- Prologue
- WTO: Structure and functions
- Tariff and Non-Tariff Barriers to Trade
- WTO agreements
- Agreement on Agriculture (AoA)
- What is Bali summit and Peace clause?
- What is Trade Facilitation Agreement?
- Why Modi opposed Trade Facilitation Agreement
Prologue
Consider this a “Fork” of the Economic Survey chapter 9 on Agriculture and food production.
WTO: Structure and functions
Q. Write a note on origin, structure and functions of WTO? 200 words
1944: Bretton Woods summit leads to birth of three institutions
| Institution | KEY IDEA |
|---|---|
| World bank | Cheap loans for development projects in third world |
| IMF | Balance of payment and Exchange rates |
| GATT |
|

| MinisterialConference |
|
|---|---|
| GeneralCouncil |
has two bodies, with separate chairmen
|
| DirectorGeneral |
|
WTO Functions
- Ensure the developing countries benefit from world trade, especially the least Developed countries.
- Reduce barriers to international trade – both tariff barriers and non-tariff barriers.
- Get the members Enter into multilateral trade agreements to achieve above objectives.
- Provide forum for negotiation and dispute settlement for the members, if the agreements are violated.
- Cooperate with UN, World and IMF for a global economic policy that improves livelihood, protects environment and promotes sustainable Development.
Tariff and Non-Tariff Barriers to Trade
All countries want to protect domestic industries and prevent entry of foreign players. So, they create two types of barriers to International trade:
| Tariff Barrier | If US President Obama imposes 56% custom duty on Indian Cars. |
|---|---|
| Non-Tariff Barrier | If Obama tries to restrict entry of Indian cars without imposing heavy taxes on Indian cars, for example
|
- World Trade organization (WTO) aims to reduce such tariff and non-tariff barriers to international trade.
- But what if China starts manufacturing cheap cars with poor breaks, bad steering and carcinogenic paint. Can Obama ban such dangerous foreign products? Does WTO permit that?
- Yes, WTO made two special agreements for “safety”:
| Non-food products | Technical Barriers to Trade Agreement (TBT) |
|---|---|
| Food Products |
|
WTO agreements

Gist of the whole controversy surrounding India, WTO and TFA
Q. Write a note on WTO agreements 200 words
Five categories of agreements (or 6, depending on which book you refer!)
T1: Goods
- General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)
- Agreements on
- Agriculture
- Textile
- Antidumping
- Safety / quality checks related
- Sanitary and phytosanitary agreement (SPS)
- Technical barriers to trade (TBT)
- Trade related investment measures (TRIMS)
- Subsidies and countervailing measures (SCM)
T2: Services
- General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- To ensure that services’ import/export enjoys the same principles of free and fair trade, just like the trade in goods.
T3: IPR
- Trade related intellectual property rights (TRIPS)
- Protects seven categories of IPR viz.
|
|
T4: Dispute settlement
- to enforce the trade agreements and commitments made by individual member country
- once a complaint is filed, first, the parties are allowed to sort the issue through mutual consultation
- If that fails, formal adjudication by an expert panel.
| T5: Policy review | T6: plurilateral agreements |
| Periodically, WTO carries out audit/inspection/review of the trade policy of member states and gives them constructive feedback. | Not signed by all countries:
|
~204 words
WTO has many other agreements but hard to memorize and fit into a 200 word answer anyways.
For exams in 2014-17, the important agreement is AoA. (Because it’ll stay in news due to 10% food subsidy issue)
Agreement on Agriculture (AoA)

| Pillar | What they want from member states? |
|---|---|
| 1.Market access | reduce import duties |
| 2.export competition | reduce export subsidies |
| 3.domestic support | reduce Amber box subsides |
AoA classifies subsidies into two parts:
| DOMESTIC SUBSIDY | EXPORT SUBSIDIES |
| mostly by third world to keep help farmers and keep vote bank happy | mostly by first world, to keep their MNC-corporatized farmer lobby happy. |
| to increase food production, food security | to capture “Foreign market” by flooding their cheaper products |
| India doesn’t give much “export” subsidies to farmers- except a select horticulture and floriculture Items | |
AoA further classifies them into 3 parts
|
AoA wants members to reduce export subsides
|
Green blue and Amber subsidies
- Just like traffic signal has three colors: green (GO), orange (caution) and red (STOP).
- Similarly, WTO classifies DOMESTIC AGRICULTURE subsides into three categories: green (GO), blue and amber (reduce).
- There is no “RED” box meaning WTO doesn’t wish to completely STOP subsides, because it is impractical anyways!
| Box | subsidies |
|---|---|
| GREEN |
|
| BLUE |
|
| AMBER |
|
Amber box: De Minimus limits
Q. Explain De-Minimus limits in WTO’s agreement on agriculture. Why is India opposed to it? (200 words)
- Under WTO’s agreement on agriculture (AoA), domestic-subsidies are classified into three groups: Green, Blue and Amber.
- Amber box subsidies create trade distortion because they encourage excessive production e.g. fertilizers, seeds, electricity and irrigation subsidies.
- Therefore, WTO wants to limit the amber box subsidies.
- De Minimus is the Minimal amounts of Amber box subsides permitted by WTO, even though they distort trade.
- De minimus limits are calculated on the agriculture production of the given member state in 1986-88.
| Country | De-Minimus: Amber box subsides quota |
|---|---|
| Developed | 5% of agriculture production in 1986-88 |
| Developing | 10% |
| Least developed | Exempted.** |
** Besides if they’re L.D.C=> they’ve no “AUKAAT” to give truckload of subsidies anyways.
Why is India opposed?
India fears it’ll have to cut down its food subsidy to comply with WTO’s De-minimus level
- In 1986: USA agriculture production was far ahead of India. So, their 5% De-minimus quota will be far bigger than our 10% quota (in absolute figures).
- Input costs have skyrocketed in these decades. But, De-minimus doesn’t consider inflation factor.
- So, if India has to limit its (Amber box) agro. subsides to a non-inflation adjusted 86’s production, we cannot continue the MSP to farmers or food security to poors.
- These subsidized foodgrains are meant for feeding the poors only, they do not distort international trade.
~190 words
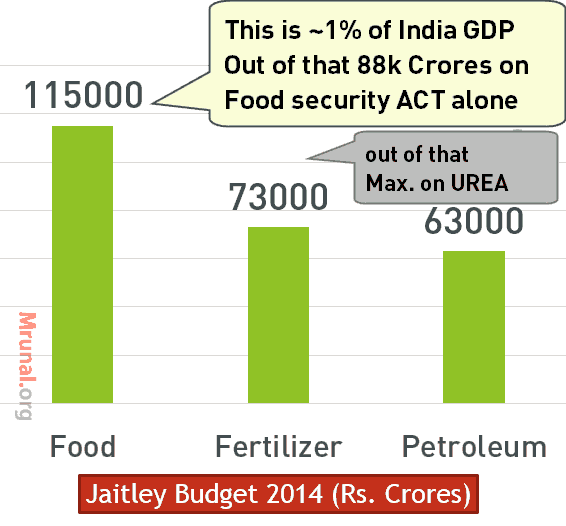
| Subsidy component | RE-2013 | BE-2014 |
|---|---|---|
| Food | 92000 | 115000 |
| Petroleum | 85480 | 63427 |
| Fertilizer | 67971 | 72970 |
Ranking 2013: Food > Petroleum > Fertilizer
Ranking 2014: Food > Fertilizer > Petroleum
What is Bali summit and Peace clause?
Q. What is hell is “Bali Package” and “Peace clause”? (200 words)
- December 2013: 9th WTO ministerial conference held at Bali, Indonesia
- “Bali Package” is the collection of three prime outcomes of this summit.
| Trade facilitation agreement |
|
| LDC exports |
|
| food stockholding |
|
- as per the original Agreement on agriculture (AoA), the developed and developing countries have to keep their Amber box subsidies within De-minimus level i.e. 5% and 10% of their agriculture production in 1986-88 respectively.
- India opposed this base year and limits, because it’d make impossible to implement the food security programs for the poor and MSP for the farmers.
- Therefore, as a measure of temporary relief, Bali summit enacted a “peace clause” for the AoA
Salient features of Peace Clause
- No member, can drag any developing country to Dispute settlement mechanism of WTO.
- for violation of De-minimus limits in AoA
- Provided that the said developing country
- is paying subsidies for staple foodcrops
- for public stockholding program
- For food security purpose.
- is providing annual information of its food security Program to WTO.
- Permanent solution will be taken no later than 11th ministerial conference i.e. at December 2017.
~215 words.
What is Trade Facilitation Agreement?

Manniram is happy knowing that Modi has refused to sign TFA!
Q. Write a note on the salient features of Trade facilitation agreement (200 words)
| ORIGIN | 9th WTO ministerial conference held at Bali, Indonesia in 2013 |
| AIM | reduce red tapes and bureaucratic hassles in customs clearance |
Under TFA, Every member:
- Will have to publish a detailed list of procedure for import-export, fees, inspection rules, penalties etc.
- Minimize the proof documents and clearance required for customs clearance.
- Make all the information available on INTERNET to foreign traders, governments and interested parties
- Provide electronic payment of fees, duties, taxes.
- Setup a single window mechanism to help trader submits all documents at a single point- preferably online.
- Trader should be notified immediately, If goods are detained at customs.
- Provide faster customs clearance to perishable goods (Fruits, veggies, flowers).
- Member must not ask foreign traders to compulsorily route their applications/fees via local customs brokers/middlemen.
- Give Advance ruling, as and where applicable. (Recall advance ruling provision on taxes, under Budget-2014.)
Least developed countries
They’ll get financial and technical help to comply with above rules.
| LEVEL | body to implement Trade facilitation agreement |
|---|---|
| NATIONAL |
|
| INTERNATIONAL |
|
Benefits of TFA:
A simplified customs clearance mechanism will boost international trade, and thereby it will
| will increase in global GDP | $1 trillion (~Rs 60 lakh crore) |
| will create more jobs | 21 million |
| deadline to sign TFA | 2014, July, 31stBut India refused. |
| Agreement becomes effective from | 2015 |
~280 words. But in exam, all points can’t recalled so it’ll automatically “FIT” the 200 words limit!
Why Modi opposed Trade Facilitation Agreement
Q. Why has India refused to sign Trade Facilitation agreement? (200 words)
- WTO’s Trade Facilitation agreement (TFA) aims reduce the redtape and bureaucratic hassles in customs clearance and thereby facilitate international trade.
- But, TFA maintains that it doesn’t “diminish” the rights and obligations of members under other agreements of WTO.
- For example, under the Agreement on Agriculture (AoA) if a developing country is giving Amber box subsidies beyond 10% of its national agriculture production (base year 1986), THEN other members will be justified in putting trade sanction or WTO-complaint against the said country.
- 2013: In Bali Summit, the then UPA Government agreed to sign TFA, after WTO “Peace clause”, which gave temporary exemption to developing countries from 10% de-minimus provision until 2017.
- 2014: Change of regime,
Modi Government has refused to sign TFA before deadline (31st July 2014), because:
- Once India has signed TFA, the developed countries may stonewall her demands for a rational change in base year and ceiling limits on agro. Subsidies.
- Then India will have to cut down agro. Subsidies in MSP and food security programs, else they’ll put sanctions on us, soon as Peace-clause “temporary” deadline is over in 2017!
- And yet, we’ll have to keep giving them easy customs clearance because we signed the TFA!
Therefore, Government has decided to use TFA signature as a “Bargaining Chip” for a permanent solution of food subsidies issue.
~220 words

![[Win23] Economy Pill4ABC: Sectors: Agri, Mfg, Services, EoD, IPR related annual current updates for UPSC by Mrunal Patel](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/win234b-500x383.jpeg)

![[Economy] BOT-PPP Model for Highways, Right to Repair, WTO & Foodgrains Exports- Weekly Mrunal Digest from Jul week1-2022 (WMD)](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/ppp-bot-500x383.jpg)
So what is the solution? I think WTO should revise the agreement which would be something like:
For any member country ‘x’, the cap should be specifically calculated using its average inflation rate, with the base year same as before..
So, suppose the inflation factor in US is say,3.. Then the cap would be 3*some constant…. Inf factor in India is say,15.. Then the cap would be 15*the constant…
:D I went too deep… M the next Azevêdo.
1.sir what is relation between MSP and ERP(external reference price) and how ERP is decided by WTO.
2. I think developed country is giving subsidy more then 5% then how can they presser on India to reduce subsidy by 10%.
What is the main fact of 1991 economy? and how indian economy was damage?
sir, please write about the recent WTO summit, nairobi…. plzzzzzzzzzz sir plzzzzzz :)
WTO bali conference and peace clause and patent rights plz explain
Wow! Great to find a post knnkicog my socks off!
Awesome sir , you explained it in best manner .thank you so much sir