Prologue
Economic Survey Chapter 13, Total five subparts:
- UNDP’s Human Development report 2014, poverty [coming soon]
- Healthcare, women and children [you’re here]
- Demographic Dividend: Education, youth, Skill Development [done]
- Minorities, SC, ST, PH, Elderly, Sports & Defense [done]
- Rural and urban infrastructure [done]

Only covering topics mentioned in Budget 2014 or Economic Survey 2013
[Act 1] Health
- As such I’ve taken data from Economic Survey 2013, page 236, 237 and 247.
- But at certain places, National Health Profile 2013 (NHP) has provided new data, therefore, I’ve included it with (*) mark.
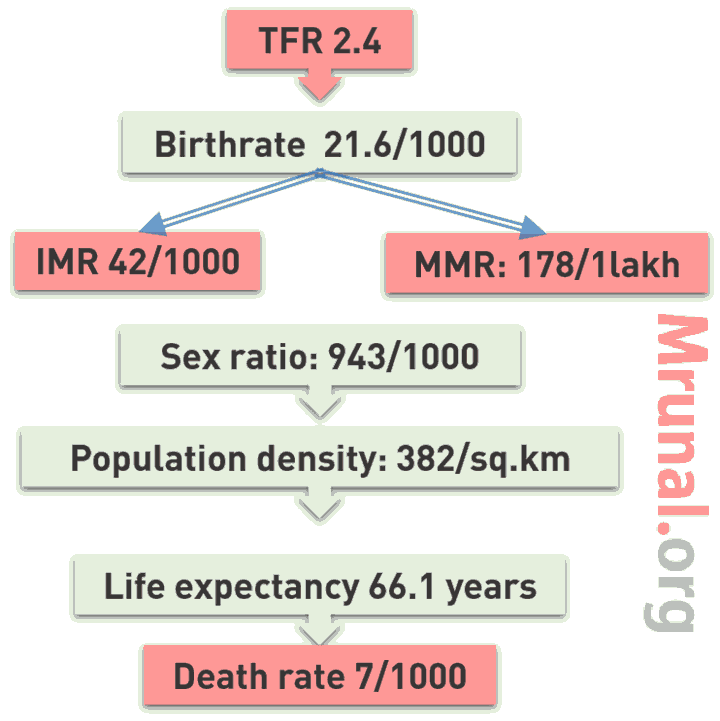
General Dong का नाम लेके नम्बर याद कर लो ताकि MCQ में जवाब WRONG ना हो जाए!
| STATISTICS | NUMBER |
|---|---|
Total Fertility Rate:
|
|
Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR)
|
|
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
|
|
Child Mortality Rate
|
|
Birth Rate per 1000 mid-year population
|
21.6 |
Death rate per 1000 mid-year population
|
7 |
Decedal Population Growth Rate
|
17.7% |
Population Density per sq.km
|
All India 382* |
Sex Ratio*
|
All India: 943/1000 |
| Child Sex Ratio (0-6 age group) | 914, constantly declining since ‘71 |
| Life Expectancy @Birth |
|
National Population Policy 2000
Q. Write a note on the salient features of National Population policy (100 words)

I doubt even the Babu/politicians who made this target remembers it!
| present | Policy target | |
|---|---|---|
| MMR | 178 | below 100 per 1 lakh live birth |
| IMR | 42 | 30 per 1000 live births |
| TFR | 2.4 | 2.1 (replacement level) |
- promote girl marriage after age of 20
- Compulsory registration of birth and death.
- 80% institutionalized deliveries, to reduce MMR
- Compulsory school education, reduce dropout rate
- Achieve Stable population by 2045
- promote sterilization, family planning, 2-children norm, safe abortions, HIV control, universal immunization
- BPL couple undergoing sterilization will get free health insurance.
National health profile 2013
- Central bureau of Health intelligence under Health Ministry has prepared it.
- This comprehensive database helps in Policy making, tracking Millennium development goal (MDG) targets
- Overall, just statistical data, hardly any recommendations. Therefore, not much important for exam. (except those rankings given in above table)
- Here are some gem “statistics”: 125 Cr. People but barely 9 lakh Allopathic doctors and 6 lakh beds, highest Swine flu cases in Delhi but most deaths reported in Gujarat, 21% rise in Cancer in Next 6 years and so on. You can see – not much exam worthiness.
Health Schemes
Previous schemes, acts available at- wp.me/p2tsJl-1Ec it’s a mile long list, cost:benefit bad hence not dwelling in to them. Only focusing on topics discussed in survey / budget.
National health missions
| NUHM | NRHM |
|---|---|
| National Urban Health Mission | National Rural Health mission |
| Cities above 50,000 population | upto 50,000 population villages, town |
These missions provide infrastructure, services, drugs and human resources for public health.
Reproductive and Child health (RCH)
| Janani Suraksha | Janani Shishu Suraksha |
|---|---|
|
Free drugs, Diet, Medical checkup, transport to home, and caesarean deliveries. |
Mother and child tracking system (MCTS)
- Under national E-governance plan (NeGP)
- Government keeps maintains data of the mothers with their addresses, telephone numbers, etc.
- This contact database is used for ante-natal (before birth) and post-natal (immediately after birth) check-up of mothers and vaccination for their babies.
Indira Gandhi Matritva Sahyog Yojana (IGMSY)
- By Women and Child Development Ministry under “National mission for empowerment of women.” (NOT by Health Ministry)
- To compensate mothers for wage-loss during childbirth and childcare.
- Available to all women for first two children.
- Not available to women who get paid maternity leave.
- Conditional cash transfer via Direct benefit transfer (DBT)
- Condition: she should get pre-natal checkups, get vaccination for infant, attend counseling session etc.
PM Modi’s Health reforms:
He listed 17 point agenda, out of which 3 points for health:
- A district health knowledge institute at every district hospital.
- B.Sc course in community health (3 years)
- Ashok: male community health worker, on the lines of the female ASHA workers.
ASHA
Q. What is the role of ASHA worker in community healthcare system of India? (100 words)
- Under National Rural health mission (2005)
- Every village/large habitat has a female Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) – chosen by and accountable to the Panchayat.
- She acts as the interface between the community and the public health system and schemes related to health, nutrition and hygiene- including toilets under Nirmal Bharat Abhiyan.
- She also generates awareness about female infanticide, family planning, STD/HIV
- She carries a Drug Kit containing generic AYUSH, allopathic drugs for common ailments, Rehydration Therapy (ORS), Iron Folic Acid Tablet(IFA), chloroquine, pills, condoms etc.
- She receives performance based incentive depending on number of children immunized under Polio vaccination drive, No. of institutionalized deliveries under Janani Suraksha Yojana, no. of pregnant no. of TB patients covered under DOTS therapy and so on.
Safe drinking water
- Budget 2014 gave additional funding give to National rural drinking water program.
- It’ll provide safe drinking water to 20,000 habitations affected with arsenic, fluoride, heavy/ toxic elements, pesticides/ fertilizers
- Via community water purification plants
- Time limit? next 3 years
| Health 4 ALL | the two key initiatives
|
| Elderly | National Institutes of Ageing will be set up in Delhi and Chennai |
| Food and drug | Additional money for modernizing state labs for checking drugs and foods. |
| Rural health research | 15 new institutes will be setup |
| Dental |
|
| AIIMS | 4 new AIIMS will be setup under PMSSY |
PMSSY
- Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY)
- Two components:
- setup new AIIMs institutes
- upgrade existing Government medical colleges.
| 6 Already finished | 4 new Proposed in budget 2014 |
|---|---|
|
|
Additionally, Budget 2014 promised to setup 12 new Government medical colleges. (Present number is 58).
Economic Survey: Health reform points
- Existing Schemes have created Good infrastructure but at bad locations- without good facilities for transport, communication and electricity.
- There is already brain drain, Staff Shortage, women doctors-nurses reluctant to serve in rural areas because of safety issues.
- Government schemes only focus on “inputs” e.g. how much money allotted, how many beds, health centers built?
- But they donot focus on “reduction” – how many cases of malaria, diarrhea, child mortality reduced?
- Therefore, survey recommends a shift in public health policy and budget Expenditure. Prime focus should be on hygiene and malnutrition- it’ll automatically reduce the disease incidence.
[Act 2] Women and Children
As such infinite topic, but I’m only covering the terms, schemes, policies, acts given in economic survey / budget.
National policy for children 2013
| 1974 | National Policy for children |
| 2003 | National Charter for Children |
| 2013 | National Policy for children |
Q. Write a note on the salient features of National Policy for children (100 words)
- Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD) will be the nodal agency for all child related schemes.
- Child definition includes all aged below 18 years
- National plan > State > District > Local level plans will be prepared.
- will setup Action groups to monitor implementation of this policy
- Priority: Survival, health, nutrition, development, education, protection and participation of Children.
- Then you can cite a few schemes and statistics to reach 100 word limit.
Sidenote: National policy for empowerment of Women – was made in 2001. Hence not going into its details. Compared to that Children policy (2013) and Youth policy (2014) more important since they were made in recent times.
Women and Child: Administrative Legal initiatives
>70% Indian population consists of women and children. Government has taken following initiatives to protect them:
- 2005: started Gender budgeting started. It received ~6% of total budget outlet.
- 2012: Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POSCO) Act
- 2013:
- Committee under Dr. Pam Rajput for “status of women in India” (2 years deadline)
- Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act
- Criminal Law (Amendment) Act 2013, also known as Anti-rape law.
Anti-Sexual Harassment law 2013
Q. Write a note on the salient features of Prevention of Sexual Harassment Act 2013 (200 words)
- Based on definition of Vishakha judgment, and even covered areas/aspects not under Vishakha judgment.
- Protects all women employee, of all ages, organized or unorganised sectors, public or private, permanent or dailywage.
- Even covers women clients, customers and domestic workers as well.
- Even protects against harassment in non-office places such as transportation, sports complex, nursing home, educational institution etc.
| ICC | LLC |
|---|---|
| Internal complaints Committee | Local complaints Committee |
|
|
| Committee will have 4 members. | 5 |
| chairman: senior woman employee | Chairman: woman with experience of social work, fighting for women’s causes. |
- Conciliation permitted, only if victim requests.
- Employer has to setup ICC Committee, arrange workshops etc. Rs.50000 fine for employer, if he violates any rules under this act.
| Stage | Deadline |
|---|---|
| victim can file complaint in | 3 months |
| ICC/LCC Committee has to finish inquiry within | 2 months |
| Employer/district officer has to take action based on Committee report within | 2 months |
Anti-Rape law 2013
Q. Write a note on the salient features of Criminal Law (Amendment) Act 2013 (100 words)
Based on the report of Justice JS Verma Committee after Delhi Gangrape in December 2012.
Salient feature are following:
- It amends IPC, CrPC, POSCO and Indian Evidence Act to increase punishment for sexual offenders.
- Adds new sexual offenses under IPC: acid attack, public disrobing of women, voyeurism and stalking.
- Stalking and voyeurism: non-bailable, if caught second time.
- Acid attack: upto 10 years jail time.
- Rape- jail time no less than 20 years, and can be extended to life sentence.
- Death sentence for serial rapists.
National mission for empowerment of Women
Q. Write a note on salient features of National mission for empowerment of women (100 words)
- under ministry of women and child Development (2010)
- also known as “Mission Poorna Shakti”
- Provides Single window service and convergence for all women specific schemes across various central ministries and departments.
- Provides funding for women skill Development, micro-credit and research.
- Focus areas:
- Prevent child marriage, domestic violence, sexual abuse, prostitution.
- Provide education, financial inclusion, health-sanitation services, vocational training and better representation in Panchayati raj institutions.
- Recall that Woman & Child Development ministry implements “Indira Gandhi Matritva Sahyog” as part of this national mission.
Nirbhaya Fund 2013
Q. Write a short note on Nirbhaya Fund (100 words)
- Started in Budget 2013
- Provides funding for women safety projects by ministries, department, private sector and NGOs.
- Example projects: CCTV @Public places, GPS and emergency buttons in public transport; helplines, Toll free numbers; self-defense lessons for women
- Interim Budget made Nirbhaya fund “non-lapsable” (meaning, even if money is unspent, it’ll not go back in the consolidated fund of India.)
- Total 2000 crore rupees in this fund.
- Jaitley budget 2014: we’ll setup Rape “Crisis Management Centers” In Delhi- in all public and private hospitals, using money from Nirbhaya fund.
Rape Crisis Centre: Maneka Gandhi Proposal
- After Badayun (UP) gangrape and public hanging of two girls.
- There will be one Rape Crisis Centre per district.
- They will provide medical, police and legal service to rape victims.
- They will be linked with a national helpline.
(New) Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao
in Budget 2014. Details yet to be worked out. But CM Modi had started a scheme “Beti Bachao” in Gujarat. Let’s check its salient features
- Census 2001: Gujarat child sex ratio was 883/1000. Therefore in 2005, then CM Modi began “Beti Bachao” scheme to save the girl child.
- He setup State monitoring agency to enforce Pre Natal Diagnostic Technique Act, PNDT Act in a strict manner.
- Workshops NGO, spiritual leaders, Anganwadi workers.
- Even Gujarat HC ran its own legal awareness campaign.
- At Community gatherings and mass-marriage ceremonies, couples made to take vow of protecting the girl child.
- Success? Partial success-Yes, Gujarat’s child sex ratio improved from 883 to 890 in 2011.
Budget 2014: women schemes
Jaitley only gave list, no specific salient features given. Hence nothing much to write.
- Safety in public transport (50 cr)
- Safety in large cities- project under Ministry of Home Affairs, 150 cr.
- Rape crisis Management centers in Delhi hospitals, using Nirbhaya fund.
- Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao
- School Syllabus to include a new topic: Gender Mainstreaming
- National program on Malnutrition for children. Its strategy will be worked out in next 6 months.

![♿️ [Polity/Rights issues] Colour-coded card system for PHYSICALLY HANDICAPPED (PH) certificate](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/WP_PH_CARD_TYPES-500x383.jpeg)
![[Polity] imp latin judicial terms for UPSC MCQs – Audi alteram partem, CORAM NON JUDICE etc](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Polity-Judicial_terms-500x383.jpeg)
![[Polity] SC Subcategorisation – Madiga vs Mala in Telangana; Demand by Karnataka State Govt](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Polity_PM_Modi_madiga_SC_Subcat-500x383.jpg)
![[Polity] Separation of Powers: Govt Rejects GAY candidate from judge position, SC-Collegium discloses the bias in public](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/gay-500x383.png)
Bouncer from d government.Now it’s a fierce battle awaiting.This whole drama wasted valuable time.Time to ignore all new protests which are coming from Jantar Mantar.24 is finalised D Day
UNDP -MDG 5 – MMR – TO BE REDUCED BY 3 QUARTER. IT SHUD BE 109
When ESIC-SSO exam will be held.there z no information on websites???
You can call ESIC RECRUITMENT
Sh. G.S. Giri Jt. Director(Rectt.) – 011-23230963 xtn – 250
Please update here if you get any information from them !
Guys can somebody plz solve this prob and explain
The sum of the digits of a two-digit number is 9. Also, nine times this number is
twice the number obtained by reversing the order of the digits. Find the number.
let tens digit be x and unit digit be y
so acc to ques x+y=9……………………..eqn 1
now tens digit and units u need to consider
so 9(10x+y)=2(10y+x)…………………………..eqn2
so x=1 and y=8
so 18
thnx….
x+y= 9 ….equation (1)
9(10x+y)=2(10y+x)…equation (2)
solve it
u will get the required number 18..
Sudhir bhai orally hota hai solve..
Answer is 18.
No. Should be smaller..because we have to multiply ut by 9..
There are only 8.. 2 digit no.
81- 72- 63- 54- 45- 36- 27-18..
Select 18 and check the condition s
Mrunal Sir,
Need your help to find out a book for “banking knowledge” section of SBI Special Management Executive which ll be held on 19 sept.
I searched it on Google buy couldn’t find suitable one.
Reply if u read this message.
Thanks
if government can’t scrap CSAT then make it qualifying…
may be this will placate the protesters demands and also satisfactory results will be meet….
hope so everyone would confluence one’s view over this …
Guyz english comprehension in last 3 exam are not merely of 20 marks but
1: 2011=36 ques=90 marks
2: 2012=40ques=100 marks
3: 2013=31ques=77.5 marks
So this year exam csat will be of 100 to 130 max
bst f luck
its not ENGLISH COMPREHENSION,its ENGLISH PASSAGE
ITS ONLY 8 Qs
They’re referring to only the english comprehension part. There are 3 passages with 8-9 questions which have no translation in Hindi. The entire reading comprehension section is not being scrapped/unmarked, Also, wait for UPSC’s final word about how this is going to work out.
Ok thnx.. my bad I wasnt aware abt that :)
What the indecisiveness of government has done. Now translate papers into all languages.
What is Treasury Bench in parliament ?
the bench which holds the treasure aka money aka the government of india
The front bench to the right of the Speaker in Lok Sabha, traditionally reserved for members of the Government. Please correct me if I am wrong.
I was confused over this point which you mentioned , “members of the Government”, as in the secretarial staff of the house or the member of extended COM ? Please clarify
CSR udpate : the latest abstract of census puts CSR at 919 instead of the provisional 914.
http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=103437
Totally disturbed yar….csat revise karu ya nahi???
Itna ghussa aa raha hai inn protestors pe…
must read:http://ibnlive.in.com/news/the-upsc-csat-controversy-have-we-diagnosed-the-symptoms-rightly/490403-3.html
DEAR ASPIRANTS,
dont get disturbed or frustrated with any kind of move by govt or upsc….we have to face all since exam is fast approaching in 19 days all we need is stable mind set …jus think over past how u prepared ,how long u have been waiting for this exam,…..jus think of ur inspirational person( parents , personalities, etc..). go ahead real competition lies among 1 lack serious aspirants and 16000 among them will qualify jus focus on 16000 . be calm and confident…. all is urs…. all the best :)
i m little bit confused with CPI,WPI data ,somewhere i read that CSO publisize the data on monthly basis and somewhere i have read that OEC under commerce ministry publisize the data of WPI on weekly basis,and now recently wpi is being used or not by RBI or Planning Commision for policy making or replaced by CPI as In NEER and REER recently,plese someone clearly explain???
thanxx MUGI,bcoz i was so confused.
Mrunal sir please explain the term Held To Maturity (HTM)………….thank you sir
Hi,
Correction: MMR is deaths of mothers during pregnancy or within 42 days from termination of pregnancy per 1 lakh live births.
Also, for exam purpose we need to follow only Census 2011 numbers right?
Thanks,
Arun
Hey..do we need to remember oll d schemes given by mrunal sir for d prelims exam….m confused….