and mains Mock Test Series scheme under mrunal.org….
Pappu also eagerly waiting for this
Ekdum sateek material, Mrunal sir ek baar mil jaaye to charan sparsh.
sahi me bhai……”charan sparsh ” for Mrunal sir..hamare Gurudev
Correct me if i am wrong!
But isn’t this new labelling system for imported electronic items? so that the import of substandard electronics can be checked?
i mean ONLY for imported electronics?
PEOPLe , if you want to see optionals removed from CSE , please read and sign this petition http://www.ipetitions.com/petition/removal-of-optionals-from-cse-mains-examination :) Please help me get the required number of signatures
thaku u sir
THANKS SIR
sir, what is credit to gdp ratio ?
hi mrunal, bell metal is same as bronze(cu+sn) with higher percentage of sn, are belll metal and kansa are different? Also, Glass=soda ash(Na2co3)+limestone(caco3)+silica(sio2). Am I correct?
nice.
Amazing sir… Hatsss off to uu….u r a likewise of anand kumar for us…